Salmon is a popular fish known for its delicious taste and impressive nutritional profile. It is packed with essential nutrients that offer numerous health benefits. Salmon is an excellent source of high-quality protein, healthy fats, and a range of vitamins and minerals. This fish is low in calories and carbohydrates, making it a great option for those looking to maintain a healthy weight or follow a low-carb diet. In this article, we will delve into the nutritional value of salmon, exploring its calorie, protein, and carbohydrate content to provide a better understanding of why it is considered a superfood.
Nutritional Value Of Salmon
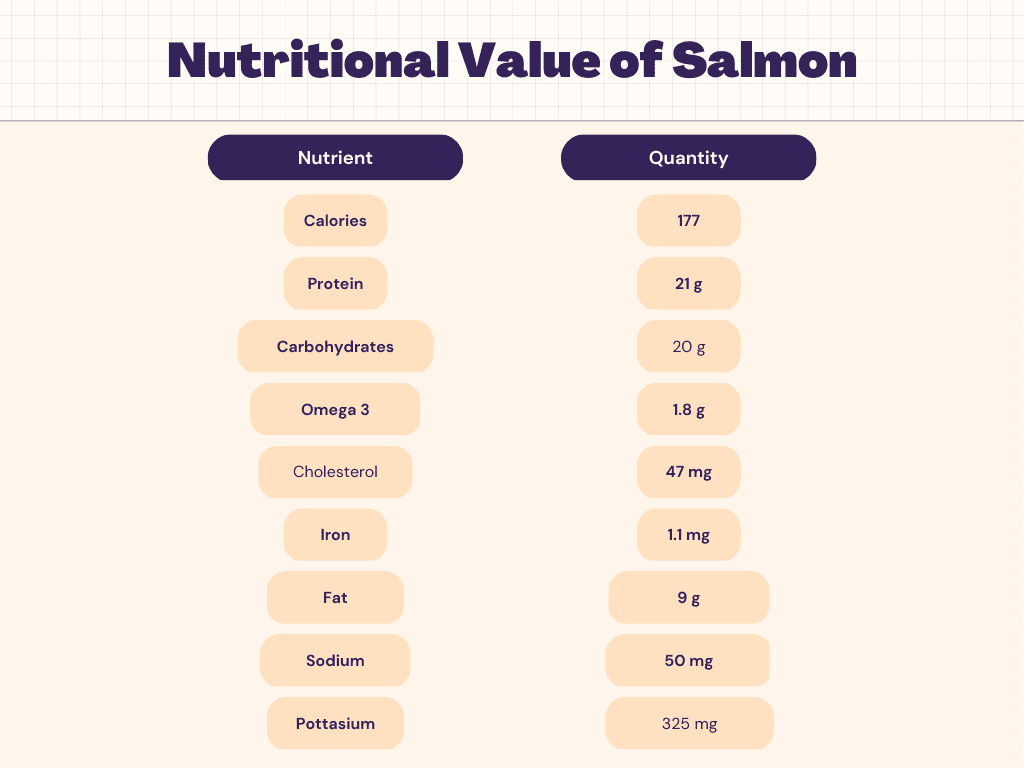
Nutritional Facts of Salmon
Carbs In Salmon
Salmon is a type of fish that is low in carbohydrates. 100 grams (3.5 ounces) of cooked salmon contains about 0 grams of carbohydrates.
It is a good source of protein and healthy fats, such as omega-3 fatty acids, which are beneficial for heart health and may help to reduce inflammation in the body. Additionally, salmon is also rich in vitamins and minerals such as vitamin D, B vitamins, and potassium.
Protein In Salmon
Squash is a low-protein vegetable. While it does contain some protein, the amount is relatively small compared to other protein sources.
For example, 1 cup (205 grams) of cooked winter squash contains approximately 2 grams of protein, while 1 cup (116 grams) of cooked summer squash contains about 1 gram of protein.
While squash may not be a significant source of protein, it is a nutritious vegetable that is rich in vitamins, minerals, and fiber. Winter squash varieties such as butternut, acorn, and pumpkin are particularly high in vitamin A, vitamin C, potassium, and other nutrients. Summer squash, such as zucchini and yellow squash, is also a good source of vitamin C and fiber.
