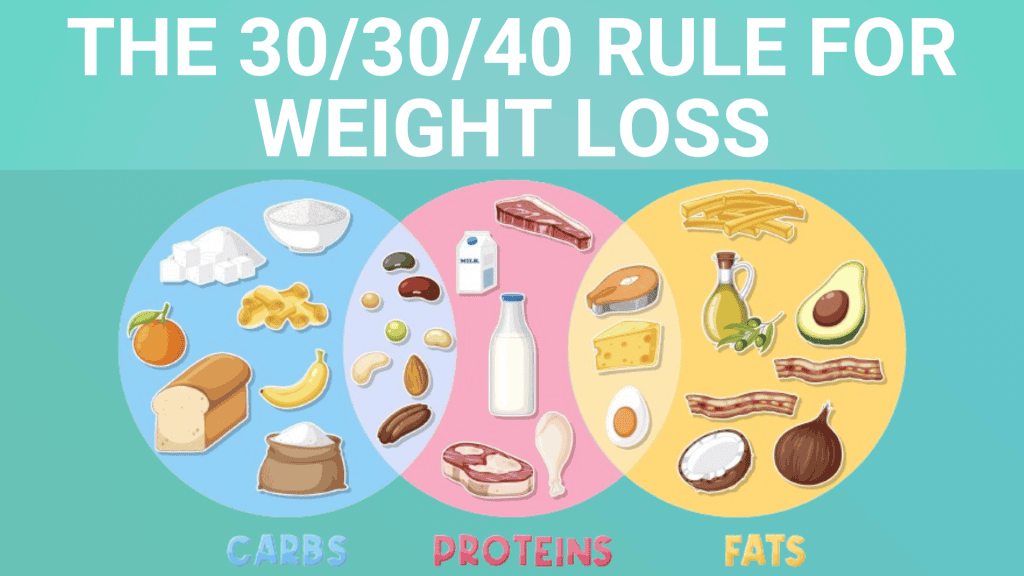
The 30/30/40 rule for weight loss involves a balanced macronutrient mix, which has been shown to help with weight loss and overall health improvement. The 30 30 40 rule, also called the Zone Diet, is a popular eating plan developed over 30 years ago by Dr. Barry Sears, an American biochemist known for his book The Zone. This diet focuses on maintaining a specific balance of macronutrients: 40% carbohydrates, 30% protein, and 30% fat. The idea is to optimize hormonal balance to control inflammation in the body. Carbohydrates have a low glycemic index, releasing sugar slowly into the bloodstream, keeping you feeling fuller for longer periods. Protein sources should be lean, like chicken, fish, or tofu, while fats such as olive oil, avocados, or nuts should primarily be monounsaturated. This combination is believed to help stabilize blood sugar levels and maintain energy throughout the day.
There are two main methods to implement the Zone Diet: the hand-eye method and the Zone food block method. The hand-eye method is straightforward and suitable for beginners, and it involves using your hand and eye to estimate portion sizes. One-third of your plate should be lean protein, about the size of your palm. Two-thirds should be low-glycemic index carbs, and monounsaturated fat should be added. This 30-30-40 rule helps regulate meal timing and portion control, preventing long gaps between meals. Conversely, it restricts high-sugar fruits, starchy vegetables, refined carbs, and foods with added sugars. Proponents claim benefits such as weight loss, improved energy levels, and better overall health by focusing on these food choices and maintaining the prescribed macronutrient balance.
What is the 30/30/40 Rule?
The 30 30 40 rule for weight loss suggests that 40% of your total daily calories should come from carbohydrates, 30% from protein, and 30% from fat. This macronutrient distribution supports improvements in body composition, overall health, and wellness across various populations. The 30 30 40 rule is a dietary guideline that balances the three main macronutrients—carbohydrates, proteins, and fats—to optimize weight loss and overall health. This approach ensures that you get a balanced intake of essential nutrients, which is crucial for maintaining energy levels, supporting muscle growth, and promoting overall well-being.
Carbohydrates, which should make up 40% of your intake, are the body’s primary energy source, and complex carbs like whole grains, fruits, and vegetables ensure you get essential vitamins, minerals, and fiber. Proteins, at 30%, are vital for building and repairing tissues, producing enzymes and hormones, and supporting immune function; consuming adequate protein helps preserve muscle mass during weight loss, increases satiety, and boosts metabolism, with lean meats, fish, eggs, dairy, legumes, and plant-based proteins being excellent sources. Fats, also at 30%, are essential for absorbing fat-soluble vitamins, supporting cell growth, protecting organs, and keeping the body warm, with healthy fats from avocados, nuts, seeds, and olive oil providing these benefits without contributing to weight gain when consumed in appropriate amounts along with weight loss drinks.
