Hyperthyroidism(overactive thyroid) is a medical condition that occurs when the thyroid gland produces too much thyroid hormone(overactive thyroid). This hormone plays a crucial role in regulating many bodily functions, including metabolism, heart rate, and body temperature. When the thyroid gland is overactive, it can lead to a range of hyperthyroidism symptoms(hyperthyroid symptoms), including weight loss, rapid heartbeat, and anxiety. There are several potential hyperthyroidism causes(what causes hyperthyroidism/hyperthyroidism causes), including autoimmune disorders, thyroid nodules, and excessive iodine intake. With proper diagnosis and treatment, many people with hyperthyroidism are able to effectively manage the condition and live healthy, normal lives. Find thyroid test at home here!
What is Hyperthyroidism?
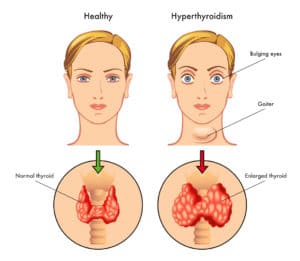
Hyperthyroidism(overactive thyroid) is a medical condition in which the thyroid gland(overactive thyroid), located in the neck, produces an excess of thyroid hormones. These hormones play a crucial role in regulating metabolism, heart rate, body temperature, and other bodily functions. When the thyroid gland produces too much hormone, it can lead to a range of hyperthyroidism symptoms(hyperthyroid symptoms), including weight loss, rapid heartbeat, anxiety, and tremors. Hyperthyroidism(overactive thyroid) can be caused by several hyperthyroidism causes(what causes hyperthyroidism), including autoimmune disorders, thyroid nodules, and excessive iodine intake. Treatment options for hyperthyroidism include medications, radioactive iodine therapy, surgery, and beta-blockers. With proper diagnosis and treatment, many people with hyperthyroidism are able to effectively manage the condition and live healthy, normal lives.
What are the Symptoms of Hyperthyroidism?
Hyperthyroidism symptoms(hyperthyroid symptoms) can vary from person to person, and some people may experience few or no symptoms(symptoms of hyperthyroidism in females/symptoms of hyperthyroidism in males) at all. However, common hyperthyroidism symptoms(symptoms of hyperthyroidism in females/symptoms of hyperthyroidism in males) may include:
- Weight loss despite an increased appetite
- Rapid heartbeat or heart palpitations
- Increased sweating
- Tremors or shaking
- Nervousness or anxiety
- Difficulty sleeping
- Changes in bowel patterns, such as diarrhea
- Increased sensitivity to heat
- Muscle weakness or fatigue
- Menstrual irregularities
In some cases, hyperthyroidism(overactive thyroid) can also cause eye problems, such as bulging eyes or double vision. This is more common in cases of Graves’ disease, an autoimmune disorder that is a common hyperthyroidism causes(what causes hyperthyroidism).
If you are experiencing any of these hyperthyroidism symptoms(symptoms of hyperthyroidism in females/symptoms of hyperthyroidism in males), it is important to see a healthcare professional for a proper diagnosis and treatment. Hyperthyroidism can be effectively managed with proper medical care and knowing the symptoms of hyperthyroidism in females/symptoms of hyperthyroidism in males.
Symptoms of Hyperthyroidism in Females
The hyperthyroidism symptoms in females(hyperthyroid symptoms) are similar to those in males, and can include:
- Weight loss despite an increased appetite
- Rapid heartbeat or heart palpitations
- Increased sweating
- Tremors or shaking
- Nervousness or anxiety
- Difficulty sleeping
- Changes in bowel patterns, such as diarrhea
- Increased sensitivity to heat
- Muscle weakness or fatigue
- Menstrual irregularities
In addition to these common hyperthyroidism symptoms(hyperthyroid symptoms), hyperthyroidism in females can also cause specific symptoms(what causes hyperthyroidism) related to reproductive health, such as:
- Changes in menstrual cycles, including lighter or heavier periods, or missed periods
- Fertility issues, such as difficulty getting pregnant
- Breast discharge or enlargement
- Changes in libido or sexual function
It is important for women who experience any of these Hypothyroid or hyperthyroidism symptoms(hyperthyroid symptoms) to see a healthcare professional for a proper diagnosis and treatment. Hyperthyroidism can have an impact on reproductive health and overall well-being if left untreated.
