In diet and nutrition, ketosis has gained significant attention as a metabolic process related to weight loss and improved energy levels. But what exactly is ketosis, and how does it affect our bodies? In this blog we shall discuss the symptoms and causes of ketosis, shedding light on the science behind this dietary phenomenon. Before we proceed, it is important to note the difference between Ketosis and ketogenic diet. Ketosis causes changes in metabolism, while a ketogenic diet is a way to achieve ketosis.
What is Ketosis?
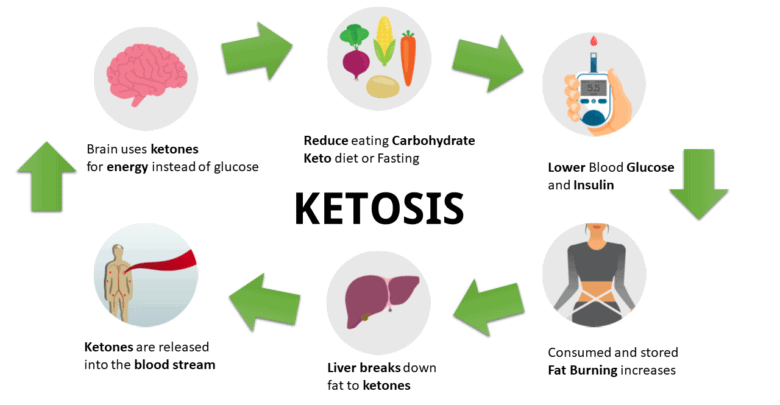
Ketosis is a metabolic state in which your body burns stored fat for energy instead of carbohydrates. It happens when you consume low-carb.
Usually, your body uses glucose (sugar) for energy. You get glucose from the carbohydrates you eat. When you eat a lot of carbohydrates, your body produces insulin, which helps your cells absorb glucose from the bloodstream. Your body’s insulin levels drop if you don’t eat many carbohydrates. This causes your body to break down stored fat and glycogen (glucose stored in your liver and muscles) for energy. When this happens, your body produces ketones. Ketosis can be caused by several things, including:
- Eating a ketogenic diet: When you eat a keto diet plan, your body produces ketones, which your body can use for energy instead of glucose.
- Fasting: When you fast, your body’s insulin levels drop and blood sugar levels rise. This can lead to ketosis. Fasting for an extended period is one of the ways ketosis causes the body to start producing ketone bodies for energy.
- Diabetes: When you have diabetes, your body may be unable to use glucose for energy, leading to ketosis.
- Other medical conditions: Ketosis can also be caused by other medical conditions, such as alcoholism, cancer, and thyroid disorders.
What is the Ketosis Diet?
The ketogenic diet, also known as the keto diet, is a very low-carb, high-fat diet. When you eat a keto diet, your body produces ketones, a fuel that your body can use for energy instead of glucose.
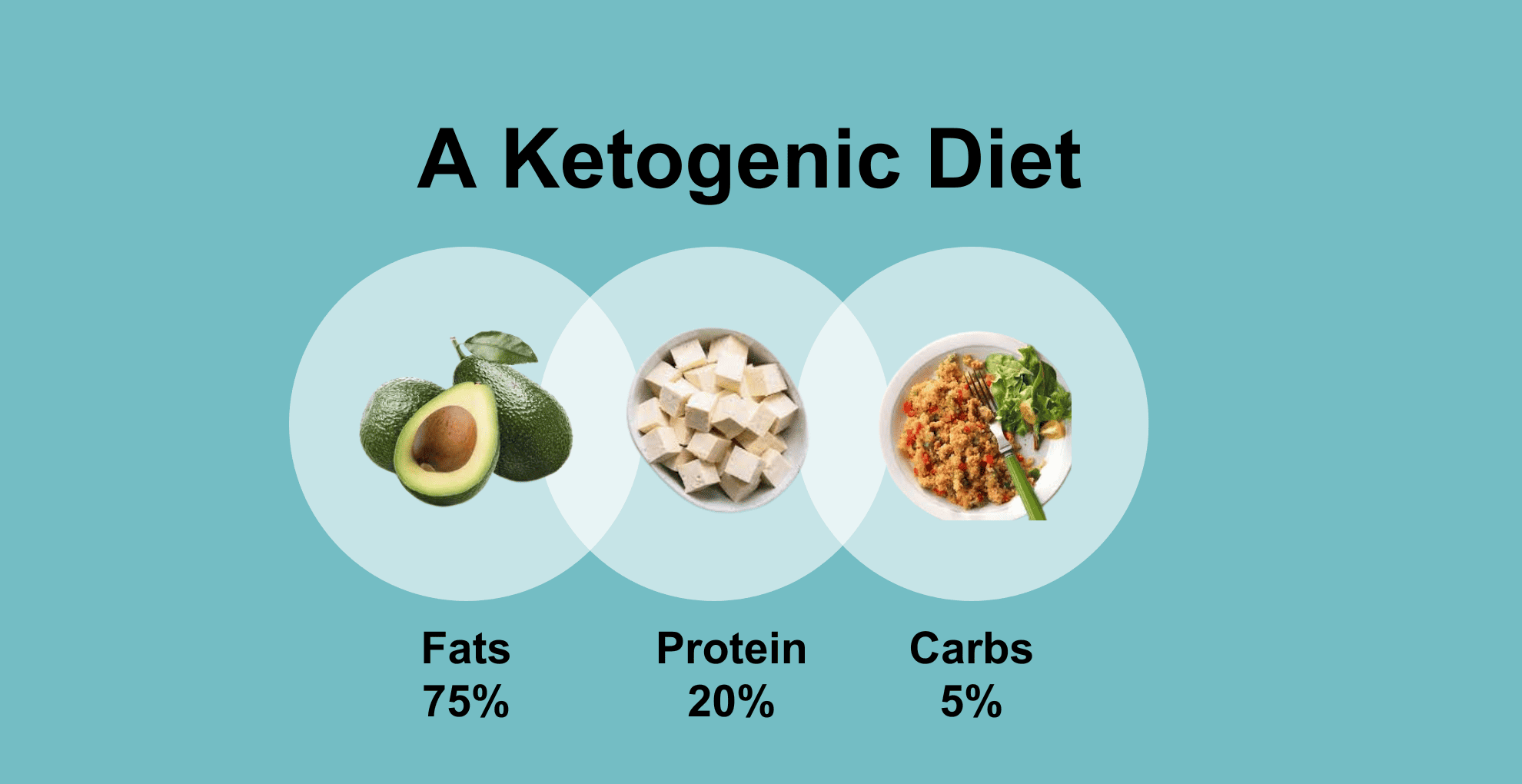
The keto diet restricts carbohydrates to 20–50 grams per day. This is much lower than the recommended daily intake of carbohydrates for most adults, which is 130 grams per day. The keto diet is high in fat, moderate in protein, and very low in carbohydrates. A keto diet consists of
- Fats: 70–80%
- Proteins: 10–20%
- Carbohydrates: 5–10%
0 calorie foods can be a valuable addition to a ketogenic diet as they help promote satiety without significantly affecting your daily carbohydrate intake.
How Many Carbs Do I Need for Ketosis?
To enter ketosis, you should limit your daily carbohydrate intake to no more than 50g. Additionally, regarding protein consumption, males can typically consume 50-60g of protein daily, while females can aim for 40-50g while in ketosis. The number of carbs required to stay in Ketosis is as follows;