How Does the 30/30/40 Rule for Weight Loss Work?
The 30 30 40 rule works by balancing your intake of carbohydrates, proteins, and fats to create a sustainable and effective weight loss plan. This rule suggests that you should get 40% of your calories from carbohydrates, 30% from proteins, and 30% from fats. Let’s explain how each part of this rule helps with weight loss.
Carbohydrates (40%)
Carbohydrates are your body’s main energy source, and your body breaks them down into glucose, which fuels your muscles and brain. You should focus on complex carbohydrates like whole grains, vegetables, legumes, and 5 fruits to avoid for weight loss. These carbs are digested more slowly, giving you a steady energy supply and preventing those blood sugar spikes that lead to cravings and overeating. A study has found that diets rich in whole grains can lower the risk of obesity and type 2 diabetes because they positively affect metabolism and insulin sensitivity.
Proteins (30%)
Proteins are crucial for muscle repair and growth, and your body uses them to build and maintain muscle mass, which is important because muscle burns more calories at rest than fat. So, having more muscle means you burn more calories throughout the day. Plus, protein has a high thermic effect, so your body uses more energy to digest it, helping with weight loss. Research shows that a high-protein diet can increase thermogenesis and satiety, contributing to weight loss. Another study found that a high-protein diet helps preserve lean muscle mass during weight loss, which boosts metabolic health.
Fats (30%)
Fats often get a bad reputation regarding weight loss, but healthy fats are essential as they help with nutrient absorption, hormone production, and keeping you full. Eating enough healthy fats, like those in avocados, nuts, seeds, and olive oil, makes you feel satisfied and less likely to overeat. Moreover, fats slow down the digestion of carbohydrates, leading to more stable blood sugar levels. Diets high in healthy fats, like the Mediterranean diet, are linked to lower risks of heart disease and obesity. Additionally, a study showed that healthy fats can help with weight management by making you feel fuller and longer and reducing overall calorie intake, which will help you to answer How to Lose 8 kg in a Month.
The Zone Diet is an alternate name for the 30 30 40 diet plan, which is designed to optimize hormone levels and control inflammation through balanced nutrition. Following its principles can achieve a state known as “the Zone,” where various health benefits are maximized.
Understanding “The Zone”
“The Zone” is a state in which your body operates at peak efficiency by balancing hormone levels to control inflammation. Achieving this state has numerous health benefits, including How to Lose 1 kg in a Week:
- Losing Extra Body Fat: The Zone Diet aims to help individuals lose body fat quickly by balancing macronutrient intake. Research shows that a balanced diet with appropriate carbohydrates, proteins, and fat proportions can support weight loss and metabolic health.
- Maintaining Wellness into Older Age: The Zone Diet’s anti-inflammatory effects may contribute to better overall health and reduced risk of age-related diseases. Chronic inflammation is linked to conditions like heart disease, diabetes, and cancer.
- Slowing Down the Rate of Aging: Reducing inflammation can slow the aging process at the cellular level. Studies indicate that lower levels of inflammation are associated with slower biological aging and a lower risk of age-related diseases.
- Improving Physical and Cognitive Performance: Proper hormonal balance and reduced inflammation can enhance physical performance and cognitive function. Omega-3 fatty acids, a key diet component, are known to support brain health and cognitive function.
Steps to Follow for the 30/30/40 Weight Loss Rule
The 30/30/40 rule for weight loss is a dietary guideline focusing on a balanced intake of macronutrients: 40% carbohydrates, 30% protein, and 30% fat. This method supports weight loss and nutrient sufficiency. Here’s a guide on effectively implementing the 40 30 30 rule in your diet. This balance is intended to stabilize blood sugar levels, reduce inflammation, and improve overall health. The diet is divided into three steps: Entering the Zone, Customizing Your Plan, and Lifelong Maintenance.
STEP 1: Entering the Zone
This stage focuses on familiarizing oneself with the 30 30 40 rule, which is an important factor in the diet plan. During this period, one must understand portion sizes and meal combinations that follow the specific macronutrient ratio. This foundational knowledge is crucial for successfully progressing to the next stages.
