By separating the fat globules from the buttermilk by churning milk or cream, manufacturers and home cooks can produce butter. They occasionally also include salt and food coloring. According to several research, butter and other high-fat dairy products reduce the risk of developing diabetes, obesity, and heart disease, although keep in mind that butter contains a lot of calories and saturated fat. For decades, scientists have argued about the health advantages of butter. Vitamin D, an essential ingredient for the formation and development of bones, may be found in butter. Additionally, it contains calcium, which is crucial for strong bones.
Nutritional Value of Butter
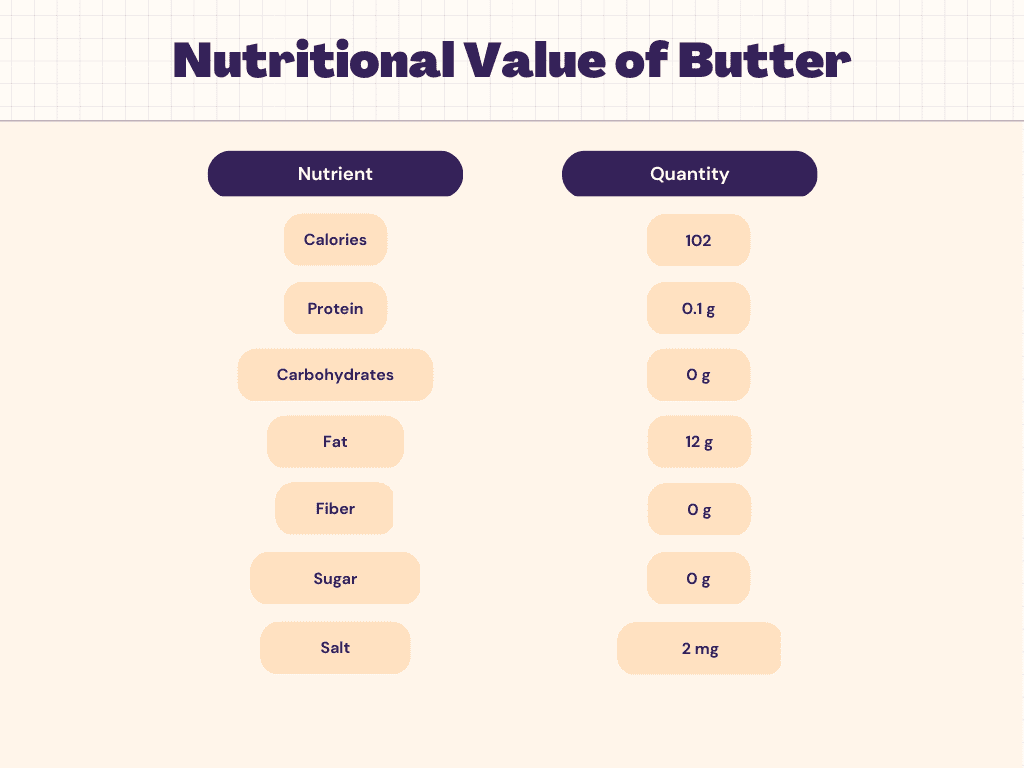
Nutritional Facts of Butter
Carbs
Butter is a low-carb, low-glycemic food since it has no carbs.
Fat
Butter contains a variety of fats, although the majority of the fat is saturated fat (just over 7 grams per tablespoon). A tablespoon of butter has 30.5 mg of cholesterol.
Protein
A single serving of butter contains essentially little protein, even though it is derived from milk.
Health Benefits Of Butter
- Helps lower the chances of Cancer – Beta-carotene, which your body transforms into vitamin A, is abundant in butter. Lung and prostate cancer chances are reduced by beta-carotene.
- It might benefit your eyes – Butter’s beta-carotene content may aid in reducing the rate of age-related macular degeneration or vision loss.
- It might help strengthen your bones – Vitamin D, an essential ingredient for the formation and development of bones, may be found in butter. Additionally, it contains calcium, which is crucial for strong bones.
- It may contribute to healthier skin – Vitamin E, which contributes to the health of the skin, is also present in butter. The nutrient lessens skin irritation, lessens UV sun damage and enhances the speed of wound healing.
- Helps in Weight Management – It contains nutrients including calcium, which builds bones, and has been linked to a lower risk of obesity. A low-carb diet, which includes butter, may help people lose weight more quickly or better maintain their weight than a low-fat diet. Check our Weight Loss Plans.
- Might help with Diabetes – Butter has a glycemic index of 50, which is below the “low range” of glycemic index values. Unexpectedly, butter’s monounsaturated and polyunsaturated fats aid to regulate blood sugar levels. Diabetic individuals should consume unsalted or grass-fed (organic) butter. Since unsalted butter contains no sodium, it is also beneficial for people with diabetes. Check our Diabetes Plans.
Vitamins & Minerals in Butter
Butter contains 97 micrograms of vitamin A per tablespoon, or around 14% of the recommended daily allowance (RDA) for women and 11% for men, which is beneficial for your health.
The Bottom Line
A common dairy product made from cow’s milk is butter. It is a spread that is made from milk fat that has been isolated from other milk components. It is also used in cooking and baking. It has a rich flavor. Due to its high saturated fat content, butter has recently been linked to heart disease. But nowadays, butter is generally seen as healthful, at least when used in moderation.
FAQs
How much Butter can we consume in a day?
It’s suggested to limit your intake to 1-2 teaspoons (14–28 grams) each day, along with other nutritious fats like avocados, nuts, seeds, coconut oil, avocado oil, olive oil, and fatty seafood. The moderate use of butter may reduce the risk of obesity, diabetes, and cardiac issues.
Should I eat Butter before or after exercise?
Be well-fueled before an exercise. According to studies, consuming carbohydrates before working out might enhance exercise performance and may even enable you to go out for longer or more intensely. When you exercise, you could feel lethargic or dizzy if you don’t eat.
What are the benefits of Butter?
- Lowers the chances of cancer
- Helps with eye health
- Helps with bone health
- Helps to get healthier skin
- Helps with weight loss if taken in moderation
- Might help with diabetes