Pumpkins are a beloved fall staple, often used in seasonal decor, desserts, and drinks. However, these versatile vegetables are more than just a festive decoration or a tasty treat. Pumpkins are also a nutrient-dense food that can provide a variety of health benefits. In this article, we will explore the nutritional profile of pumpkins, including their calorie, protein, and carbohydrate content. By understanding the nutritional value of pumpkins, you can make informed decisions about how to incorporate them into your diet and enjoy their many health benefits.
Nutritional Value of Pumpkin
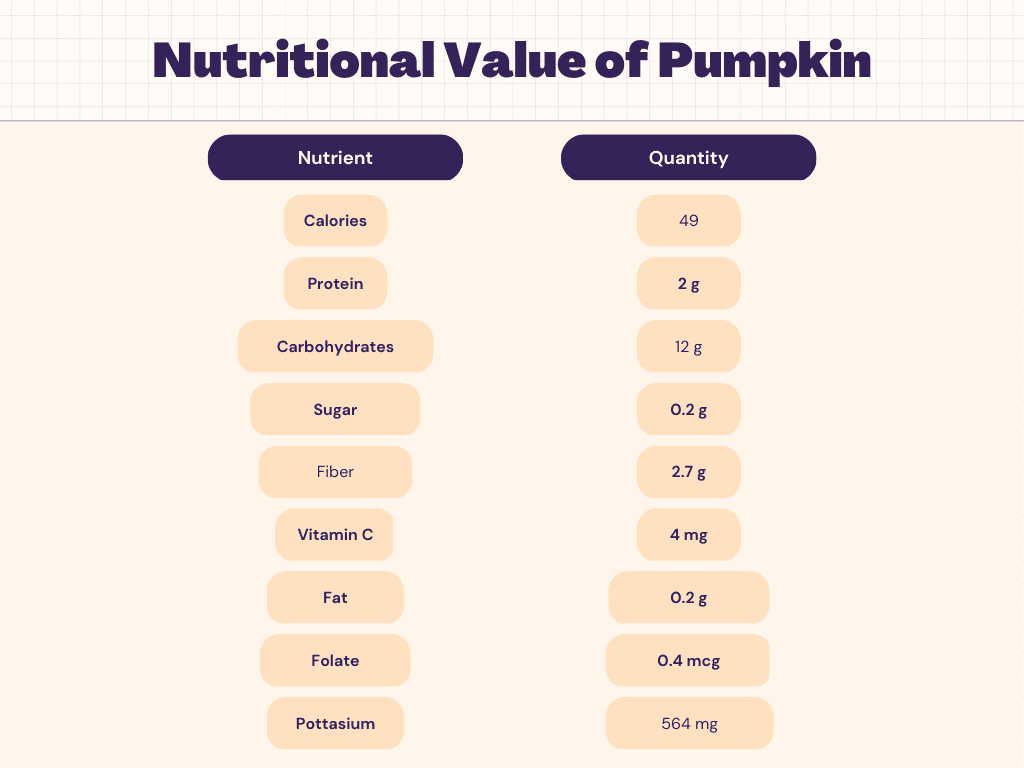
Nutritional Facts of Pumpkin
Carbs In Pumpkin
Carbohydrates are one of the primary macronutrients found in pumpkins. One cup of cooked pumpkin contains approximately 12 grams of total carbohydrates, which is relatively low compared to other starchy vegetables. However, over half of these carbohydrates come from dietary fiber, which is essential for digestive health and can help regulate blood sugar levels. The remaining carbohydrates in pumpkin come from naturally occurring sugars, such as glucose, fructose, and sucrose. While these sugars may cause a slight increase in blood sugar levels, they are balanced by the fiber content of pumpkin, which slows down the absorption of sugar into the bloodstream. Overall, the carbohydrates in pumpkin make it a nutritious and satisfying food choice that can help support a healthy diet.