Blood Sugar Control: A study found that individuals who followed the Zone Diet significantly improved blood sugar control. The diet’s 40-30-30 ratio helps in maintaining steady glucose levels, which is crucial for diabetes management and prevention.
Inflammation Reduction: Research highlights that the Zone Diet significantly reduced markers of inflammation, such as C-reactive protein (CRP), and reduces inflammation, which is linked to a lower risk of chronic diseases, including heart disease and arthritis.
STEP 2: Customizing Your Plan
Customizing Your Plan is the second stage of the Zone Diet, where individuals personalize their meal plans to suit their personal preferences and nutritional needs. This phase lasts until the participant reaches their goal weight. During this time, individuals experiment with different food combinations while maintaining the 40-30-30 ratio to determine what works best for them. The goal is to find sustainable meal patterns that promote weight loss and health improvement.
Weight Loss: A study compared various diets and found that participants on the Zone Diet lost more weight over 12 months than those on other popular diets like Atkins, Ornish, and LEARN. On average, Zone Diet followers lost about 3.1 kgs, which was significantly higher than the weight loss observed in other diet groups.
Body Composition: Another study found that the Zone Diet significantly reduced body fat percentage and waist circumference, suggesting that it effectively targets abdominal fat, which is associated with a higher risk of metabolic diseases.
STEP 3: Lifelong Maintenance
Lifelong Maintenance is the final stage of the Zone Diet, focusing on sustaining the dietary habits developed in the previous stages. This phase focuses on continuously applying the 40-30-30 formula to maintain the achieved weight and health benefits.
Long-term Health Benefits: Studies indicate that following the 40 30 30 rule for a long time can reduce the risk of chronic diseases such as cardiovascular disease and type 2 diabetes by maintaining low levels of systemic inflammation and stable blood sugar levels.
Sustainable Weight Management: Research shows that those who maintain the Zone Diet over the long term are more likely to sustain their weight loss and avoid weight regain compared to those who follow less structured diets. The study highlighted that adherence to the 40-30-30 formula helps individuals maintain a healthy metabolism and body composition.
Benefits of the 30-30-40 Rule for Weight Loss
If you’re exploring different ways to eat healthier and improve your fitness, you might have come across the 40 30 30 meal plan, which divides your daily calories into 40% carbohydrates, 30% protein, and 30% fats. Let’s explore the benefits of the 40/30/30 macro split, exploring why it works so well and how it supports everything from muscle growth to weight loss, which helps in determining How Much Weight Can You Lose in a Month.
- Maximizes Muscle Protein Synthesis
- Provides Carbs for Energy
- Balances Hormones with Healthy Fats
- Enhances Satiety
- Eliminates Strict Calorie Counting
- Supports Fat Loss and Muscle Maintenance
- Customizable to Individual Preferences
1. Maximizes Muscle Protein Synthesis
The 30 30 40 rule is fantastic for muscle protein synthesis (MPS), which is the process where your body repairs and builds muscle tissue. To build and maintain muscle, you need to consume enough protein, and this diet ensures that 30% of your daily calories come from this crucial macronutrient, which is around 150 grams of protein per day if you’re following a 2000 calorie diet plan. In fact, a study found that eating between 1.6 and 2.2 grams of protein per kilogram of body weight daily can effectively stimulate MPS and support muscle growth for those engaged in resistance training. So, by sticking to the 40 30 30 rule, you’re ensuring your body has the right amount of protein to repair muscles after a workout and build new muscle mass.
2. Provides Carbs for Energy
Now, let’s talk about carbohydrates, the body’s main energy source, which is especially important if you’re doing intense workouts. In the 30 30 40 rule, 40% of your daily calories come from carbohydrates, which is about 250 grams per day on a 2500 Calorie diet plan. Carbohydrates help replenish the muscle glycogen stores that get depleted during exercise. Research has shown that eating carbs both before and after workouts can improve performance and speed up recovery by restoring glycogen levels. This balance ensures you have the energy you need for exercise while supporting recovery and overall performance.
3. Balances Hormones with Healthy Fats
Healthy fats are crucial for hormone production and metabolic health, and 30% of fat intake in the 40/30/30 split, which equals about 67 grams of fat per day on a 2,000-calorie diet, supports the production of hormones like testosterone and estrogen. These hormones are not just for reproductive health but are also essential for muscle growth and fat metabolism. Furthermore, fats like omega-3 and omega-6 fatty acids have been shown to reduce inflammation and support hormonal balance. In fact, a well-balanced intake of these fats can lead to improved metabolic functions and more efficient fat-burning. So, by including a good amount of healthy fats in your diet, the 40-30-30 rule helps keep your hormones in check, which is crucial for both fitness and overall health.