Symptoms of Hyperthyroidism in Males
The hyperthyroidism symptoms in males are generally similar to those in females and can include:
- Weight loss despite an increased appetite
- Rapid heartbeat or heart palpitations
- Increased sweating
- Tremors or shaking
- Nervousness or anxiety
- Difficulty sleeping
- Changes in bowel patterns, such as diarrhea
- Increased sensitivity to heat
- Muscle weakness or fatigue
In some cases, hyperthyroidism in males can also cause specific hyperthyroidism symptoms(what causes hyperthyroidism) related to reproductive health, such as:
- Erectile dysfunction
- Changes in libido or sexual function
- Breast enlargement
It is important for men who experience any of these hyperthyroidism symptoms(hyperthyroid symptoms) to see a healthcare professional for a proper diagnosis and treatment. Hyperthyroidism can have an impact on reproductive health and overall well-being if left untreated.
Symptoms of Hyperthyroidism in Teens & Children
Hyperthyroidism is a relatively rare condition in children and teenagers, but when it does occur, the hyperthyroidism symptoms(symptoms of hyperthyroidism in infants/symptoms of hyperthyroidism in children) can be similar to those in adults. However, some symptoms may be more pronounced in children and teenagers. Common symptoms of hyperthyroidism in teens and children(symptoms of hyperthyroidism in infants/symptoms of hyperthyroidism in children) may include:
- Hyperactivity or restlessness
- Difficulty concentrating or paying attention
- Weight loss or failure to gain weight
- Increased appetite
- Rapid heartbeat or heart palpitations
- Sweating or increased sensitivity to heat
- Increased thirst and urination
- Fatigue or weakness
- Muscle weakness or tremors
- Stunted growth or delayed puberty
In addition to these hyperthyroidism symptoms(symptoms of hyperthyroidism in infants/symptoms of hyperthyroidism in children), hyperthyroidism in children and teenagers can also cause eye problems, such as bulging eyes or eye irritation. It is important for parents or caregivers of children who experience any of these symptoms(hyperthyroid symptoms) to seek medical attention promptly. Hyperthyroidism can be effectively treated in children and teenagers with proper medical care, allowing them to grow and develop normally. Read more about this in-depth in our Thyroid Blogs.
Symptoms of Hyperthyroidism in Infants
Hyperthyroidism is a rare condition in infants, but when it occurs, it is usually caused by an overactive thyroid gland that is present at birth (congenital). Hyperthyroidism symptoms(symptoms of hyperthyroidism in infants/symptoms of hyperthyroidism in children) can be subtle and may develop slowly over time, making it difficult to diagnose. However, some common symptoms of hyperthyroidism in infants may include:
- Difficulty sleeping or excessive sleepiness
- Poor feeding or difficulty gaining weight
- Rapid heartbeat or heart palpitations
- Sweating or increased sensitivity to heat
- Tremors or shaking
- Bulging fontanelle (the soft spot on the top of the head)
- Jaundice (yellowing of the skin and eyes)
- Diarrhea or frequent bowel movements
- Muscle weakness or floppiness
- Irritability or fussiness
It is important for parents or caregivers to seek medical attention promptly if they suspect their infant has hyperthyroidism or see symptoms of hyperthyroidism in infants/symptoms of hyperthyroidism in children(hyperthyroid symptoms). Early diagnosis and treatment can prevent complications and promote normal growth and development. Hyperthyroidism in infants is usually treated with medications or, in rare cases, surgery.
Causes of Hyperthyroidism
Hyperthyroidism is a condition that occurs when the thyroid gland produces too much thyroid hormone. There are several potential causes of hyperthyroidism(what causes hyperthyroidism), including:
- Graves’ disease: This is the most common cause of hyperthyroidism, accounting for approximately 70-80% of cases. It is an autoimmune disorder that causes the immune system to attack the thyroid gland, resulting in excessive production of thyroid hormone.