Protein In Pumpkin
Protein is a vital macronutrient that plays a crucial role in the growth and repair of the body’s tissues. While pumpkin is not a significant source of protein, it does contain a moderate amount of this nutrient. One cup of cooked pumpkin provides about 2 grams of protein, which is equivalent to the protein content of a small egg. While this amount may not seem like much, it can contribute to the overall protein intake of a well-rounded diet. Additionally, pumpkin seeds are a rich source of plant-based protein and contain all the essential amino acids that the body needs to build and repair muscle tissue. Roasted pumpkin seeds are a popular snack and can be easily incorporated into salads, trail mixes, or granola bars. Overall, the protein content in pumpkin and its seeds can help provide essential nutrients that support overall health and wellness.
Health Benefits Of Pumpkin
Pumpkins offer several health benefits due to their rich nutrient profile, making them a nutritious addition to a balanced diet. Here are some of the potential health benefits of pumpkin:
- Rich in Nutrients: Pumpkins are a good source of several vitamins and minerals, including vitamin A, vitamin C, potassium, and fiber which helps in PCOS. Check our PCOS Plans here.
- Supports Eye Health: The high concentration of beta-carotene in pumpkins can help support eye health and reduce the risk of age-related macular degeneration.
- Boosts Immunity: The vitamin C and other antioxidants present in pumpkins can help boost immunity and protect against disease.
- Regulates Blood Sugar: The fiber and low glycemic index of pumpkin can help regulate blood sugar levels and reduce the risk of type 2 diabetes. Check our Diabetes Plans here.
- Supports Heart Health: The potassium and fiber in pumpkin can help support heart health by reducing blood pressure and cholesterol levels.
- Promotes Weight Loss: The low-calorie and high-fiber content of pumpkin can help promote weight loss by reducing calorie intake and increasing feelings of fullness. Check our Weight Loss Plans here.
- Anti-Inflammatory Properties: The antioxidants and phytochemicals present in pumpkin can help reduce inflammation in the body and prevent chronic diseases like Thyroid. Check our Thyroid Plans here.
Overall, pumpkin is a nutritious food that offers several health benefits, making it a great addition to any healthy diet.
Vitamins & Minerals in Pumpkin
Pumpkins are a rich source of several vitamins and minerals that are essential for maintaining optimal health. Here are some of the key vitamins and minerals found in pumpkin:
- Vitamin A: Pumpkin is an excellent source of vitamin A, providing over 245% of the daily value per cup. Vitamin A is crucial for maintaining healthy vision, immune function, and skin health.
- Vitamin C: One cup of pumpkin contains about 19% of the daily value of vitamin C. Vitamin C is an antioxidant that helps protect the body against damage from free radicals, supports immune function, and aids in collagen production.
- Potassium: Pumpkin is a good source of potassium, providing 16% of the daily value per cup. Potassium is essential for maintaining healthy blood pressure and heart function.
- Fiber: Pumpkin is a good source of fiber, with one cup providing over 11% of the daily value. Fiber is essential for digestive health, helps regulate blood sugar levels, and promotes feelings of fullness.
- Iron: Although pumpkin is not a significant source of iron, one cup still provides about 3% of the daily value. Iron is important for healthy blood cell production and oxygen transport throughout the body.
- Calcium: Pumpkin is a good source of calcium, providing about 2% of the daily value per cup. Calcium is essential for healthy bones and teeth.
Overall, the vitamins and minerals found in pumpkin make it a nutritious food that can contribute to overall health and well-being.
The Bottom Line
Pumpkin is a nutrient-dense food that offers several health benefits. It is rich in vitamins and minerals, including vitamin A, vitamin C, potassium, fiber, iron, and calcium. These nutrients are essential for maintaining healthy vision, immune function, skin health, digestive health, and bone health. Additionally, pumpkin contains antioxidants and phytochemicals that have anti-inflammatory properties and can help reduce the risk of chronic diseases. The carbohydrates in pumpkin come primarily from dietary fiber and natural sugars, which can help regulate blood sugar levels. While pumpkin is not a significant source of protein, its seeds are a rich source of plant-based protein. Incorporating pumpkin into a balanced diet can offer several health benefits, including supporting heart health, boosting immunity, promoting weight loss, and reducing inflammation.