4. Enhances satiety
Satiety is that feeling of fullness you get after eating, and it plays a huge role in managing your appetite and preventing overeating. The combination of protein and fats in the 40/30/30 ratio is particularly effective at keeping you full. Research shows that diets high in protein and fats can be more filling than those high in carbohydrates, which helps reduce overall calorie intake. This means that with the 40/30/30 macro split, you’re likely to feel satisfied for longer periods, which can be helpful if you manage your weight while simply sticking to a healthy eating plan. The balance of nutrients helps you feel full and supports weight management.
5. Eliminates Strict Calorie Counting
One of the biggest perks of the 40/30/30 macro split is that it eliminates the need for strict calorie counting. Instead of obsessing over every single calorie you consume and constantly thinking of How many calories should i eat in a week, this diet focuses on keeping the right balance of macronutrients, which makes it flexible and easier to stick to a healthy diet without the stress of exact calorie calculations. You can enjoy a wider variety of foods while still meeting your nutritional goals, making the 40 30 30 ratio effective and practical for long-term success.
6. Supports Fat Loss and Muscle Maintenance
This balanced diet provides the right mix of protein, carbs, and fats to help you lose fat while keeping your muscles intact. Studies have demonstrated that a well-balanced macronutrient ratio can help achieve these goals simultaneously; by following the 40/30/30 macro split, you’re setting yourself up to reduce body fat and maintain lean muscle successfully. This balance helps you get that toned, athletic look while supporting overall fitness and health.
7. Customizable to Individual Preferences
Customizability is another fantastic aspect of the 40/30/30 macro split because it isn’t a one-size-fits-all plan. Instead, it allows you to adjust your carbohydrate and fat intake based on your personal preferences and dietary needs. This kind of personalization makes it easier for people to stick with the diet and meet their individual goals. Research has shown that personalizing your diet plan improves satisfaction, which is key for long-term success. With the 40-30-30 ratio, you can adjust it to fit your lifestyle while maintaining the overall nutrient balance. This flexibility makes it an adaptable and enjoyable option for many people.
Does the 30-30-40 Rule Help with Weight Loss?
Yes, the 30/30/40 rule, which suggests that 30% of your daily calories should come from protein, 30% from fats, and 40% from carbohydrates, can really help with weight loss because it promotes a balanced diet, reduces overeating, and supports your metabolic health. A balanced diet is essential for overall health and effective weight management, and this macronutrient distribution makes sure you get the right nutrients without eating too much of anything. The rule’s focus on protein intake is especially important because protein helps preserve muscle mass when you’re losing weight, and muscle is important for keeping a healthy metabolism. By making sure 30% of your calories come from protein, the rule helps you keep your muscles even if you’re eating fewer calories.
Studies have shown that diets with more protein are better at preserving muscle, and a balanced macronutrient intake can stop you from overeating because protein and fats make you feel fuller, and carbohydrates cut down on snacking and overeating, helping you create a caloric deficit in your body wants. The 40 30 30 rule also boosts calorie burn because protein and fats take more energy to digest, which helps improve the body’s composition by cutting fat and keeping lean muscle. Moreover, data from nutrition studies show that balanced diets like the 30 30 40 rule lead to better weight management, stable blood sugar levels, less hunger, and better satiety, all of which are crucial for long-term weight loss and if one includes exercises like Skipping for Weight Loss with this rule, it will help them significantly.
Risks or Side Effects of the 30/30/40 Weight Loss Rule
The Zone Diet is a popular diet plan, often known as the 30 30 40 rule, which suggests eating 30% protein, 30% fat, and 40% carbohydrates. While this meal plan is generally safe and can offer several benefits, it’s crucial to understand its potential risks and side effects. So, let’s dive into what you need to know.
- Digestive Issues from Higher Protein Intake
- Importance of Healthy Fats
- Questionable Claims and Limited Evidence
- Inflammation and Blood Values
- Optimal Macronutrient Ratio
1. Digestive Issues from Higher Protein Intake
When you suddenly increase your protein consumption, a higher protein diet can sometimes lead to digestive problems like bloating, constipation, and diarrhea. Your body needs time to adapt, and you might experience some digestive discomfort during this period. Ensure you drink plenty of water and eat enough Fiber rich foods, which can help with these issues. For instance, a study has found that a high-protein diet can increase the risk of gastrointestinal problems, especially if fiber intake is not increased alongside it.
