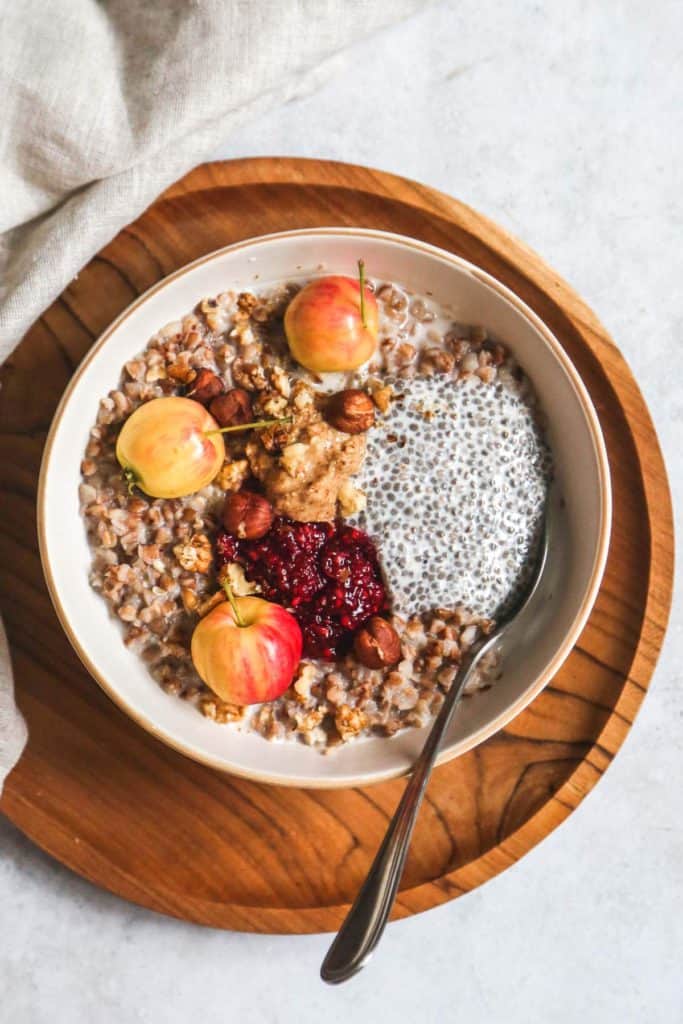
Buckwheat is a versatile and nutritious grain that has been enjoyed for centuries all over the world. Despite its name, it is not related to wheat and is actually a seed that is packed with essential nutrients such as calories, protein, and carbohydrates. These nutrients make buckwheat a great addition to any balanced diet, providing the body with energy, supporting muscle growth, and aiding in the digestion and absorption of other foods. Whether you’re looking for a gluten-free alternative to traditional wheat-based products or simply want to add some variety to your meals, the health benefits of buckwheat make it a great choice for anyone looking to live a healthier lifestyle.
Nutritional Value of Buckwheat
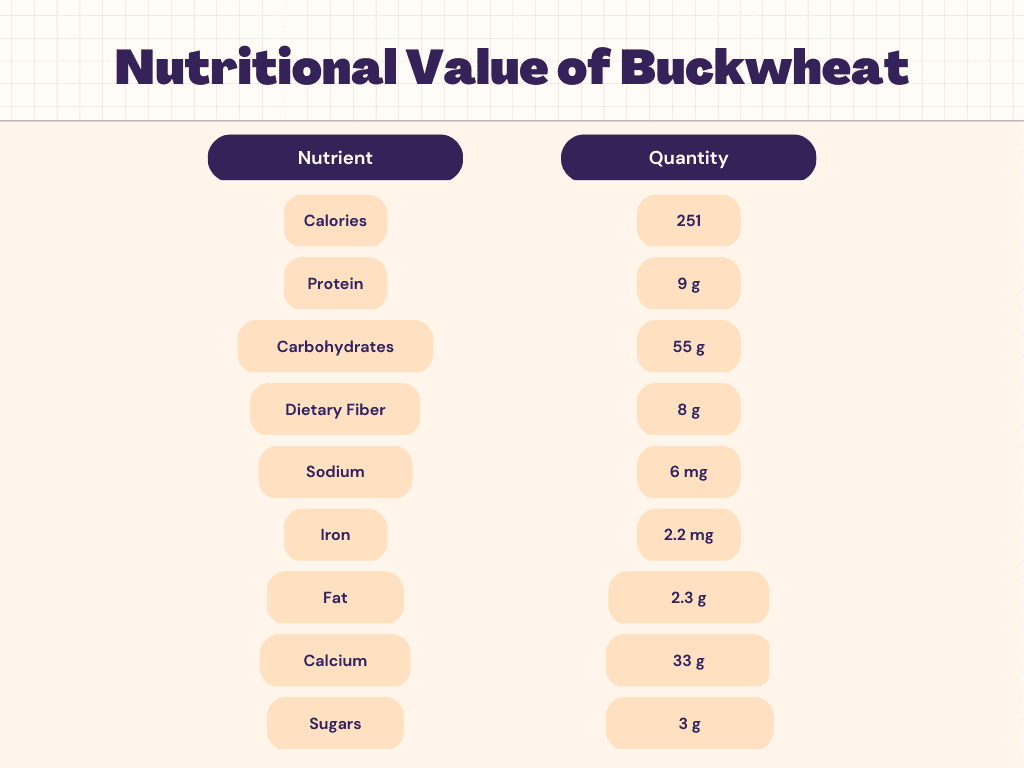
Nutritional Facts of Buckwheat
Carbs In Buckwheat
Carbohydrates are one of the most essential nutrients found in buckwheat, making up a significant portion of its overall nutritional content. One cup (168g) of cooked buckwheat contains 55g of carbohydrates, which is equivalent to 18% of the daily recommended intake based on a 2,000-calorie diet. The majority of the carbohydrates in buckwheat come in the form of complex carbohydrates, which are known for their slow release of energy into the body. This slow release helps to keep blood sugar levels stable and provides the body with a constant source of fuel, making buckwheat an excellent option for those who need to maintain a steady energy level throughout the day. Additionally, the high fiber content in buckwheat can help to regulate digestion and promote a feeling of fullness, making it an excellent option for those who are looking to control their weight.
