Kale is a leafy green vegetable that is often considered a superfood due to its high nutritional content. It is low in calories, yet high in nutrients, including protein, carbohydrates, vitamins, and minerals. Kale is a great source of vitamins A, C, and K, as well as minerals like calcium and iron. In addition, it contains a variety of phytochemicals and antioxidants that offer numerous health benefits, including improved digestion, reduced inflammation, and improved heart health. Whether you are looking to add more nutrients to your diet or simply enjoy the taste of kale, this versatile vegetable is a great option to consider.
Nutritional Value of Kale
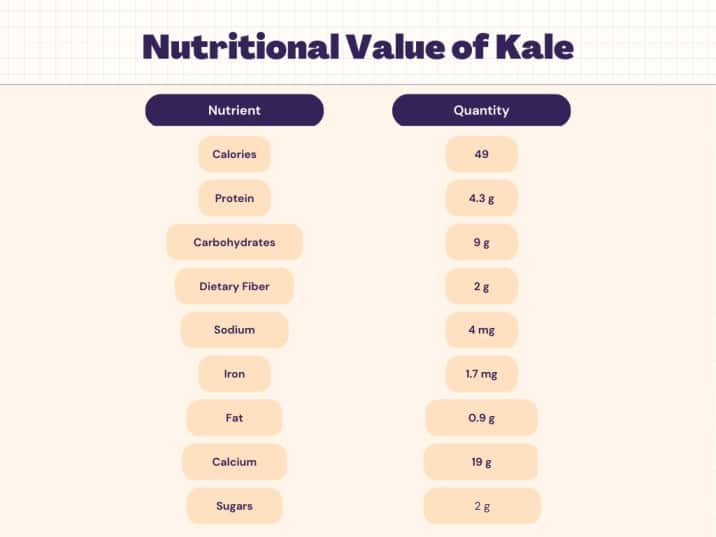
Nutritional Facts of Kale
Carbs In Kale
Kale is a leafy green vegetable that is low in carbohydrates, making it a great option for people who are watching their carb intake. Per 100 grams of raw kale, there are approximately 9 grams of carbohydrates, which is relatively low compared to other vegetables. Additionally, kale is a good source of dietary fiber, with about 2 grams per 100 grams of raw kale. This fiber helps to slow down the absorption of carbohydrates into the bloodstream, which can help regulate blood sugar levels and keep you feeling fuller for longer. Overall, while kale may not be as low in carbohydrates as some other leafy greens, it is still a healthy and nutritious vegetable that can be a great addition to a balanced diet.
Protein In Kale
Kale is a surprisingly good source of plant-based protein, making it a popular choice among vegans and vegetarians. While it may not contain as much protein as animal-based sources, per 100 grams of raw kale, there are approximately 4.3 grams of protein. This protein is made up of various amino acids that are important for the body’s growth and repair, and kale is particularly rich in the amino acid lysine. Protein is an essential macronutrient that helps to build and maintain muscle mass, regulate hormones, and support a healthy immune system. Including kale in your diet can be a great way to boost your protein intake while also getting a range of other vitamins and minerals that are beneficial for overall health.
Health Benefits Of Kale
Kale is a highly nutritious vegetable that provides many health benefits, including for those with PCOS, diabetes, thyroid conditions, and those who are trying to lose weight.
For PCOS: Kale is a great source of fiber, which can help regulate insulin levels in the body and improve symptoms of PCOS. Additionally, kale contains high levels of vitamin C, which has been shown to lower inflammation and improve insulin sensitivity in women with PCOS. Check our PCOS Plans here.
For diabetes: Kale is a low-carb vegetable that is also rich in fiber, which can help regulate blood sugar levels and improve insulin sensitivity. The antioxidants in kale may also help reduce oxidative stress and inflammation, which are often elevated in people with diabetes. Check our Diabetes Plans here.
For thyroid: Kale is a good source of iodine, which is important for healthy thyroid function. It also contains sulfur compounds that can help the body detoxify and reduce the risk of thyroid dysfunction. Check our Thyroid Plans here.
For weight loss: Kale is a low-calorie and low-carb vegetable that is high in fiber, making it a great choice for those trying to lose weight. The fiber in kale can help keep you feeling full and satisfied, while the protein and other nutrients can help support muscle growth and maintenance. Additionally, the antioxidants in kale may help reduce inflammation, which can contribute to weight gain and obesity. Check our Weight Loss Plans here.
Overall, kale is a versatile and nutrient-dense vegetable that can provide a range of health benefits for various conditions and goals. It is easy to incorporate into meals, whether raw in salads or cooked in soups, stir-fries, or as a side dish.
Vitamins & Minerals in Kale
Kale is a highly nutritious vegetable that is loaded with vitamins and minerals. Here are some of the key nutrients found in kale:
- Vitamin A: Kale is a rich source of vitamin A, providing more than 100% of the recommended daily intake in a 100-gram serving. Vitamin A is important for vision, immune function, and skin health.
- Vitamin C: Kale is an excellent source of vitamin C, with a 100-gram serving providing over 200% of the recommended daily intake. Vitamin C is a powerful antioxidant that helps to protect the body against oxidative stress and supports a healthy immune system.
- Vitamin K: Kale is one of the best sources of vitamin K, with a 100-gram serving providing more than 600% of the recommended daily intake. Vitamin K is important for blood clotting and bone health.
- Calcium: Kale is a good source of calcium, providing about 15% of the recommended daily intake in a 100-gram serving. Calcium is important for bone health and muscle function.