2. Importance of Healthy Fats
Saturated fats, found in foods like butter and red meat, can negatively impact heart health when consumed beyond the limits. The 30 30 40 rule focuses on prioritizing healthy fats such as those from avocados, nuts, and olive oil. These fats support heart health and overall well-being, whereas excessive intake of saturated fats can lead to increased cholesterol levels and a higher risk of cardiovascular disease. According to health experts, replacing saturated fats with unsaturated fats can reduce the risk of cardiovascular disease by about 30%.
3. Questionable Claims and Limited Evidence
The 30 30 40 rule makes several health claims that it can improve athletic performance, but a study has found that athletes following the diet did lose weight, experienced reduced endurance, and increased fatigue compared to those on other diets, like the 7 day weight loss diet plan. This shows a potential downside for those who need energy and endurance in the long term.
4. Inflammation and Blood Values
The diet suggests that achieving specific blood values will put the body in a healthy state, or “the Zone.” While some studies indicate that the 40 30 30 rule can improve certain blood values, more research is needed to determine its impact on reducing inflammation. Current evidence does not strongly support the claim that the 30 30 40 macronutrient ratio significantly reduces inflammation. For example, Zone Diet might improve markers of inflammation, but the results could be more consistent, and further research is required.
5. Optimal Macronutrient Ratio
The Zone Diet or 30 30 40 rule specifies the ratio of 40% carbohydrates, 30% protein, and 30% fat, but very little evidence supports this as the optimal ratio for weight loss and health benefits. A study compared this ratio to a diet with 60% carbs, 15% protein, and 25% fat. It found that while individuals on the Zone-type diet lost more weight, this could be due to the higher protein intake rather than the specific ratio itself. Additionally, the study found no major differences in blood sugar, fat, and cholesterol levels between the two groups, suggesting that the health benefits of the Zone Diet may be less claimed.
Dos & Don’ts – 30-30-40 Rule
The 40 30 30 diet, also known as the macronutrient or zone diet, revolves around balancing carbohydrates, proteins, and fats in specific ratios: 40% carbohydrates, 30% protein, and 30% fat. This diet plan optimizes nutrition for better weight management and could be a great alternative to the 30 30 30 rule for weight loss.
Dos
Inclusivity: The 40 30 30 meal plan includes all food groups to ensure that you get a wide range of nutrients. This makes it easier to stick with long-term without cutting out major food groups and makes it flexible enough to add to any meal plan, such as the 7 week diet plan for weight loss.
Evidence-Based: Studies show that the benefits of maintaining balanced macronutrient ratios in this diet focus on moderate protein, carbs, and fat intake, which balances the macronutrient distribution and helps preserve lean body mass during weight loss.
Balanced Nutrition: The 30 30 40 diet focuses on a mix of carbohydrates, proteins, and fats, ensuring you get all the essential nutrients your body needs. This balance is crucial for keeping your metabolism in check and enhancing physical performance, which supports overall metabolic health.
Sustainability: The guidelines of the 40 30 30 diet promote healthy and sustainable eating habits that restrict calories by identifying how many calories should i burn a week and maintaining balanced macronutrient ratios, which can lead to weight loss and help in keeping the weight off.
Don’ts
Calorie Miscalculation: While focusing on macronutrient ratios, it is easy to overlook total calorie intake. This is crucial because achieving weight loss goals depends on controlling overall calorie consumption. Therefore, paying attention to both macronutrient balance and total calorie intake is important.
Individual Differences: The 40 30 30 diet doesn’t consider metabolism, activity levels, and nutritional needs. For example, someone who is very active may need more calories than what’s typically recommended by this diet. Hence, personalized adjustments may be necessary to fit your specific health and fitness goals.
Potential Underconsumption: Active individuals or those with higher calorie requirements might find the calorie levels suggested by the 40 30 30 rule too restrictive. If carefully managed, this could lead to sufficient energy and essential nutrients. Thus, closely monitoring your energy levels and nutritional intake is important. This tells you how many calories you require and helps you find out How many calories can walking 1000 steps burn.
Meal Plan for the 30-30-40 diet
Creating a balanced 40 30 30 meal plan is important for maintaining good health and energy levels throughout the day, and food blocks help with that. Food blocks are a way of portioning food to ensure a balanced intake of proteins, carbohydrates, and fats. Each block represents a specific amount of these macronutrients, allowing for precise control of your healthy food chart.