Health Benefits Of Salmon
Salmon is a nutritious food that can provide a range of health benefits for individuals with PCOS, diabetes, and thyroid conditions, and those looking to manage their weight. Here are some of the potential benefits:
- Benefits for PCOS: Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) is a common hormonal disorder that can cause menstrual irregularities, infertility, and other health issues. The omega-3 fatty acids found in salmon may help to reduce inflammation, which can improve symptoms of PCOS such as insulin resistance and high blood sugar levels. Additionally, salmon is a good source of vitamin D, which has been linked to improved fertility and reduced risk of PCOS. Check our PCOS Plans here.
- Benefits for Diabetes: Salmon is a low-carbohydrate, high-protein food that can help to regulate blood sugar levels. The omega-3 fatty acids in salmon can also help to reduce inflammation, which is a risk factor for type 2 diabetes. Additionally, vitamin D in salmon may help to improve insulin sensitivity and reduce the risk of diabetes complications. Check our Diabetes Plans here.
- Benefits for Thyroid: Thyroid disorders such as hypothyroidism can cause weight gain, fatigue, and other symptoms. Salmon is a good source of selenium, a mineral that is important for thyroid function. Selenium helps to regulate thyroid hormone production and may reduce inflammation in the thyroid gland. Check our Thyroid Plans here.
- Benefits for Weight Loss: Salmon is a high-protein, low-carbohydrate food that can help to promote satiety and reduce hunger. Eating salmon as part of a balanced diet may help to reduce overall calorie intake and promote weight loss. Additionally, the omega-3 fatty acids in salmon may help to improve insulin sensitivity, which can reduce the risk of weight gain and obesity-related health issues. Check our Weight Loss Plans here.
It is worth noting that while salmon can offer potential health benefits, it should not be relied on as a sole treatment for any health condition.
Vitamins & Minerals in Salmon
Salmon is a nutritious food that is rich in a variety of vitamins and minerals. Here are some of the key nutrients found in salmon:
- Protein: Salmon is a rich source of protein, with approximately 20-25 grams of protein per 100 grams (3.5 ounces) of cooked salmon.
- Omega-3 fatty acids: Salmon is a great source of omega-3 fatty acids, which are essential fatty acids that play a critical role in brain function, heart health, and inflammation reduction.
- Vitamin D: Salmon is one of the few food sources of vitamin D, which is essential for bone health and may also have benefits for the immune system, heart health, and other areas of health.
- Vitamin B12: Salmon is also a good source of vitamin B12, a nutrient that is important for the nervous system and red blood cell production.
- Selenium: Salmon is a rich source of selenium, a mineral that is important for thyroid function, immune system health, and antioxidant activity.
- Potassium: Salmon is a good source of potassium, a mineral that helps to regulate blood pressure and heart health.
- Other nutrients: Salmon also contains a range of other vitamins and minerals, including vitamin B6, niacin, riboflavin, thiamin, and phosphorus.
Eating salmon as part of a balanced diet can provide a range of important nutrients that are beneficial for overall health and well-being.
The Bottom Line
Salmon is a highly nutritious fish that is rich in protein, healthy fats, and various essential vitamins and minerals. It is a great source of omega-3 fatty acids, which have been linked to numerous health benefits, including reduced inflammation, improved brain function, and a lower risk of heart disease. In terms of nutrition, a 3-ounce (85-gram) serving of cooked salmon typically provides around 140 calories, 22 grams of protein, and less than 1 gram of carbohydrates. These values make salmon an excellent choice for people who are looking to increase their protein intake while keeping their carbohydrate and calorie intake in check. Overall, salmon is a nutritious and delicious food that can be incorporated into a healthy, balanced diet.
FAQs
How much Salmon can I eat in a day?
The amount of salmon you can eat in a day depends on various factors, such as your age, sex, weight, and overall health. However, the American Heart Association recommends consuming at least two servings of fatty fish, such as salmon, per week. A serving size is typically around 3.5 ounces (100 grams) of cooked fish or about the size of a deck of cards.