- Thyroid nodules or goiter: Nodules or growths on the thyroid gland can produce excess thyroid hormone, leading to hyperthyroidism. A goiter, or enlarged thyroid gland, can also cause hyperthyroidism.
- Subacute thyroiditis: This is an inflammation of the thyroid gland that can cause temporary hyperthyroidism. It may be caused by a viral infection or autoimmune disorder.
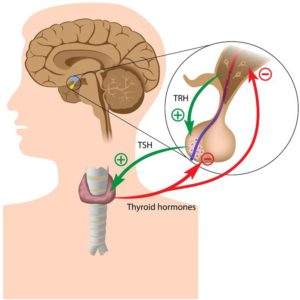
- Pituitary gland dysfunction: The pituitary gland produces thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH), which stimulates the thyroid gland to produce thyroid hormone. In rare cases, a pituitary gland tumor or other pituitary gland dysfunction can cause excessive TSH production, leading to hyperthyroidism.
- Medications: Certain medications, such as amiodarone, lithium, and interferon-alpha, can interfere with thyroid hormone production and cause hyperthyroidism.
- Other rare causes: In rare cases, hyperthyroidism may be caused by genetic mutations or other underlying health conditions.
It is important to identify the underlying cause of hyperthyroidism to ensure appropriate treatment and thyroid Management.
When to see a doctor for Hyperthyroidism
If you experience symptoms of hyperthyroidism, it is important to consult your doctor promptly. Some common symptoms of hyperthyroidism include rapid heart rate, weight loss, increased appetite, anxiety, and tremors. Left untreated, hyperthyroidism can lead to serious complications, such as heart problems, bone loss, and eye problems.
If you are experiencing any of the following signs or symptoms, you should seek medical attention immediately:
- Chest pain or rapid heart rate: Hyperthyroidism can cause heart problems, such as an irregular or rapid heartbeat, which can be dangerous and require immediate medical attention.
- Severe anxiety or panic attacks: Hyperthyroidism can cause anxiety and panic attacks, but if they become severe or persistent, it is important to seek medical help.
- Difficulty breathing or shortness of breath: Severe hyperthyroidism can cause breathing difficulties, which can be life-threatening and require emergency medical care.
- Severe weight loss or muscle weakness: Rapid weight loss or muscle weakness can be signs of advanced hyperthyroidism, which requires prompt medical attention.
- Vision changes or eye problems: Hyperthyroidism can cause eye problems, such as bulging eyes or double vision, which can indicate a serious condition that requires medical evaluation.
- Severe nausea, vomiting, or diarrhea: These symptoms can be signs of a potentially life-threatening condition called thyroid storm, which requires emergency medical treatment.
What are the risk factors associated with Hyperthyroidism?
There are several risk factors associated with hyperthyroidism, including:
- Gender: Women are more likely than men to develop hyperthyroidism.
- Age: Hyperthyroidism is more common in people over the age of 60.
- Family history: Having a family history of thyroid problems increases your risk of developing hyperthyroidism.
- Autoimmune disorders: Certain autoimmune disorders, such as Graves’ disease, increase the risk of hyperthyroidism.
- Radiation exposure: Exposure to radiation, such as during cancer treatment or from nuclear accidents, can increase the risk of hyperthyroidism.
- Iodine intake: Too much iodine, either through diet, Thyroid Recipes, or supplements, can cause hyperthyroidism in some people.
- Medications: Some medications, such as amiodarone or interferon, can increase the risk of hyperthyroidism.
- Pregnancy: Hyperthyroidism can develop during pregnancy or shortly after giving birth, especially in women with a history of thyroid problems.
It is important to be aware of these risk factors and discuss any concerns with your healthcare provider. Regular thyroid screenings and check-ups can help identify hyperthyroidism early and prevent serious complications. Become our next Next Thyroid Success Story!
How common is Hyperthyroidism?
Hyperthyroidism is a relatively common condition, with an estimated prevalence of 1.2% in the general population. It is more common in women than in men, and the incidence tends to increase with age. Hyperthyroidism is most commonly caused by autoimmune disorders, such as Graves’ disease, but it can also be caused by other factors such as thyroid nodules or inflammation of the thyroid gland. The incidence and prevalence of hyperthyroidism may vary depending on geographic location, genetics, and other environmental factors. Early diagnosis and treatment can help manage the symptoms of hyperthyroidism and prevent serious complications.
