Beetroot, or simply beets, is a root vegetable that has become increasingly popular due to its numerous health benefits. Not only are beets low in calories, but they also contain an impressive array of essential nutrients such as protein and carbohydrates. In this article, we will delve deeper into the nutritional profile of beets, explore the number of calories they contain, and analyze the amount of protein and carbs that are packed into this vibrant vegetable. Whether you are an athlete looking for a natural energy source or simply seeking to improve your overall health, understanding the nutrition of beets can be a valuable tool in achieving your goals.
Nutritional Value Of Beetroot
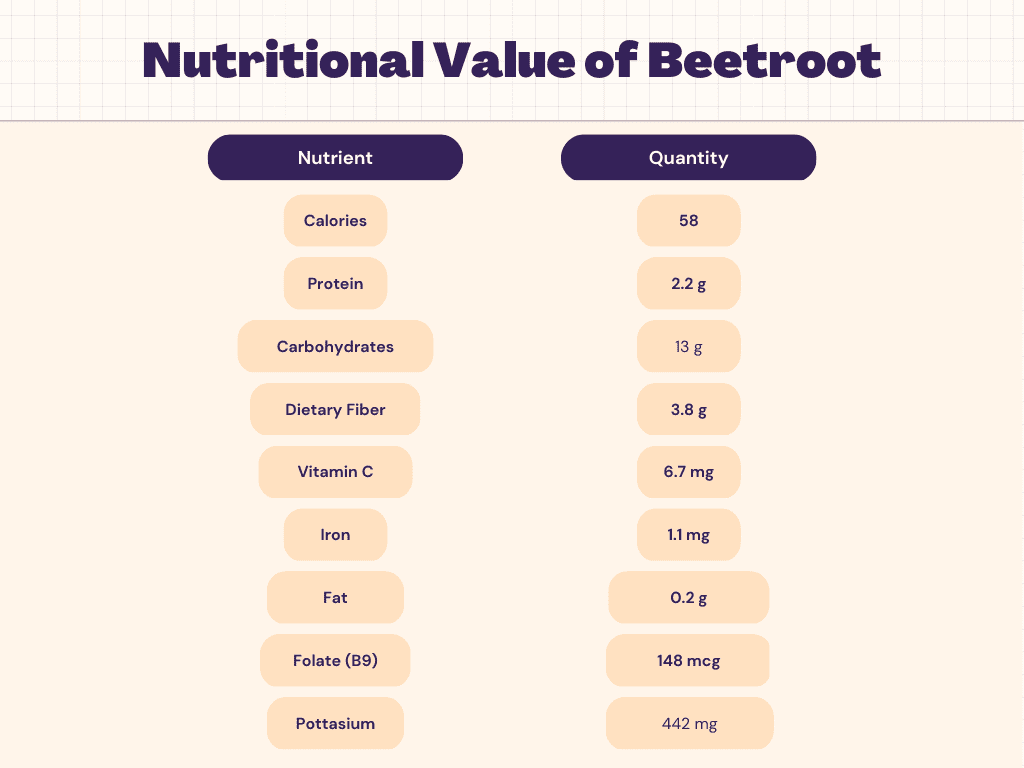
Nutritional Facts of Beetroot
Carbs In Beetroot
Beetroot is a root vegetable that is low in calories but rich in nutrients, including carbohydrates. One cup of raw beetroot contains around 13 grams of carbohydrates, including both fiber and sugar. The fiber in beetroot is particularly beneficial as it helps to slow down the absorption of sugar into the bloodstream, preventing spikes in blood sugar levels. Additionally, the sugar in beetroot is natural and comes from fructose, a type of sugar found in fruits and vegetables. This makes beetroot a good source of carbohydrates for those looking to maintain stable blood sugar levels or those who are looking for a natural energy source. Overall, the carbohydrates in beetroot can be a valuable addition to a healthy, balanced diet.