| Carbs requirement for the body in Ketosis (% of overall intake in a day) | ||||
|
Standard Ketogenic Diet
|
Carbs | Fats | Protein | |
| 10% | 70% | 20% | ||
You can buy Keto diet plan which will help you by providing exclusive guidelines for achieving weight loss through ketosis and better determining how much carbs are required in your body.
Ketosis and the Ketogenic diet
In this section, we shall note the difference between these two terms in detail.
| Ketosis | Ketogenic Diet |
| Ketosis is a metabolic state where your body shifts from primarily using carbohydrates for energy to using fat. During this process, the liver converts fats into molecules called ketones, which become the body’s primary energy source. Ketosis can occur for various reasons, including fasting, intense exercise, or low-carb diets. | The ketogenic or keto diet is a specific dietary approach designed to induce and maintain a state of ketosis. It involves consuming a very low-carbohydrate, high-fat, and moderate-protein diet. The primary goal is to reduce carbohydrate intake to the point where the body enters ketosis. On a keto diet, carbs comprise around 5-10% of daily caloric intake, fats account for approximately 70-75%, and protein constitutes 15-20%. |
|
How Does Ketosis Work? Your brain needs about 120 grams of sugar daily, but it can’t save any for later. This sugar comes from the carbs you eat. So, if you eat fewer carbs, your body gets less sugar. When that happens, your body takes the stored sugar from the liver and sometimes breaks down your muscles to get more sugar. After 3-4 days of doing this, the hormone insulin decreases when all the stored sugar is gone, and your body starts using fat for energy. The liver turns fat into something called ketones, which can be used by your body when there’s no sugar around. That’s when you’re in a state called ketosis. |
How Does Ketogenic Diet Work? The ketogenic diet works by changing the way your body gets energy. Instead of using carbs, you eat very few, making your body use fat for energy. There is no “standard” ketogenic diet with a specific ratio of macronutrients defined for you. This diet reduces total carbohydrate intake to less than 50 grams a day. Ketogenic Diet for weight loss: Monitoring your calorie consumption with low calorie foods ensures you’re still in line with your overall health and weight management goals. |
In summary, ketosis is the metabolic state where your body uses fat for energy, while the ketogenic diet is a dietary approach aimed at achieving and sustaining ketosis through control of carbohydrate intake.
What are the Benefits of Ketosis?