Meal Plan for Men
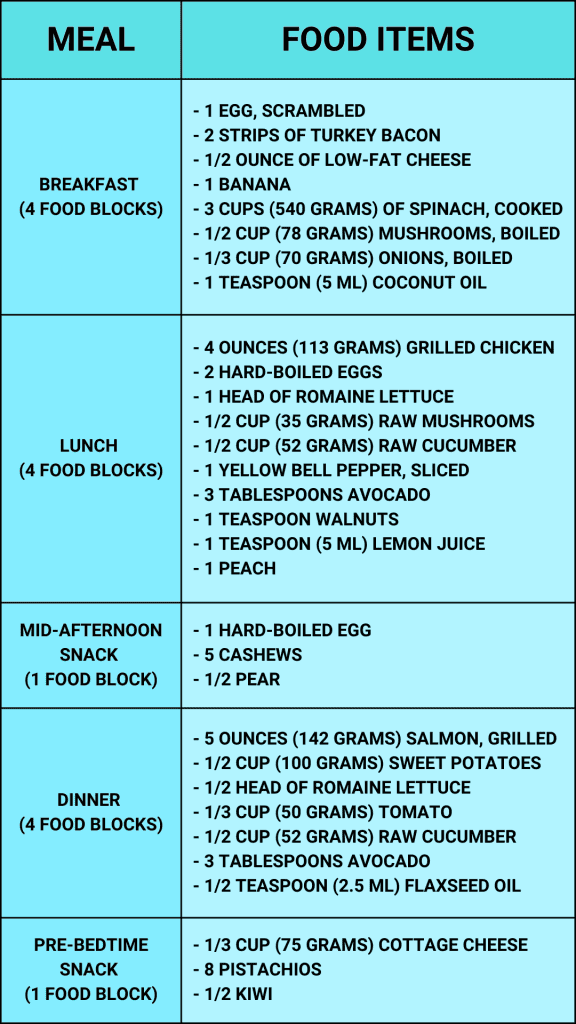
For men, a 14-block meal plan can provide the right proportions of macronutrients needed to support a healthy lifestyle. Here’s a detailed look at a sample meal plan for men that includes 14 food blocks.
Breakfast (4 Food Blocks): Scrambled Eggs with Turkey Bacon, Vegetables, and Fruit
- 1 egg, scrambled: Eggs are a great source of high-quality protein.
- 2 strips of turkey bacon: Turkey bacon adds more protein with less fat than regular bacon.
- 1/2 ounce of low-fat cheese: Add a small amount of healthy fat and protein.
- 1 banana: Provides essential vitamins and fiber.
- 3 cups (540 grams) of spinach, cooked: Rich in iron, vitamins, and fiber.
- 1/2 cup (78 grams) mushrooms, boiled: A good source of B vitamins and minerals.
- 1/3 cup (70 grams) onions, boiled: Adds flavor and nutrients.
- 1 teaspoon (5 ml) coconut oil: Healthy fats for heart health.
Lunch (4 Food Blocks): Grilled Chicken and Egg Salad with Fruit
- 4 ounces (113 grams) grilled chicken, skinless: Lean protein source.
- 2 hard-boiled eggs: Adds additional protein.
- 1 head of romaine lettuce: Provides a low-calorie base with hydration.
- 1/2 cup (35 grams) raw mushrooms: Nutrient-dense and low in calories.
- 1/2 cup (52 grams) raw cucumber, sliced: Hydrating and low in calories.
- 1 yellow bell pepper, sliced: Rich in vitamins A and C.
- 3 tablespoons avocado: Healthy fats and fiber.
- 1 teaspoon walnuts: Adds a bit of crunch and healthy fats.
- 1 teaspoon (5 ml) lemon juice dressing: Low-calorie flavor enhancer.
- 1 peach: Sweet and fiber-rich fruit option.
Mid-Afternoon Snack (1 Food Block): Boiled Egg, Nuts, and Fruit
- 1 hard-boiled egg: Quick and portable source of protein.
- 5 cashews: Healthy fats and a small amount of protein.
- 1/2 pear: Provides fiber and a natural source of carbohydrates.
Dinner (4 Food Blocks): Grilled Salmon, Lettuce, and Sweet Potatoes
- 5 ounces (142 grams) salmon, grilled: Rich in omega-3 fatty acids and high-quality protein.
