Squash is a versatile and delicious vegetable that can be used in a variety of dishes. It is also a great source of nutrition, providing a range of essential vitamins, minerals, and nutrients. In terms of macronutrients, squash is low in calories, moderate in protein, and high in carbohydrates. In this article, we will take a closer look at the nutritional benefits of squash and explore how it can be incorporated into a healthy and balanced diet. Whether you’re a seasoned squash enthusiast or new to this versatile veggie, there’s plenty to learn about its nutritional profile and how it can benefit your overall health and well-being.
Nutritional Value Of Squash
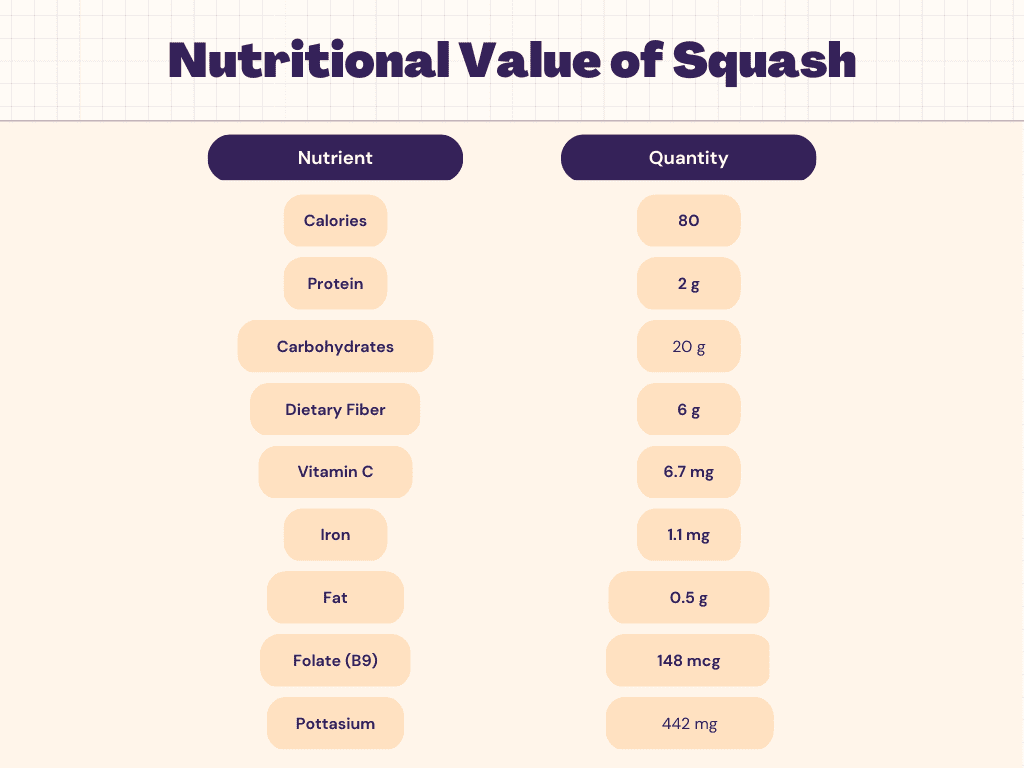
Nutritional Facts of Squash
Carbs In Squash
Squash is a good source of carbohydrates, which are an important source of energy for the body. One cup of cooked squash contains about 20 grams of carbohydrates, including about 6 grams of dietary fiber. The fiber in squash can help regulate blood sugar levels and support digestive health by promoting regularity. Squash also contains complex carbohydrates, which take longer to digest and provide sustained energy. Unlike simple carbohydrates found in processed foods and sugary drinks, complex carbohydrates in whole foods like squash is a healthy part of a balanced diet. If you are watching your carbohydrate intake, it’s important to be mindful of portion sizes and to balance your intake with other macronutrients such as protein and healthy fats.
Protein In Squash
Squash is not a particularly rich source of protein, but it does contain some of this essential macronutrient. One cup of cooked squash contains approximately 2 grams of protein. While this amount is relatively small compared to other protein-rich foods, squash can still be a valuable addition to a balanced diet. Protein is important for maintaining and repairing tissues in the body, as well as supporting immune function and other critical processes. If you’re looking to boost your protein intake, consider pairing squash with other protein-rich foods such as beans, tofu, or lean meats. Alternatively, you can add protein-rich toppings or sauces to your squash dishes, such as nut butter, cheese, or yogurt.
Health Benefits Of Squash
Squash is a nutrient-dense food that offers a range of health benefits for a variety of conditions, including PCOS, diabetes, thyroid disorders, and weight loss.
- PCOS: Squash is a low-glycemic-index food, which means it releases glucose into the bloodstream at a slow and steady pace, helping to regulate blood sugar levels. This can be particularly beneficial for women with PCOS, who may struggle with insulin resistance and blood sugar imbalances. Squash is also rich in fiber, which can help reduce insulin resistance and improve hormonal balance. Check our PCOS Plans here.
- Diabetes: Squash is an excellent source of dietary fiber and has a low glycemic load, which makes it a great food for people with diabetes. The fiber in squash helps slow down the absorption of sugar into the bloodstream, which can help prevent blood sugar spikes and dips. Squash is also rich in vitamins and minerals, which can help support overall health and well-being. Check our Diabetes Plans here.
- Thyroid: Squash is a good source of vitamin A, which is important for thyroid health. The thyroid gland requires adequate levels of vitamin A to function properly, and a deficiency in this nutrient can lead to thyroid disorders. Squash is also a good source of other important vitamins and minerals, including vitamin C, magnesium, and potassium, which can help support thyroid health. Check our Thyroid Plans here.