Protein In Beetroot
While the beetroot is not typically considered a significant source of protein, it does contain some amount of this essential nutrient. One cup of raw beetroot provides around 2.2 grams of protein. While this amount is relatively low, it can still contribute to a person’s daily protein intake, especially when combined with other protein sources. Additionally, beetroot contains a variety of other important nutrients, such as fiber, vitamins, and minerals, making it a nutritious addition to any diet. For those who are looking to increase their protein intake, incorporating beetroot into a balanced diet alongside other protein-rich foods can be an effective strategy.
Health Benefits Of Beetroot
Beetroot is a nutrient-dense vegetable that has been associated with numerous health benefits. Here are some potential benefits of beetroot for PCOS, diabetes, thyroid, and weight loss:
- PCOS: Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS) is a hormonal disorder that affects many women. Beetroot is a rich source of antioxidants and contains phytochemicals that help to regulate hormones, including insulin and androgens. This may be beneficial for women with PCOS as it can help to manage insulin resistance, a common symptom of the condition. Check our PCOS Plans here.
- Diabetes: Beetroot is a low glycemic index food, meaning it doesn’t cause a significant spike in blood sugar levels. It is also high in fiber, which can slow down the absorption of sugar into the bloodstream, further stabilizing blood sugar levels. This makes beetroot a potentially beneficial food for those with diabetes or those looking to prevent the condition. Check our Diabetes Plans here.
- Thyroid: Beetroot is a good source of iodine, which is essential for thyroid health. Iodine is necessary for the production of thyroid hormones, which regulate metabolism and other bodily functions. Adequate intake of iodine may help to prevent thyroid disorders, such as hypothyroidism. Check our Thyroid Plans here.
- Weight Loss: Beetroot is low in calories and high in fiber, which can help to promote feelings of fullness and reduce overall calorie intake. Additionally, beetroot contains compounds called nitrates, which can help to improve exercise performance, making it a potentially beneficial food for those looking to lose weight. Check our Weight Loss Plans here.
While these potential benefits are promising, it’s worth noting that more research is needed to fully understand the effects of beetroot on these conditions. Additionally, beetroot should not be used as a replacement for medical treatment or a balanced diet.
Vitamins & Minerals in Beetroot
Beetroot is a nutrient-dense vegetable that contains an array of essential vitamins and minerals. Here are some of the key nutrients found in beetroot:
- Vitamin C: One cup of raw beetroot provides about 6.7 milligrams of vitamin C, which is approximately 11% of the daily value. Vitamin C is an antioxidant that helps to protect the body from damage caused by free radicals.
- Folate (B9): One cup of raw beetroot contains about 148 micrograms of folate, which is approximately 37% of the daily value. Folate is important for DNA synthesis and repair, and it plays a crucial role in fetal development.
- Potassium: One cup of raw beetroot provides about 442 milligrams of potassium, which is approximately 9% of the daily value. Potassium is an electrolyte that helps to regulate fluid balance, muscle contractions, and nerve signals.
- Magnesium: One cup of raw beetroot contains about 31.5 milligrams of magnesium, which is approximately 8% of the daily value. Magnesium is involved in over 300 biochemical reactions in the body, including muscle and nerve function, blood pressure regulation, and protein synthesis.
- Iron: One cup of raw beetroot provides about 1.1 milligrams of iron, which is approximately 6% of the daily value. Iron is essential for the production of hemoglobin, a protein in red blood cells that carries oxygen throughout the body.
- Other vitamins and minerals found in beetroot include vitamin B6, phosphorus, manganese, and copper.
Overall, beetroot is a rich source of essential vitamins and minerals that are important for overall health and well-being. Incorporating beetroot into a balanced diet can be a simple and delicious way to boost nutrient intake.
The Bottom Line
Beetroot is a nutrient-dense vegetable that contains an array of essential vitamins and minerals, including vitamin C, folate, potassium, magnesium, and iron, among others. It is a low-calorie vegetable that can be beneficial for those with diabetes and PCOS, and it may also promote thyroid health and aid weight loss. Beetroot is a low glycemic index food that is high in fiber, making it a good source of carbohydrates for those looking to maintain stable blood sugar levels. Additionally, beetroot contains phytochemicals that help to regulate hormones and antioxidants that protect the body from free radicals. Overall, incorporating beetroot into a balanced diet can be a simple and effective way to boost nutrient intake and potentially improve overall health.
