The Indian name for pearl millet is bajra. One of the earliest grains to be farmed. It is available anywhere in the world and is frequently consumed in rural India. It has several health advantages and is a great source of numerous nutrients. Fiber and critical amino acids are plentiful in pearl millet. Bajra is healthy and resistant to heat, drought, and several types of pollution that harm other grains. It is a healthier alternative for those with celiac disease and gluten allergies because it is non-glutinous. They are loaded with nutrients like iron, phosphorus, magnesium, and zinc as well as minerals like thiamine, riboflavin and folic acid, as well as important amino acids, antioxidants, and beta carotene.
Nutritional Value of Bajra
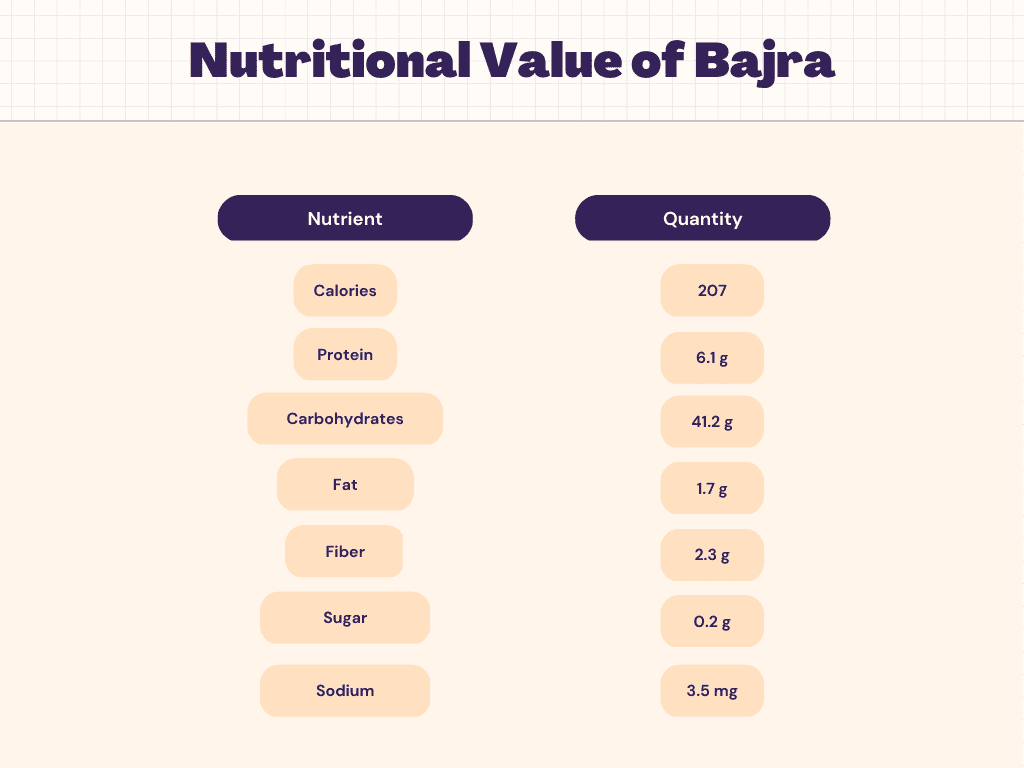
Nutritional Facts of Bajra
Carbs
A cooked cup of millet contains about 207 calories. Carbohydrates account for the majority of calories. One cup contains 41.2 grams of carbohydrates, 2.3 grams of fiber, and 0.2 grams of sugar that is present naturally. Starch makes up the remaining millet’s carbs.
Fats
Fats Millet is a low-fat meal by nature. There are only 1.7 grams of fat per cup. The majority of the fat (0.9 grams) is polyunsaturated, with the remaining 0.3 grams coming from monounsaturated fat and the remainder from saturated fat (0.3 grams).
Protein
Per cup serving, millet has 6.1 grams of protein. Although quinoa has more protein than some other grains and starches (such as white rice), at 8 grams per one-cup serving, this is still a pretty high amount.
Health Benefits Of Bajra
- Security for Gluten-Free Diet – Millet is a safe option for those who need to eat dietary fiber, protein, and healthful carbohydrates yet have celiac disease or non-celiac gluten sensitivity. Millet is inherently gluten-free, just like quinoa, sorghum, and amaranth.
- Contributes to Increasing Daily Fiber Consumption – Dietary fiber content in millet is not very high. It contains more fiber than brown rice (3.5 grams per cup) but less than other grains like quinoa (5 grams per cup) and barley (6 grams per cup).
- Maybe Prevents Chronic Illness – When cells are exposed to free radicals, oxidative stress may develop, which is prevented by antioxidants. Many disorders, including cancer, cardiovascular disease, diabetes, Alzheimer’s disease, and others are known to be impacted by oxidative stress.
- Helps in weight loss and maintenance – According to research, eating whole grains with a low-calorie density, such as bajra, may be beneficial if you’re trying to lose weight. The bajra has a 1.2 calorie density. A top-notch, gluten-free source of fiber that helps with weight loss and maintenance is bajra. Check our Weight Loss Plans.
- Helps with diabetes management – Given its high nutritious content and moderate 54 glycemic index, bajra is a great option for diabetes people. The high protein and fiber content, however, reduces the glycemic load. It aids in reducing blood sugar rises and slowing glucose absorption. Check our Diabetes Plans.
Vitamins & Minerals in Bajra
With 0.3 mg, or almost 13% of the daily value, of manganese, millet is a good source of the mineral (DV). Moreover, 44 mg of magnesium, or about 10% of the daily requirement, is provided. 100 mg of phosphorus (8% DV) and 0.16 mg of copper (17% DV) are provided. Niacin (1.3 mg or approximately 8% of the daily value) and thiamin (0.11 mg or about 9% of the daily value) are two vitamins found in millet. In smaller levels, you’ll also get riboflavin, folate, and vitamin B6.
The Bottom Line
It has several health advantages and is a great source of numerous nutrients. Fiber and critical amino acids are plentiful in pearl millet. Bajra is healthy and resistant to heat, drought, and several types of pollution that harm other grains.
FAQs
What is the right time to eat Bajra?
While it pairs well with winter fare, pearl millet, also known as bajra, is one of the typical grains that Indians enjoy eating during the winter. Yet it’s also drunk in sweltering summers to keep the body cool and prevent heatstroke.
What are the benefits of Bajra?
- High protein content
- a lot of fiber
- For vegetarians, a complete protein
- Free of gluten
- Beneficial for Diabetics
- Beneficial for the Heart
- Reduces Cholesterol
- Blood Pressure Lowering