Mammals’ mammary glands produce milk, a very nourishing liquid, to nourish their young during the first few months of life. Cow’s milk is used to make a wide range of foods, including cheese, cream, butter, and yogurt. These foods, sometimes known as dairy or milk products, are a staple of the contemporary diet.
Nutritional Value of Milk
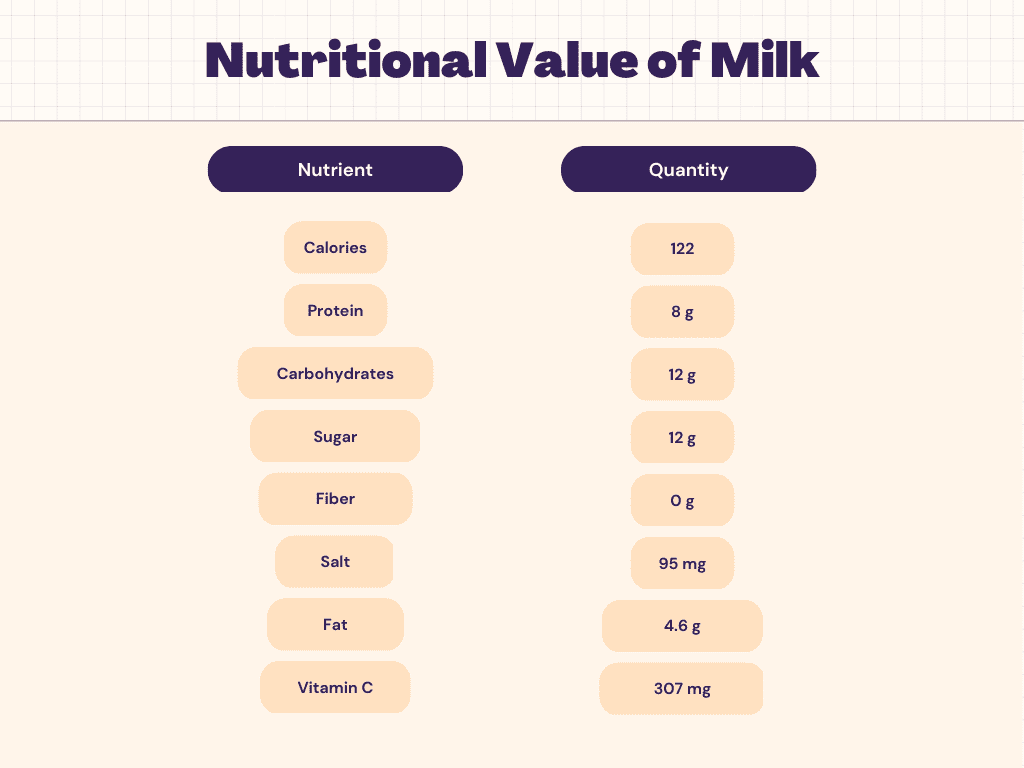
Nutritional Facts of Milk
Carbs
All of the carbs in simple milk are provided by lactose. A few milk products additionally contain added sugars. Limiting your consumption of these sweetened dairy products may be a good idea if you’re attempting to consume fewer added sugars. Each serving of chocolate, strawberry-flavored, and iced milk has 10 to 18 grams of added sugar.
Fats
It is simpler to pick between various fat contents because milk is marketed according to its fat content: Nonfat milk has 0% fat, 1% or 2% reduced-fat milk is available, and whole milk has 4% fat. Saturated fat makes up more than half of the fat in milk.
Protein
With 8 grams of protein per cup, milk is a good source of protein. All nine of the necessary amino acids that humans require are present in milk proteins. Milk contains 18% whey protein and 82% casein protein.
Calories
Since nonfat milk offers fewer calories per cup (90) compared to whole milk’s 149, whole milk is a suitable source of protein for those following a low-calorie diet.
Health Benefits Of Milk
- Improves bone density – Milk and other dairy products provide calcium and vitamin D, which are crucial for strong, healthy bones and may help prevent osteoporosis.
- Helps in the management of weight – consuming dairy products may help prevent weight gain in women in this age group who start at a normal weight. Check our Weight Loss Plans.
- Improves muscle performance – Milk consumption after resistance training increased muscle mass, strength increases, and fat reduction in younger women.
- Keeps the blood pressure in check – A review study also discovered that taking calcium supplements marginally lowers blood pressure in those who do not have hypertension, suggesting that they may have a preventive effect.
Vitamins & Minerals in Milk
Calcium, phosphorus, vitamin D, riboflavin, and vitamin B12 are all present in milk in extremely good amounts. Additionally, milk in the US has vitamin D added to it. In addition, it is a good source of zinc, pantothenic acid, selenium, potassium, and thiamin.
The Bottom Line
Milk is a great source of numerous types of lipids and high-quality protein. Around 5% of milk is made up of carbohydrates, mainly the indigestible lactose. Calcium, phosphorus, riboflavin, vitamin B12, and other vitamins and minerals are all abundant in milk. It is frequently fortified with additional vitamins, particularly vitamin D. Numerous hormones found in milk aid in the growth of the newborn calf. Milk, a calcium-rich food, may encourage improved bone mineral density, lowering your risk of osteoporosis. Blood pressure reduction has also been associated with milk and its byproducts.
FAQs
How much milk can I drink in a day?
Many dietary recommendations suggest drinking milk to fulfill daily needs for calcium, animal proteins, and vitamin B12. The official dietary recommendations for adults in the United States call for three cups, or 732 mL, of milk each day.
Should I drink Milk before or after exercise?
Onsgard asserts that drinking dairy products post-workout is preferable to doing so before or while. She claims that milk takes a long time to digest because it contains protein, carbs, and fat.
What are the benefits of Milk?
- Helps prevent weight gain
- It helps in building bone density
- Improves muscle performance and mass
- Reduces the chances of Cancer
- Lowers the risk of hypertension
What is the best time to drink Milk?
The researchers contend that shortly after exercise, rather than before night, is the ideal time to consume milk to encourage muscle building and weight loss. You should, however, modify your intake accordingly.