Protein In Buckwheat
Protein is another essential nutrient that is abundant in buckwheat. One cup (168g) of cooked buckwheat contains 9g of protein, which is equivalent to 18% of the daily recommended intake based on a 2,000-calorie diet. This makes buckwheat a great option for vegetarians and vegans, as well as anyone who is looking to increase their protein intake. The high protein content in buckwheat makes it an excellent source of essential amino acids, which are the building blocks of muscle and other tissues in the body. This, in turn, makes buckwheat a great option for those looking to build muscle, recover from workouts, or maintain a healthy and active lifestyle. Additionally, the combination of complex carbohydrates and protein in buckwheat makes it a great option for those who are looking to maintain a balanced diet and a steady source of energy throughout the day.
Health Benefits Of Buckwheat
Buckwheat has a number of potential health benefits that make it a great option for people with various health conditions, including Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS), diabetes, thyroid problems, and weight loss.
For PCOS, the high fiber and protein content in buckwheat can help to regulate hormones and reduce insulin resistance, which are common issues for women with PCOS. Additionally, buckwheat is low in glycemic index, meaning that it does not cause sudden spikes in blood sugar levels, making it a great option for women with PCOS who need to manage their blood sugar levels. Check our PCOS Plans here.
For diabetes, buckwheat can help to regulate blood sugar levels and improve insulin sensitivity. The slow release of energy from the complex carbohydrates in buckwheat, combined with its high fiber content, helps to keep blood sugar levels stable and prevent sudden spikes in blood sugar. Check our Diabetes Plans here.
For thyroid problems, buckwheat is a great source of selenium, a mineral that is important for thyroid health. Additionally, the high fiber and protein content in buckwheat can help to regulate metabolism and promote a feeling of fullness, making it a great option for those with thyroid problems who are looking to control their weight. Check our Thyroid Plans here.
For weight loss, the high fiber and protein content in buckwheat can help to regulate metabolism and promote a feeling of fullness, making it a great option for those who are looking to control their weight. Additionally, the slow release of energy from the complex carbohydrates in buckwheat helps to prevent sudden spikes in blood sugar, which can lead to cravings and overeating. Check our Weight Loss Plans here.
It’s important to note that while buckwheat may offer these health benefits, it should always be part of a balanced diet and combined with regular exercise. Consult with a healthcare professional before making any major changes to your diet.
Vitamins & Minerals in Buckwheat
Buckwheat is a nutritious grain that is high in several essential vitamins and minerals. Some of the key vitamins and minerals found in buckwheat include:
- Magnesium: Buckwheat is an excellent source of magnesium, a mineral that is important for heart health, bone health, and blood sugar control.
- Phosphorus: Buckwheat is a good source of phosphorus, a mineral that is important for bone health, as well as kidney, heart, and muscle function.
- Manganese: Buckwheat is a rich source of manganese, a mineral that is important for bone health, wound healing, and metabolism.
- Fiber: Buckwheat is a good source of fiber, which is important for digestive health, regulating blood sugar levels, and supporting weight management.
- Protein: Buckwheat is a good source of plant-based protein, making it a great food choice for people following a vegetarian or vegan diet.
- B-complex vitamins: Buckwheat is a good source of B-complex vitamins, including niacin, thiamin, and vitamin B6, which are important for energy metabolism, brain function, and red blood cell formation.
- Iron: Buckwheat is a good source of iron, a mineral that is important for red blood cell formation, oxygen transport, and immune function.
- Zinc: Buckwheat is a good source of zinc, a mineral that is important for immune function, wound healing, and taste and smell perception.
Overall, buckwheat is a highly nutritious grain that is rich in essential vitamins and minerals. Incorporating buckwheat into your diet can help to support overall health and well-being, as well as provide important nutrients to support specific health goals and conditions.