Faqs
How much Pumpkin can I eat in a day?
The amount of pumpkin you can eat in a day depends on several factors, including your overall dietary needs, health status, and personal preferences. Generally speaking, there is no specific limit on how much pumpkin you can eat in a day, as it is a low-calorie and nutrient-dense food.
However, if you have certain medical conditions or dietary restrictions, you may need to limit your pumpkin intake. For example, if you have diabetes, you may need to be mindful of your pumpkin consumption due to its natural sugar content. Similarly, if you are on a low-carbohydrate or low-fiber diet, you may need to limit your pumpkin intake.
In general, one cup of cooked pumpkin provides approximately 49 calories, 12 grams of carbohydrates, 2 grams of protein, and 3 grams of fiber. As part of a balanced diet, you can safely consume pumpkin in moderation without any adverse effects. It is always best to consult with a healthcare professional or registered dietitian to determine the appropriate amount of pumpkin and other foods to include in your diet based on your individual needs and health status.
Should I eat Pumpkin before or after exercise?
Whether to eat pumpkin before or after exercise depends on your personal preferences and goals. Generally speaking, pumpkin can be a nutritious addition to a pre-or post-workout meal or snack.
Before exercise: Consuming a meal or snack that includes pumpkin before exercise can provide you with the energy and nutrients needed to fuel your workout. The carbohydrates in pumpkin can help provide a steady supply of energy during exercise, while the fiber can help promote feelings of fullness and prevent blood sugar crashes. You could try incorporating pumpkin into a pre-workout smoothie or oatmeal bowl.
After exercise: Consuming a meal or snack that includes pumpkin after exercise can help replenish your energy stores and promote recovery. The carbohydrates in pumpkin can help restore glycogen levels, while the protein can aid in muscle repair and growth. You could try incorporating pumpkin into a post-workout smoothie or adding it to a meal with a source of protein, such as grilled chicken or tofu.
Overall, whether you eat pumpkin before or after exercise is ultimately up to you and what works best for your body and goals. It’s important to listen to your body and experiment with different meal timing and combinations to determine what works best for you.
What are the benefits of Pumpkin?
Pumpkin offers several health benefits due to its nutrient content. Here are some of the benefits of consuming pumpkin:
- Promotes Eye Health: Pumpkin is a great source of vitamin A, which is essential for maintaining healthy vision. Vitamin A helps protect the eyes from damage and may help prevent age-related vision loss.
- Supports Immune Function: Pumpkin is high in vitamin C, an antioxidant that helps boost the immune system and protect the body against infections.
- Aids Digestion: The fiber content in pumpkin promotes digestive health by helping to regulate bowel movements, promoting feelings of fullness, and reducing the risk of constipation.
- Supports Heart Health: Pumpkin contains potassium, which is essential for maintaining healthy blood pressure levels and heart function. The fiber in pumpkin may also help lower cholesterol levels, reducing the risk of heart disease.
- Promotes Weight Loss: Pumpkin is low in calories and high in fiber, which can help promote weight loss by reducing hunger and promoting feelings of fullness.
- Reduces Inflammation: Pumpkin is a good source of antioxidants, which have anti-inflammatory properties. Consuming pumpkins may help reduce inflammation in the body and lower the risk of chronic diseases.
Overall, incorporating pumpkin into your diet can provide several health benefits and contribute to overall health and well-being.
What is the best time to eat Pumpkin?
There is no specific “best time” to eat pumpkin as it can be consumed at any time of the day. Pumpkin is a versatile food that can be incorporated into many different dishes and meals, including breakfast, lunch, dinner, and snacks.
However, the best time to eat pumpkin may depend on your personal preferences and goals. For example, if you are looking to promote satiety and regulate blood sugar levels, you may want to include pumpkin in your breakfast or snack. On the other hand, if you are looking to replenish energy stores and promote recovery after exercise, you may want to include pumpkin in a post-workout meal or snack.
Ultimately, the timing of your pumpkin consumption will depend on your individual dietary needs and preferences. You can experiment with different meal combinations and timing to determine what works best for you.