Peanut butter is a popular spread made from ground peanuts. It is a delicious and convenient food that is enjoyed by many people around the world. In addition to its rich and creamy taste, peanut butter is also a good source of nutrients, including protein, healthy fats, and fiber. In this article, we will explore the nutritional value of peanut butter, including its calorie, protein, and carbohydrate content, as well as the health benefits associated with consuming peanut butter as part of a balanced diet.
Nutritional Value of Peanut Butter
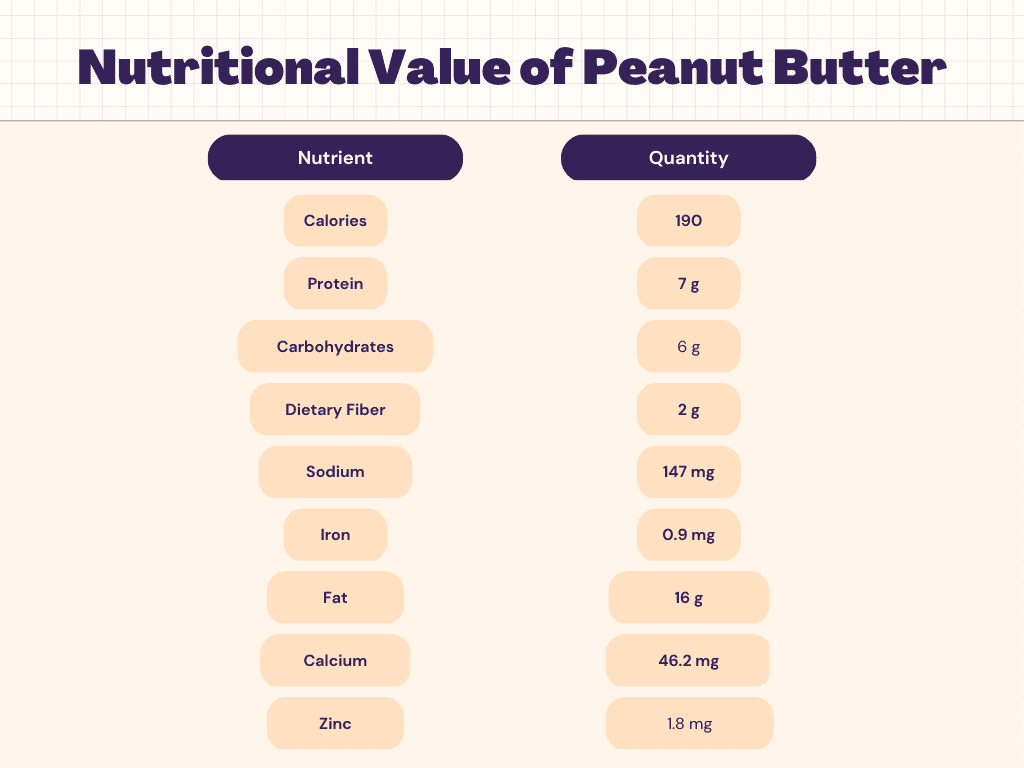
Nutritional Facts of Peanut Butter
Carbs In Peanut Butter
Peanut butter is relatively low in carbohydrates, with 2 tablespoons (32 grams) containing about 6 grams of carbohydrates. However, it is important to note that some types of peanut butter may contain added sugar or other sweeteners, which can increase the carbohydrate content. To keep the carb count low, it is important to choose natural peanut butter without added sugars or other ingredients. Additionally, the type of bread or crackers that you pair with peanut butter can also impact the overall carb count of your snack or meal. For those following a low-carb diet or monitoring their carbohydrate intake, it is important to keep the total carb count in mind when including peanut butter in your diet.
Protein In Peanut Butter
Peanut butter is a good source of protein, with 2 tablespoons (32 grams) containing about 7 grams of protein. Protein is essential for building and repairing tissues in the body and is also important for maintaining muscle mass and promoting satiety. Peanut butter is a particularly good source of plant-based protein, which can be beneficial for vegetarians or those looking to reduce their intake of animal products. Additionally, peanut butter is considered a “complete protein,” meaning it contains all nine essential amino acids that the body cannot produce on its own. Including peanut butter as part of a balanced diet can be a great way to ensure you are meeting your daily protein needs.
Health Benefits Of Peanut Butter
Peanut butter offers several potential health benefits for those with various health concerns, including:
- PCOS: The protein and healthy fats in peanut butter can help to stabilize blood sugar levels and promote feelings of fullness, which can be beneficial for women with PCOS. Check our PCOS Plans here.
- Diabetes: Peanut butter is relatively low in carbohydrates and contains healthy fats and protein, making it a good option for those with diabetes looking to manage their blood sugar levels. Check our Diabetes Plans here.
- Thyroid: Peanut butter is a good source of selenium, which is important for thyroid health. Additionally, the healthy fats in peanut butter can help to support the absorption of other important nutrients, like vitamin E. Check our Thyroid Plans here.