The Bottom Line
Buckwheat is a nutritious grain that is high in several essential vitamins and minerals, including magnesium, phosphorus, manganese, fiber, plant-based protein, B-complex vitamins, iron, and zinc. Incorporating buckwheat into your diet can support overall health and well-being, as well as provide essential nutrients to support specific health goals and conditions, such as heart health, bone health, blood sugar control, digestive health, weight management, energy metabolism, brain function, red blood cell formation, immune function, wound healing, and taste and smell perception.
Faqs
How much Buckwheat can I eat in a day?
The amount of buckwheat you can eat in a day depends on a variety of factors, such as your age, gender, weight, height, and physical activity level. However, as a general guideline, a serving size of buckwheat is typically considered to be 1/2 cup of cooked grain. This serving size provides about 100-150 calories and 20-25 grams of carbohydrates, depending on the variety and cooking method.
It is important to keep in mind that buckwheat is a source of carbohydrates and will contribute to your overall daily carbohydrate intake. As such, it is important to consider your overall dietary goals and patterns, as well as your individual health needs and restrictions, when determining the right amount of buckwheat to eat in a day.
For most people, incorporating buckwheat into a balanced diet, along with a variety of other whole grains, fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and healthy fats, can be a nutritious and delicious way to meet their daily nutrient needs. If you have specific dietary concerns or health conditions, it may be helpful to consult with a healthcare professional or registered dietitian to determine the right amount of buckwheat for your individual needs.
Should I eat Buckwheat before or after exercise?
Whether you should eat buckwheat before or after exercise depends on your individual goals and needs, as well as the intensity and duration of your workout.
If you are looking to fuel your workout, eating a small serving of buckwheat before exercise can provide you with sustained energy to help you perform at your best. Buckwheat is a good source of carbohydrates, which are the primary source of energy for your muscles during exercise. However, it is important to keep in mind that buckwheat is a slow-digesting carbohydrate, so it may not provide a quick burst of energy like some other foods might.
If you are looking to replenish glycogen stores and support recovery after exercise, eating a serving of buckwheat after exercise can be a good option. The carbohydrates in buckwheat can help to replenish glycogen stores in your muscles, which can help you to feel less tired and perform better in your next workout. Additionally, the protein in buckwheat can help to support muscle repair and growth.
Overall, the best time to eat buckwheat will depend on your individual goals and needs, as well as the intensity and duration of your workout. If you have specific questions or concerns, it may be helpful to consult with a healthcare professional or registered dietitian to determine the best approach for your individual needs.
What are the benefits of Buckwheat?
Buckwheat is a nutritious grain that offers a range of health benefits. Some of the most notable benefits of buckwheat include:
- Heart health: Buckwheat is a good source of magnesium, which is important for maintaining heart health. Magnesium helps to regulate blood pressure and prevent heart disease.
- Blood sugar control: Buckwheat has a low glycemic index, meaning it has a slow and gradual impact on blood sugar levels. This makes it a good choice for people with diabetes or other blood sugar issues.
- Digestive health: Buckwheat is a good source of fiber, which is important for digestive health. Fiber helps to promote regularity, prevent constipation, and support overall gut health.
- Weight management: Buckwheat is a low-calorie grain that can help to support weight management goals. The fiber in buckwheat can help you to feel full and satisfied, reducing the likelihood of overeating or snacking on unhealthy foods.
- Energy metabolism: Buckwheat is a good source of B-complex vitamins, which are important for energy metabolism. B vitamins help to convert food into energy and support overall health and well-being.
- Brain function: Buckwheat is a good source of magnesium, which is important for brain function. Magnesium helps to support cognitive function, memory, and mood.
- Immune function: Buckwheat is a good source of antioxidants, which are important for immune function. Antioxidants help to protect your body against damage from harmful substances, such as free radicals.
- Wound healing: Buckwheat is a good source of zinc, which is important for wound healing. Zinc helps to support skin health, cell growth, and immune function.
Overall, incorporating buckwheat into a balanced diet, along with a variety of other whole grains, fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and healthy fats, can be a nutritious and delicious way to support overall health and well-being.
What is the best time to eat Buckwheat?
The best time to eat buckwheat will depend on your individual needs and goals. Here are a few suggestions for when to eat buckwheat:
- Breakfast: Buckwheat can be a nutritious and filling option for breakfast. You can make buckwheat porridge, add it to smoothies, or use it as a base for granola.
- Lunch: Buckwheat can be used as a base for salads, or as a substitute for rice or pasta in lunch dishes.
- Dinner: Buckwheat can be used as a side dish for dinner, or as a base for stews and soups.
- Snacks: Buckwheat can be made into crackers, used as a base for energy bars, or as a topping for yogurt or oatmeal.
Regardless of when you eat buckwheat, it is important to pair it with a variety of other whole grains, fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and healthy fats to ensure that you are getting a balanced and nutritious diet. Additionally, it is important to listen to your body and eat when you are hungry, and stop eating when you are full.