It’s worth noting that while salmon is generally considered to be a healthy food, it is possible to consume too much of any food, including fish. Salmon and other fatty fish can contain trace amounts of pollutants and toxins, such as mercury, which can build up in the body over time. The FDA and EPA recommend that women who are pregnant, planning to become pregnant, or nursing, as well as young children, limit their consumption of certain types of fish, including salmon, to reduce their exposure to these contaminants.
Overall, if you have concerns about the amount of salmon or other types of fish you should be eating, it’s a good idea to talk to a healthcare professional who can provide personalized recommendations based on your individual needs and circumstances.
Should I eat Salmon before or after exercise?
If you’re looking to fuel your body before exercise, eating salmon beforehand can provide you with a good source of protein and healthy fats, which can help to sustain your energy levels throughout your workout. In addition, the omega-3 fatty acids found in salmon have been shown to have anti-inflammatory effects, which can help to reduce muscle soreness and inflammation after exercise.
On the other hand, if you’re looking to recover after exercise, consuming salmon after your workout can help to replenish your body’s protein and nutrient stores. The amino acids found in salmon can help to repair and rebuild your muscles, which can aid in recovery and improve your performance during your next workout.
Ultimately, whether you choose to eat salmon before or after exercise will depend on your personal preferences and nutritional needs. If you’re trying to gain muscle or lose weight, you may want to consume salmon after exercise to aid in recovery and support muscle growth. If you’re looking to sustain your energy levels during your workout, eating salmon beforehand may be more beneficial.
What are the benefits of Salmon?
Salmon is a nutritious fish that provides a variety of health benefits. Here are some of the key benefits of eating salmon:
- High in Omega-3 Fatty Acids: Salmon is a rich source of omega-3 fatty acids, which are essential fats that our bodies need but cannot produce on their own. Omega-3s have been shown to have anti-inflammatory effects, reduce the risk of heart disease, improve brain function, and support eye health.
- High in Protein: Salmon is also a good source of high-quality protein, which is important for muscle growth, repair, and maintenance. A 3-ounce serving of salmon contains about 22-25 grams of protein.
- Rich in Vitamins and Minerals: Salmon is also a good source of several important vitamins and minerals, including vitamin B12, vitamin D, selenium, and potassium.
- Promotes Heart Health: The omega-3 fatty acids in salmon have been shown to reduce the risk of heart disease by lowering blood pressure, reducing inflammation, and decreasing triglyceride levels.
- Supports Brain Health: The high levels of omega-3 fatty acids in salmon have also been linked to improved brain function and a reduced risk of cognitive decline.
- May Help Reduce Inflammation: The anti-inflammatory properties of salmon may help to reduce inflammation throughout the body, which is linked to many chronic diseases.
- May Support Weight Loss: The high protein content of salmon can help to increase feelings of fullness and reduce appetite, which may aid in weight loss.
Overall, incorporating salmon into your diet can provide numerous health benefits, making it a great addition to a healthy and balanced diet.
What is the best time to eat Salmon?
There is no one “best” time to eat salmon, as it can be a nutritious addition to your diet at any time of day. However, the timing of your salmon consumption may depend on your individual preferences and goals.
If you’re looking to use salmon as a source of protein to help fuel your workouts, eating salmon before exercise can be a good option. This can help provide your body with the necessary nutrients to sustain energy levels during your workout.
On the other hand, if you’re looking to consume salmon as part of your post-workout recovery, you may want to eat it after your exercise session. Consuming protein after exercise can help to repair and rebuild muscle tissue and support recovery.
Salmon can also be a nutritious addition to any meal, whether it’s breakfast, lunch, or dinner. It can be enjoyed in a variety of ways, such as grilled, baked, or pan-seared, and can be paired with a range of vegetables, grains, and sauces to create a well-balanced meal.
Ultimately, the best time to eat salmon will depend on your personal preferences, nutritional needs, and fitness goals. Regardless of the time of day, incorporating salmon into your diet can provide numerous health benefits.