Corn is a staple food crop that is widely grown and consumed all over the world. It is a versatile grain that is not only delicious but also packed with essential nutrients. Corn is a good source of calories, protein, and carbohydrates, making it a staple food for many cultures and cuisines. In addition to its macronutrient content, corn also contains a variety of vitamins and minerals, including vitamins B, C, and E, as well as minerals like iron, magnesium, and potassium. Whether it’s in the form of corn on the cob, kernels, or cornmeal, incorporating corn into your diet can provide you with numerous health benefits and help you meet your daily nutritional needs.
Nutritional Value of Corn
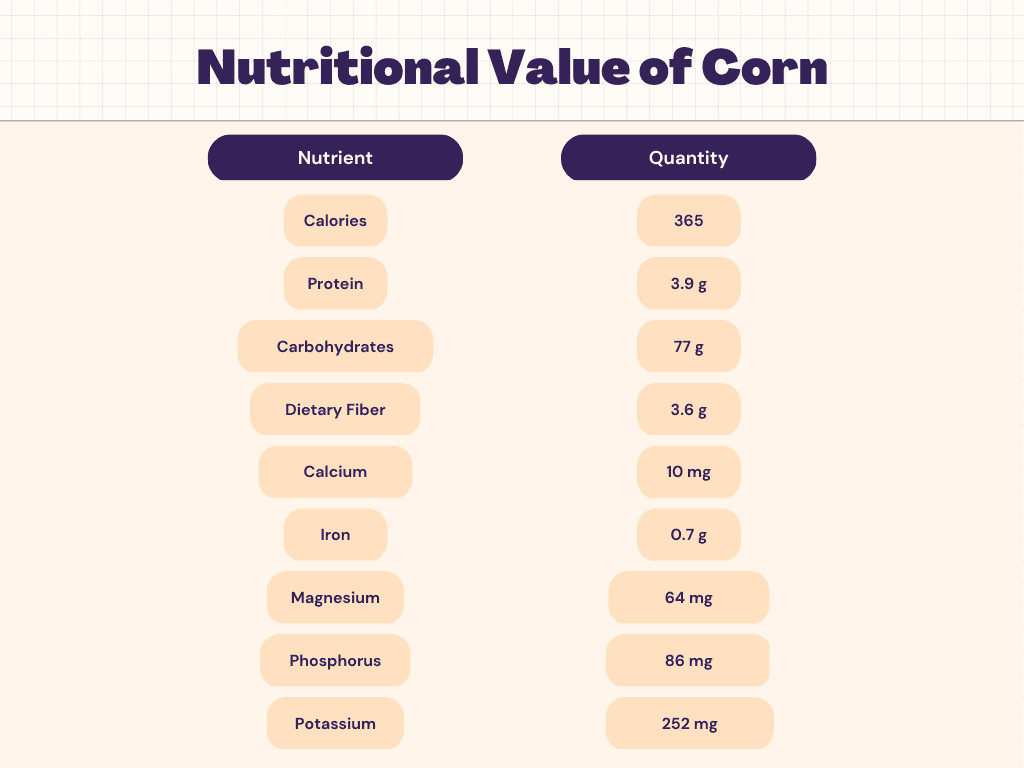
Nutritional Facts of Corn
Carbs In Corn
Corn is a starchy food that is high in carbohydrates. Of 100 grams of corn, 77 grams of the total weight come from carbohydrates. Corn contains complex carbohydrates, which are slowly broken down and absorbed by the body, providing sustained energy levels over a longer period of time. The carbohydrates in corn can also help to regulate blood sugar levels, making it a beneficial food for individuals with diabetes. Additionally, the fiber content in corn can contribute to digestive health and help regulate bowel movements. However, it is important to note that consuming large amounts of corn can also lead to an excessive intake of carbohydrates and high-calorie intake, which can contribute to weight gain. As with any food, it is important to consume corn in moderation as part of a balanced and varied diet.
Protein In Corn
Corn is a food that provides a moderate amount of protein. In 100 grams of corn, there are 3.9 grams of protein. While corn is not considered a high-protein food, it is still a valuable source of essential amino acids, which are the building blocks of protein. The protein in corn can help to build and repair tissues, as well as support the functioning of the immune system. Additionally, consuming corn as a source of protein can be beneficial for individuals who follow a vegetarian or vegan diet, as it can help to provide alternative sources of protein. However, it is important to note that the protein content in corn is relatively low compared to other protein-rich foods, such as meat, poultry, fish, and legumes. As with any food, it is important to consume corn as part of a balanced and varied diet to ensure that you are meeting your daily nutritional needs.
Health Benefits Of Corn
Corn has several health benefits for individuals with Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS), diabetes, thyroid issues, and those looking to lose weight. Here are a few key benefits:
- PCOS: Corn is a low glycemic index food, which means that it has a slow and gradual effect on blood sugar levels. This can be beneficial for individuals with PCOS, as it can help to regulate hormones and manage symptoms such as insulin resistance. Check our PCOS Plans here.
- Diabetes: Corn’s low glycemic index and fiber content can help regulate blood sugar levels and reduce the risk of blood sugar spikes, making it a beneficial food for individuals with diabetes. Check our Diabetes Plans here.