- Iron: Kale is a source of iron, with a 100-gram serving providing about 5% of the recommended daily intake. Iron is important for the production of red blood cells and the transport of oxygen throughout the body.
- Potassium: Kale is a source of potassium, with a 100-gram serving providing about 9% of the recommended daily intake. Potassium is important for regulating blood pressure and supporting heart health.
In addition to these nutrients, kale also contains other vitamins and minerals, as well as a range of antioxidants and anti-inflammatory compounds that can provide a range of health benefits.
The Bottom Line
Kale is a highly nutritious leafy green vegetable that is low in carbohydrates and rich in vitamins, minerals, and other beneficial nutrients. It is a good source of plant-based protein and dietary fiber, making it a popular choice among those with dietary restrictions or weight loss goals. Kale is also beneficial for various health conditions, including PCOS, diabetes, and thyroid disorders, due to its ability to regulate insulin levels, reduce inflammation, and support healthy thyroid function. Key nutrients found in kale include vitamin A, vitamin C, vitamin K, calcium, iron, and potassium, among others. Overall, kale is a versatile and nutrient-dense vegetable that can be incorporated into a healthy and balanced diet in a variety of ways.
Faqs
How much Kale can I eat in a day?
While kale is a highly nutritious vegetable, it’s important to consume it in moderation as consuming excessive amounts may lead to certain health issues.
The recommended daily intake of kale can vary depending on factors such as age, sex, and overall health. However, in general, it is recommended that adults consume at least 2 to 3 cups of leafy greens, such as kale, per week as part of a healthy and balanced diet.
As a general rule of thumb, it’s recommended that adults consume no more than 1 to 1.5 cups of kale per day. Consuming more than this amount may lead to digestive issues due to the high fiber content in kale, and may also lead to an excessive intake of certain nutrients such as vitamin K and beta-carotene, which can cause negative health effects in high amounts.
It’s important to note that individual nutrient requirements may vary based on factors such as age, sex, and health status, and it’s best to consult with a healthcare professional or registered dietitian to determine the appropriate intake of kale and other nutrient-rich foods in your diet.
Should I eat Kale before or after exercise?
Both timing options have potential benefits. Eating kale before exercise can provide the body with the necessary nutrients and energy to fuel the workout while eating it after exercise can help with recovery and replenish the body’s nutrient stores.
If you choose to eat kale before exercise, it’s best to consume it at least 30-60 minutes before your workout to allow time for digestion. This will help provide the body with a steady supply of energy and nutrients during the workout. Some good pre-workout kale options include adding it to a smoothie or salad or eating it as a side dish with a meal.
If you choose to eat kale after exercise, it’s best to consume it within 30-60 minutes of finishing your workout to help replenish the body’s nutrient stores and aid in muscle recovery. Some good post-workout kale options include adding it to a recovery smoothie or incorporating it into a meal with a source of protein to help support muscle repair and growth.
Ultimately, the timing of kale consumption before or after exercise will depend on personal preference, individual nutrient requirements, and overall dietary habits. It’s important to consume kale as part of a healthy and balanced diet to ensure you’re getting the nutrients your body needs to support overall health and wellness.
What are the benefits of Kale?
Kale is a highly nutritious vegetable that offers a range of health benefits. Some of the potential benefits of consuming kale include:
- Nutrient-dense: Kale is low in calories but high in nutrients, making it a great choice for those looking to increase their nutrient intake without adding too many calories to their diet.
- Antioxidant-rich: Kale is a rich source of antioxidants, including vitamins C and E, beta-carotene, and various flavonoids. Antioxidants help to protect the body against oxidative stress and may help to reduce the risk of chronic diseases such as cancer and heart disease.
- Anti-inflammatory: Kale contains several anti-inflammatory compounds, including quercetin and kaempferol. These compounds may help to reduce inflammation in the body, which can contribute to the development of chronic diseases.
- Supports heart health: Kale contains a range of nutrients that support heart health, including potassium, fiber, and antioxidants. Consuming kale may help to lower blood pressure, reduce cholesterol levels, and decrease the risk of heart disease.
- May help with weight loss: Kale is low in calories but high in fiber, which can help to keep you feeling full and satisfied. Consuming kale as part of a healthy and balanced diet may help to support weight loss or weight management goals.
- May benefit eye health: Kale is a rich source of lutein and zeaxanthin, two antioxidants that are important for eye health. Consuming kale may help to reduce the risk of age-related eye diseases such as cataracts and macular degeneration.
Overall, kale is a versatile and nutrient-dense vegetable that can be incorporated into a healthy and balanced diet in a variety of ways.
What is the best time to eat Kale?
There isn’t necessarily a “best” time to eat kale, as it can be consumed at any time of day and can offer nutritional benefits throughout the day. However, there are a few factors to consider when deciding when to eat kale:
- Before or after exercise: As mentioned earlier, consuming kale before or after exercise can provide benefits related to energy and nutrient replenishment, respectively.
- As part of a meal: Consuming kale as part of a balanced meal can help to provide a range of nutrients and support overall health and wellness. It can be incorporated into a breakfast smoothie, a lunchtime salad, or a dinner stir-fry, among other options.
- In the morning: Some people find that consuming kale in the morning, either as part of a breakfast smoothie or as a side dish with breakfast, helps to provide an energy boost and sets the tone for a healthy day.
Ultimately, the timing of kale consumption will depend on personal preference, individual nutrient requirements, and overall dietary habits. It’s important to consume kale as part of a healthy and balanced diet to ensure you’re getting the nutrients your body needs to support overall health and wellness.