The Bottom Line
Hyperthyroidism is a condition in which the thyroid gland produces too much thyroid hormone, leading to a variety of symptoms such as weight loss, rapid heartbeat, and anxiety. It can be caused by a number of factors, including autoimmune disorders, thyroid nodules, or inflammation of the thyroid gland. Hyperthyroidism is more common in women and older adults. While there is no cure for hyperthyroidism, there are a variety of treatments available to manage hyperthyroidism symptoms and reduce the production of thyroid hormones, such as medications, radioactive iodine therapy, or surgery. Home remedies and lifestyle changes may also help manage symptoms. If you suspect that you may have hyperthyroidism, it is important to see a healthcare provider for a proper diagnosis and treatment plan.
FAQs
Can Hyperthyroid symptoms appear suddenly?
Yes, hyperthyroid symptoms can appear suddenly in some cases. This can be particularly true in the case of Graves’ disease, which is the most common cause of hyperthyroidism. Graves’ disease is an autoimmune disorder that causes the thyroid gland to produce too much thyroid hormone(hyperthyroidism causes). Symptoms of Graves’ disease can appear suddenly and may include rapid heartbeat, anxiety, weight loss, and tremors. In some cases, hyperthyroidism can also be caused by a sudden increase in the release of thyroid hormones due to factors such as thyroiditis or the use of certain medications. If you experience a sudden onset of hyperthyroidism symptoms, it is important to see a healthcare provider for a proper diagnosis and treatment plan.
What are the Early Signs and Symptoms of Hyperthroid?
The early signs and hyperthyroidism symptoms(hyperthyroid symptoms) may vary from person to person, but some common ones include:
- Unexplained weight loss
- Rapid or irregular heartbeat
- Nervousness, anxiety, or irritability
- Tremors or shakiness
- Increased sweating and heat intolerance
- Fatigue or muscle weakness
- Difficulty sleeping
- Changes in menstrual patterns in women
- Increased appetite
- Changes in bowel patterns
- Eye problems such as bulging eyes or eye irritation (in Graves’ disease)
These early signs and hyperthyroidism symptoms may not always be obvious, and some people may not experience any symptoms at all. If you suspect that you may have hyperthyroidism or experience any of the above symptoms, it is important to see a healthcare provider for a proper diagnosis and treatment plan.
What are the common symptoms of Hyperthyroid?
The common symptoms of hyperthyroidism(hyperthyroid symptoms) can include:
- Unexplained weight loss
- Rapid or irregular heartbeat
- Nervousness, anxiety, or irritability
- Tremors or shakiness
- Increased sweating and heat intolerance
- Fatigue or muscle weakness
- Difficulty sleeping
- Changes in menstrual patterns in women
- Increased appetite
- Changes in bowel patterns
- Eye problems such as bulging eyes or eye irritation (in Graves’ disease)
Not everyone with hyperthyroidism will experience all of these symptoms, and the severity and combination of symptoms can vary depending on the individual and the underlying cause of the condition. It is essential to see a healthcare provider for a proper diagnosis and treatment plan if you suspect that you may have hyperthyroidism or experience any of these symptoms.
What are the warning signs of Hyperthyroid?
The warning signs of hyperthyroidism may include:
- Sudden and unexplained weight loss
- Rapid or irregular heartbeat
- Nervousness, anxiety, or irritability
- Tremors or shakiness
- Increased sweating and heat intolerance
- Fatigue or muscle weakness
- Difficulty sleeping
- Changes in menstrual patterns in women
- Increased appetite
- Changes in bowel patterns
- Eye problems such as bulging eyes or eye irritation (in Graves’ disease)
It is important to note that some people with hyperthyroidism may not experience any symptoms or may only have mild symptoms, while others may have more severe symptoms. If you experience any of these warning signs or symptoms, it is important to see a healthcare provider for a proper diagnosis and treatment plan. Hyperthyroidism can be a serious condition if left untreated, and early diagnosis and treatment are important for managing the condition and preventing complications. Read about science of thyroid to get a better understanding.