- Thyroid: Corn is a good source of selenium, which is an important mineral for thyroid health. A diet that includes corn can help to support the proper functioning of the thyroid. Check our Thyroid Plans here.
- Weight loss: The fiber content in corn can help regulate digestion and reduce feelings of hunger, making it a valuable food for individuals looking to lose weight. However, it is important to note that consuming large amounts of corn can also contribute to an excessive calorie intake, which can lead to weight gain. Check our Weight Loss Plans here.
Vitamins & Minerals in Corn
Corn is a nutritious food that provides a variety of vitamins and minerals. Here are some of the key vitamins and minerals found in 100 grams of corn:
| Vitamin/Mineral | Amount |
|---|---|
| Vitamin C | 4.5 mg |
| Vitamin B6 | 0.2 mg |
| Folate | 114 mcg |
| Calcium | 10 mg |
| Iron | 0.7 mg |
| Magnesium | 64 mg |
| Phosphorus | 86 mg |
| Potassium | 252 mg |
| Sodium | 5 mg |
| Zinc | 1.3 mg |
These vitamins and minerals play important roles in various bodily functions, such as supporting the immune system, promoting healthy skin and bones, and maintaining healthy energy levels. Additionally, the vitamins and minerals found in corn can contribute to overall health and wellness. It is important to note that the exact nutritional content of corn may vary depending on growing conditions, processing methods, and other factors. As with any food, it is best to consume corn as part of a balanced and varied diet to ensure that you are meeting your daily nutritional needs.
The Bottom Line
Corn is a nutritious food that provides a variety of vitamins, minerals, protein, and carbohydrates. It contains 3.9 grams of protein and approximately 20 grams of carbohydrates per 100 grams. Corn is a low glycemic index food, which can be beneficial for individuals with Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS), diabetes, and those looking to regulate their blood sugar levels. Corn is also a good source of fiber, vitamins such as Vitamin C, Vitamin B6, and Folate, and minerals such as Calcium, Iron, Magnesium, Phosphorus, Potassium, Sodium, and Zinc. However, consuming large amounts of corn can also contribute to an excessive calorie intake, which can lead to weight gain. Corn’s health benefits are best enjoyed as part of a balanced and varied diet.
Faqs
How much Corn can I eat in a day?
The amount of corn that you can eat in a day depends on several factors, including your age, sex, weight, activity level, and overall health. As a general guideline, it is recommended to aim for 1 to 2 servings of corn per day as part of a balanced diet. One serving of corn is typically considered to be about 1/2 cup of kernels or 1 medium ear of corn. However, individual nutritional needs may vary, and it is always best to consult with a healthcare provider or registered dietitian to determine the right amount of corn for your individual needs. Additionally, it is important to consider the other foods that you are consuming in your diet, as well as cooking and preparation methods, to ensure that you are getting the most nutritional value from your food.
Should I eat Corn before or after exercise?
Corn can be a good source of carbohydrates, which are an important source of energy for the body, especially during physical activity. Therefore, eating corn before exercise can help to provide you with the energy you need to power through your workout.
If you eat corn before exercising, it is best to consume it at least 30 minutes to an hour before starting your workout, allowing enough time for your body to digest the food and convert the carbohydrates into energy. It is also important to choose a balanced meal or snack that includes both carbohydrates and protein to support your exercise performance.
After exercise, eating corn can help to replenish your glycogen stores and provide you with the nutrients you need to recover and rebuild. However, it is important to consume carbohydrates and protein within 30 minutes to an hour after exercising to optimize recovery and repair. As with any food, it is best to consume corn in moderation and as part of a balanced and varied diet to support your overall health and wellness.
What are the benefits of Corn?
Corn is a staple food that has been consumed for thousands of years and offers a variety of health benefits. Here are some of the key benefits of corn:
- Good source of carbohydrates: Corn is a good source of carbohydrates, which are the body’s main source of energy.
- Low glycemic index: Corn has a low glycemic index, meaning it has a slower digestion and absorption rate and is less likely to cause rapid spikes in blood sugar levels.
- Fiber: Corn is a good source of fiber, which can promote digestive health and help regulate appetite.
- Vitamins and minerals: Corn is a good source of vitamins such as Vitamin C, Vitamin B6, and Folate, and minerals such as Calcium, Iron, Magnesium, Phosphorus, Potassium, Sodium, and Zinc.
- Antioxidants: Corn contains antioxidants, which can help protect the body against oxidative stress and cellular damage.
What is the best time to eat Corn?
There is no specific “best” time to eat corn, as it can be consumed as part of a balanced and varied diet at any time of day. Some people may choose to include corn as part of their breakfast, lunch, dinner, or as snack.
That being said, it is important to consider the timing of your meals and snacks in relation to your physical activity level. For example, if you are planning to exercise, eating corn 30 minutes to an hour beforehand can help to provide you with the energy you need to power through your workout. After exercise, consuming carbohydrates and protein within 30 minutes to an hour can help to optimize recovery and repair.
Ultimately, the best time to eat corn will depend on your individual needs, preferences, and lifestyle, and it is best to choose a time that works well for you and fits into your overall eating pattern.