- Weight Loss: Squash is low in calories and high in fiber, making it a great food for weight loss. The fiber in squash can help promote feelings of fullness and reduce overall calorie intake, while the low-calorie content means you can eat a large portion without consuming too many calories. Squash is also a good source of other important nutrients, such as vitamins and minerals, that can help support overall health and well-being. Check our Weight Loss Plans here.
Vitamins & Minerals in Squash
Squash is a nutrient-dense food that contains a range of essential vitamins and minerals, including:
- Vitamin A: Squash is a rich source of beta-carotene, which the body converts into vitamin A. One cup of cooked squash can provide up to 457% of the daily value (DV) of vitamin A, which is important for healthy vision, immune function, and skin health.
- Vitamin C: Squash contains a moderate amount of vitamin C, providing up to 52% of the DV per cup. Vitamin C is an important antioxidant that can help protect cells from damage and support immune function.
- Potassium: Squash is a good source of potassium, which is important for healthy blood pressure and heart function. One cup of cooked squash provides about 15% of the DV for potassium.
- Magnesium: Squash is a good source of magnesium, which is important for bone health, nerve function, and energy metabolism. One cup of cooked squash provides about 14% of the DV for magnesium.
- Vitamin B6: Squash is a good source of vitamin B6, which is important for brain function, mood regulation, and the production of red blood cells. One cup of cooked squash provides about 14% of the DV for vitamin B6.
Squash also contains smaller amounts of other important vitamins and minerals, including folate, thiamine, niacin, calcium, and iron. These nutrients can help support overall health and well-being and should be included as part of a balanced diet.
The Bottom Line
Squash is a nutrient-dense food that offers a range of health benefits due to its high content of essential vitamins, minerals, and dietary fiber. It is low in calories and carbohydrates, making it a great food for weight loss, and can help regulate blood sugar levels due to its low glycemic index. Squash is also a good source of nutrients that are important for overall health, including vitamin A, vitamin C, potassium, magnesium, and vitamin B6. These nutrients can help support healthy vision, immune function, bone health, nerve function, and energy metabolism. Squash can be beneficial for people with PCOS, diabetes, thyroid disorders, and those looking to lose weight or improve their overall health.
Faqs
How much Squash can I eat in a day?
The amount of squash you can eat in a day depends on various factors such as your age, sex, weight, activity level, and overall health status. However, in general, squash is a healthy and low-calorie food, so you can include it as part of your balanced diet without worrying too much about portion size.
A typical serving size for cooked squash is around 1 cup (or 155 grams), which provides about 40 calories, 10 grams of carbohydrates, 2 grams of fiber, and 2 grams of protein, as well as various vitamins and minerals.
You can safely consume a few servings of squash per day as part of a balanced diet, along with other fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and healthy fats.
Should I eat Squash before or after exercise?
The timing of when to eat squash in relation to exercise depends on your individual needs, preferences, and goals. In general, it is recommended to consume carbohydrates before exercise to provide fuel for the muscles and help maintain blood glucose levels during the workout.
Squash is a good source of carbohydrates and can be a healthy option to eat before exercise. It is a low glycemic index food, which means it is absorbed more slowly in the body, providing sustained energy during exercise. Consuming a small serving of cooked squash about an hour before exercise may help provide the necessary carbohydrates for optimal performance and endurance.
However, if you find that eating before exercise causes digestive discomfort or if your exercise session is short and low to moderate in intensity, you may not need to consume squash before exercise. In this case, you can simply consume squash as part of your regular meals or snacks throughout the day to meet your nutritional needs.
It is also important to remember to stay hydrated before, during, and after exercise by drinking plenty of water.
What are the benefits of Squash?
Squash offers a range of health benefits due to its nutrient density, including:
- Weight loss: Squash is low in calories and high in fiber, making it a great food for weight loss. It can help you feel fuller for longer periods and reduce calorie intake, which can lead to weight loss.
- Nutrient-dense: Squash is a good source of vitamins and minerals, including vitamin A, vitamin C, potassium, magnesium, and vitamin B6. These nutrients are important for overall health, supporting healthy vision, immune function, bone health, nerve function, and energy metabolism.
- Low glycemic index: Squash is a low glycemic index food, meaning it is absorbed more slowly in the body, providing sustained energy and helping regulate blood sugar levels. This makes it an ideal food for people with diabetes or those looking to regulate blood sugar levels.
- Rich in antioxidants: Squash is a good source of antioxidants, which help protect cells from damage caused by free radicals. These antioxidants may help reduce the risk of chronic diseases such as heart disease, cancer, and diabetes.
- Supports digestion: Squash is high in fiber, which can help support healthy digestion by promoting regular bowel movements and preventing constipation.
- Anti-inflammatory properties: Squash contains anti-inflammatory compounds, which can help reduce inflammation and may reduce the risk of chronic diseases associated with inflammation.
Overall, squash is a healthy and nutritious food that can be beneficial for overall health and well-being.
What is the best time to eat Squash?
There is no specific “best” time to eat squash as it can be consumed as part of a balanced diet at any time of day. However, some people may find that they prefer to eat squash at certain times of the day based on their individual needs and preferences.
For example, squash can be a good option for breakfast as part of a savory or sweet dish. It can be added to omelets, frittatas, and breakfast bowls, or used to make pancakes or waffles.
Squash can also be consumed as a snack or as part of a lunch or dinner meal. It can be roasted, steamed, or grilled and used in salads, soups, stews, or as a side dish.