- Weight loss: Although high in calories, peanut butter can still be a part of a healthy weight loss plan. The protein and healthy fats in peanut butter can help to promote feelings of fullness and reduce cravings, making it easier to stick to a healthy eating plan. However, it is important to keep portion sizes in mind to avoid consuming too many calories. Check our Weight Loss Plans here.
It is worth noting that some types of peanut butter may contain added sugars or other ingredients, which can impact its health. To maximize the potential health benefits of peanut butter, it is important to choose natural, minimally processed varieties without added sugars or other ingredients.
Vitamins & Minerals in Peanut Butter
Peanut butter is a good source of several vitamins and minerals, including:
- Vitamin E: Peanut butter is a good source of vitamin E, an antioxidant that helps to protect cells from damage.
- Magnesium: Peanut butter is a good source of magnesium, a mineral that is important for bone health, heart health, and nerve function.
- Phosphorus: Peanut butter is also a good source of phosphorus, another mineral that is important for bone health.
- Niacin: Peanut butter is a good source of niacin, also known as vitamin B3, which is important for energy production and maintaining healthy skin.
- Folate: Peanut butter contains small amounts of folate, a B vitamin that is important for cell growth and development.
- Iron: Peanut butter contains small amounts of iron, which is important for the production of red blood cells.
It is important to note that the exact nutrient content of peanut butter can vary depending on the specific brand and variety.
The Bottom Line
Peanut butter is a good source of several vitamins and minerals including Vitamin E, magnesium, phosphorus, niacin, folate, and iron. These nutrients are important for various functions in the body, such as bone health, heart health, nerve function, energy production, and red blood cell production. However, the nutrient content can vary depending on the brand and variety of peanut butter.
Faqs
How much Peanut Butter can I eat in a day?
The amount of peanut butter that you can eat in a day depends on your individual nutritional needs and goals. Peanut butter is a high-calorie food that is rich in protein and healthy fats, but it should be consumed in moderation. The American Heart Association recommends no more than 2 tablespoons of peanut butter per day for most adults. It is important to consider your overall calorie intake and balance your diet with a variety of nutrient-dense foods.
Should I eat Peanut Butter before or after exercise?
Both options are acceptable, and the choice depends on your individual preferences and goals. Peanut butter is a good source of protein, healthy fats, and carbohydrates, making it a suitable food for both pre-and post-exercise consumption.
Eating peanut butter before exercise can provide a source of sustained energy during the workout. The protein and healthy fats in peanut butter help to slow the absorption of carbohydrates, which can help to maintain steady blood sugar levels and prevent a rapid drop in energy.
Eating peanut butter after exercise can help to promote muscle recovery and repair. The protein in peanut butter can help to rebuild damaged muscle tissue, while the carbohydrates can help to replenish glycogen stores that were depleted during exercise.
Ultimately, the best time to eat peanut butter is whenever it fits into your overall nutrition plan and supports your exercise goals.
What are the benefits of Peanut Butter?
Peanut butter can offer several health benefits, including:
- Rich in nutrients: Peanut butter is a good source of protein, healthy fats, fiber, vitamins, and minerals, such as magnesium, phosphorus, and vitamin E.
- Helps control appetite: Peanut butter’s high protein and healthy fat content can help keep you feeling fuller for longer, which can help control your appetite and reduce the overall amount of calories you consume.
- Promotes heart health: Peanut butter contains monounsaturated and polyunsaturated fats that can help to reduce “bad” cholesterol levels, which can lower the risk of heart disease.
- May help manage blood sugar: The healthy fats and fiber in peanut butter can help regulate blood sugar levels, which may help manage diabetes.
- Good for muscle recovery: The protein content in peanut butter can aid in muscle recovery and repair after exercise.
- Promotes weight loss: While peanut butter is high in calories, studies have shown that it can still be part of a healthy weight loss diet due to its high protein and healthy fat content.
However, it is important to keep in mind that peanut butter should be consumed in moderation as it is also high in calories. Look for natural peanut butter that doesn’t contain added sugars or oils.
What is the best time to eat Peanut Butter?
The best time to eat peanut butter depends on your individual nutrition goals and preferences. Here are some options:
- As part of breakfast: Adding peanut butter to your breakfast can help you start your day with sustained energy. Spread it on whole-grain toast, mix it into oatmeal, or add it to a smoothie for a protein and fiber boost.
- As a snack: Peanut butter is a great snack option that can help keep you feeling full and satisfied between meals. Spread it on apple slices, celery, or whole-grain crackers for a quick and easy snack.
- Before exercise: Consuming peanut butter before exercise can help provide sustained energy during the workout. It’s a good source of protein, healthy fats, and carbohydrates, which can help maintain steady blood sugar levels and prevent a rapid drop in energy.
- After exercise: Eating peanut butter after exercise can help promote muscle recovery and repair. The protein in peanut butter can help rebuild damaged muscle tissue, while the carbohydrates can help replenish glycogen stores that were depleted during exercise.
Ultimately, the best time to eat peanut butter is whenever it fits into your overall nutrition plan and supports your goals. It’s important to keep in mind that peanut butter is high in calories, so it should be consumed in moderation as part of a balanced diet.