Faqs
How many beetroots can I eat in a day?
While the beetroot is a nutritious vegetable that can offer several health benefits, it’s important to keep in mind that moderation is key. There is no one-size-fits-all answer to how much beetroot you can eat in a day as it may depend on various factors such as your age, sex, weight, activity level, and overall health status.
That being said, a general guideline is to consume about 1-2 cups (or about 136-272 grams) of cooked or raw beetroot per day. It’s also important to note that beetroot is high in oxalates, which can contribute to the formation of kidney stones in some individuals. Therefore, if you have a history of kidney stones, it may be best to limit your intake of beetroot or speak with a healthcare professional to determine what’s right for you.
Overall, while beetroot can offer several health benefits, it’s important to consume it in moderation and in the context of a balanced and varied diet.
Should I eat Beetroot before or after exercise?
Beetroot contains nitrates that are converted to nitric oxide in the body, which can help to improve blood flow and oxygen delivery to the muscles during exercise. Therefore, consuming beetroot before exercise may offer potential benefits for athletic performance.
Studies have shown that consuming beetroot juice or beetroot powder before exercise can improve endurance, decrease oxygen consumption, and increase time to exhaustion. However, the optimal timing of beetroot consumption may vary depending on the individual, type of exercise, and other factors.
As a general guideline, consuming beetroot juice or beetroot powder about 1-2 hours before exercise may be beneficial for enhancing performance. It’s also important to keep in mind that beetroot can be high in fiber, which may cause digestive discomfort if consumed immediately before exercise. Therefore, it may be best to experiment with the timing and amount of beetroot consumption to find what works best for you.
Overall, while consuming beetroot before exercise may offer potential benefits for athletic performance, it’s important to consume it in the context of a balanced and varied diet and to experiment with the timing and amount of consumption to find what works best for you.
What are the benefits of Beetroot?
Beetroot is a nutrient-dense vegetable that may offer several health benefits. Here are some potential benefits of consuming beetroot:
- May help to lower blood pressure: Beetroot contains nitrates that are converted to nitric oxide in the body, which can help to improve blood flow and lower blood pressure.
- May improve athletic performance: The nitrates in beetroot may also improve endurance and exercise performance by enhancing oxygen delivery to the muscles.
- May reduce inflammation: Beetroot contains antioxidants that can help to reduce inflammation in the body, potentially reducing the risk of chronic diseases such as heart disease, cancer, and Alzheimer’s disease.
- May support liver function: Beetroot contains betaine, which can help to support liver function and detoxification.
- May promote digestion: Beetroot is high in fiber, which can help to promote healthy digestion and reduce the risk of digestive issues such as constipation.
- May improve brain function: The nitrates in beetroot may also improve cognitive function by increasing blood flow to the brain and reducing inflammation.
- May support weight loss: Beetroot is low in calories and high in fiber, making it a filling food that can help to support weight loss and weight management.
Overall, incorporating beetroot into a balanced diet may offer several potential health benefits. However, it’s important to consume beetroot in moderation and in the context of a healthy and varied diet to maximize its benefits.
What is the best time to eat Beetroot?
There is no specific “best” time to eat beetroot as it can be beneficial to consume at any time of the day. However, there are some considerations that may help to maximize its benefits.
If you’re looking to incorporate beetroot into your diet for its potential blood pressure-lowering effects, consuming it in the morning may be beneficial. The nitrates in beetroot are converted to nitric oxide in the body, which can help to improve blood flow and lower blood pressure, and consuming beetroot in the morning may help to maintain the blood pressure-lowering effects throughout the day.
If you’re looking to consume beetroot for its potential athletic performance benefits, consuming it about 1-2 hours before exercise may be beneficial. The nitrates in beetroot may help to improve endurance and exercise performance by enhancing oxygen delivery to the muscles.
Overall, the best time to eat beetroot may vary depending on your goals and preferences. It can be consumed as a part of a balanced meal or snack at any time of the day to maximize its nutrient content and potential health benefits.