- 1/2 cup (100 grams) of sweet potatoes, baked: Complex carbohydrates and vitamins.
- 1/2 head of romaine lettuce: Low-calorie base for bulk.
- 1/3 cup (50 grams) tomato: Provides vitamins and antioxidants.
- 1/2 cup (52 grams) raw cucumber, sliced: Adds crunch and hydration.
- 3 tablespoons avocado: Healthy fats and fiber.
- 1/2 teaspoon (2.5 ml) flaxseed oil: Supports heart health with healthy fats.
Pre-Bedtime Snack (1 Food Block): Cottage Cheese, Nuts, and Fruit
- 1/3 cup (75 grams) cottage cheese: High in casein protein, which is slow-digesting.
- 8 pistachios: Provide healthy fats and a small amount of protein.
- 1/2 kiwi: Provides vitamin C and natural sugars.
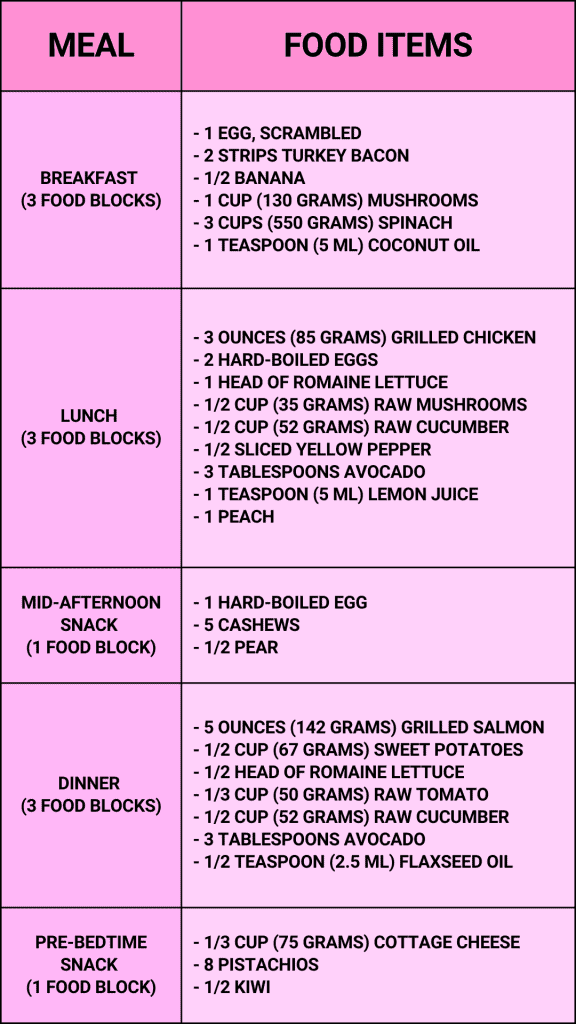
Meal Plan for Women
A meal plan for women typically includes 11 food blocks designed to meet the average nutritional needs. Here’s a detailed look at a sample meal plan for women that provides for 11 food blocks.
Breakfast (3 Food Blocks): Scrambled Eggs with Turkey Bacon and Fruit
- 1 egg, scrambled: High protein source.
- 2 strips turkey bacon: Lean protein.
- 1/2 banana: Provides fiber and natural sweetness.
- 1 cup (130 grams) mushrooms, boiled: Nutrient-rich and low in calories.
- 3 cups (550 grams) spinach, cooked: Provides iron and vitamins.
- 1 teaspoon (5 ml) coconut oil: Healthy fat for heart health.
Lunch (3 Food Blocks): Grilled Chicken and Egg Salad with Fruit
- 3 ounces (85 grams) grilled chicken, skinless: Lean protein source.
- 2 hard-boiled eggs: Adds protein.
- 1 head of romaine lettuce: Low-calorie, hydrating base.
- 1/2 cup (35 grams) raw mushrooms: Nutrient-dense and low in calories.
- 1/2 cup (52 grams) raw cucumber, sliced: Adds crunch and hydration.
- 1/2 sliced yellow pepper: Rich in vitamins and antioxidants.
- 3 tablespoons avocado: Provides healthy fats.
- 1 teaspoon (5 ml) lemon juice dressing: Low-calorie flavor.
- 1 peach: Sweet and fiber-rich.
Mid-Afternoon Snack (1 Food Block): Boiled Egg, Nuts, and Fruit
- 1 hard-boiled egg: Quick source of protein.
- 5 cashews: Healthy fats and protein.
- 1/2 pear: Provides natural sugars and fiber.
Dinner (3 Food Blocks): Grilled Salmon, Lettuce, and Sweet Potatoes
- Grilled 5 oz (142 grams) salmon: Rich in omega-3 fatty acids and protein.
- 1/2 cup (67 grams) of sweet potatoes, baked: Provides complex carbohydrates and vitamins.
- 1/2 head of romaine lettuce: Low-calorie, hydrating base.
- 1/3 cup (50 grams) raw tomato: Adds vitamins and antioxidants.
- 1/2 cup (52 grams) raw cucumber, sliced: Adds crunch and hydration.
- 3 tablespoons avocado: Healthy fats and fiber.
- 1/2 teaspoon (2.5 ml) flaxseed oil: Supports heart health with healthy fats.
Pre-Bedtime Snack (1 Food Block): Cottage Cheese, Nuts, and Fruit
- 1/3 cup (75 grams) cottage cheese: Slow-digesting casein protein.
- 8 pistachios: Provides healthy fats.
- 1/2 kiwi: Source of vitamin C and natural sugars.
Expert Review on the 30/30/40 Rule for Weight Loss
Dr. Ayush, a certified nutritionist, says the 30 30 40 rule is a smart and balanced way to lose weight, dividing daily calories into 30% protein, 30% fats, and 40% carbohydrates. It helps you feel full and keeps your muscles strong and your metabolism in great shape. Protein-rich foods like lean meats, beans, and dairy keep muscles strong and help burn calories. Healthy fats from foods like avocados and nuts provide essential fatty acids that regulate hormones and support overall health. Carbs from whole grains, fruits, and veggies give you energy and important nutrients like fiber and vitamins.
Moreover, the rule is flexible and fits with any diet plan, whether vegetarian, vegan, or eating everything. By focusing on nutrient-dense foods and keeping your protein, fats, and carbs balanced, the 30 30 40 rule isn’t just about losing weight; it’s about staying healthy in the long run and forming good eating habits. Adopting this rule as a lifestyle change can lead to significant long-term health benefits.
References
“Dietary Guidelines for Americans Guidelines and Key Recommendations – Redesigning the Process for Establishing the Dietary Guidelines for Americans.” n.d. NCBI. Accessed July 2, 2024. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK469839/.
“The Pros and Cons of the 40/30/30 Zone Diet.” 2018. Cellucor. https://cellucor.com/blogs/nutrition/the-pros-and-cons-40-30-30-diet.
Raman, Ryan, and Daniel Bubnis. 2017. “The Zone Diet: A Complete Overview.” Healthline. https://www.healthline.com/nutrition/zone-diet#TOC_TITLE_HDR_5.
FAQs
1. Is a 40-30-30 Diet Good for Weight Loss?
Yes, the 40 30 30 diet is good for weight loss because it has a balanced intake of macronutrients, such as 40% carbohydrates, 30% proteins, and 30% fats. This helps prevent hunger and overeating and makes it easier to maintain a caloric deficit, which is crucial for weight loss.
2. Is 40/30/30 Good for Cutting?
Yes, the 40 30 30 rule is good for cutting (reducing body fat while preserving muscle mass). The protein intake (30%) supports muscle growth, while the balanced carbohydrates and fats provide sustained energy and help in fat loss.
3. What is the 30-30-30 Rule for Weight Loss?
The 30 30 30 weight loss rule involves eating 30 grams of protein within 30 minutes of waking up, followed by 30 minutes of low-intensity, steady-state cardiovascular exercise.
4. How to Calculate a 40/30/30 Diet?
To calculate a 40 30 30 diet, first identify your daily caloric intake and then allocate 40% of those calories to carbohydrates, 30% to proteins, and 30% to fats. For example, if your daily caloric target is 2000 calories, you would aim for 800 calories from carbs, 600 calories from proteins, and 600 calories from fats.
5. What Does a 40/30/30 Meal Look Like?
A typical 40 30 30 meal plan consists of grilled chicken breast (protein) served with quinoa (carbohydrates) and a side of avocado (healthy fats). This combination provides a balanced mix of macronutrients to help maintain energy levels and support overall health.
6. Is 40/30/30 Too Much Protein?
A 30% protein intake in a 40 30 30 diet is appropriate and supports muscle health and satiety. However, protein needs may vary according to an individual’s activity level and health conditions.