In exploring the benefits of the keto diet, we’ll delve into how ketosis causes and brings positive changes and well-being. Here are the potential benefits;
- Epilepsy
- Weight Loss
- Reversal of Diabetes and Prediabetes
- Appetite Regulation
- Reducing the Chances of Heart Diseases
Let us discuss how ketosis causes the above mentioned in detail;
Epilepsy
The ketogenic diet was initially developed to treat drug-resistant epilepsy, primarily in children. It has significantly reduced the frequency and severity of seizures in some epilepsy patients.
Mechanism: While the exact mechanism of the ketogenic diet on Epilepsy is not entirely understood, let us see what studies discuss: the brain typically relies on quick energy from glucose metabolism to fuel seizure activity. However, when someone is on the ketogenic diet (KD), their blood glucose levels drop, and the brain starts using ketone bodies (KB) for energy. This different energy source slows down how quickly energy is available, which, in turn, can help reduce seizures.
Weight loss
In ketosis, the body primarily burns fat for energy, which can lead to weight loss, as it uses stored fat for fuel.
Appetite Suppression: Ketosis focuses on a balanced diet, which reduces hunger and cravings, making it easier to maintain a calorie deficit and lose weight.
Stable Blood Sugar: The low-carb nature of the ketogenic diet helps stabilize blood sugar levels, preventing spikes and crashes that can trigger overeating.
Reversal of Diabetes and Prediabetes
The ketogenic diet can enhance insulin sensitivity, making it easier for the body to manage blood sugar levels. By reducing carb consumption, individuals with type 2 diabetes and prediabetes can better manage their condition, as fewer carbs lead to fewer blood sugar spikes.
Appetite Regulation
The ketogenic diet can affect hormones that regulate appetite, such as ghrelin and leptin. It often decreases ghrelin, the hunger hormone, while increasing leptin levels, which signals fullness.
Steady Energy: Ketosis provides a stable energy source from fat, reducing the energy fluctuations that can lead to between-meal hunger.
Reducing the Chances of Heart Disease
Following your ketosis diet can help reduce the chances of heart disease by increasing the levels of good cholesterol and reducing the amount of triglycerides in the body.
Signs and Symptoms That You’re in Ketosis?
Ketosis symptoms, such as fatigue and dizziness, can occur during the initial stages of transitioning to a ketogenic diet. Here are the six most common and relevant Ketosis symptoms;
1. Appetite Reduction
2. Fruity Breath
3. Weight Loss
4. Increase in Focus and Energy
5. Digestive Problem
It is important to note that not everyone experiences the same ketosis symptoms, as individual responses can vary. Let us discuss the above-mentioned signs and symptoms in detail.
1. Appetite Reduction
It is one of the signs that your body is in healthy ketosis. A ketogenic diet high in fat and low in carbs can reduce your appetite as fats take longer to digest than carbs. This can reduce your overall appetite throughout the day.
2. Fruity Breath
Ketosis symptoms often include bad breath, commonly known as “keto breath,” due to the increased production of acetone, which is also present in your urine. Fruity or bad breath indicates that your body has reached full ketosis.
3. Weight loss
Ketosis symptoms can lead to significant weight loss, making it a popular choice for those seeking to shed excess pounds. If you experience weight loss, this is a sign that you are in ketosis. This occurs because your body uses fat as the only energy source.
4. Increase in Focus and Energy
Focus: Ketosis symptoms often include an improved mental focus and clarity, commonly called the “keto brain.” But, when in the starting phases, you may experience a decrease in focus and energy. This is due to your body not finding enough carbs in the diet to turn into energy. After some time when your body gets used to burning fat for energy, your brain may experience increased energy levels and focus.
Energy: Elevated ketone levels in the blood are a key indicator of ketosis, contributing to ketosis symptoms like increased energy.
5. Digestive Problems
Being in ketosis means the absence of fibre from your diet. You can experience digestive issues while starting a ketogenic diet as your body is not used to it. A change in your diet will cause your body to react differently. Including lots of vegetables and high-fibre food can help with indigestion.
The Relationship Between Ketosis and the Ketogenic Diet
The ketogenic diet is designed to induce ketosis. When you eat a very low-carb diet, your body breaks down stored fat into ketones, which it can use for energy. Ketosis can also occur through fasting. When you fast, your body does not have any glucose to use for energy, so it starts to break down fat into ketones instead. While they are closely linked, you can be in ketosis without following the ketogenic diet and follow the ketogenic diet to maintain a constant state of ketosis.
What is the Difference Between Nutritional Ketosis vs. Ketoacidosis?
In both nutritional ketosis and ketoacidosis, ketones are produced in the body, but ketoacidosis can be life-threatening.
| Nutritional Ketosis | Ketoacidosis |
| In this, your body uses fat for energy. During this phase, the body breaks down fats into ketones and used by the body for energy. | While nutritional ketosis is absolutely normal, Ketoacidosis is a complication of Diabetes where the blood sugar and ketone levels are really high due to insufficient insulin. |
| A person following a ketosis diet will have high amounts of fats and low amounts of carbs in their diet. Nutritional Ketosis can help people lose fat more effectively and in less time. | Ketoacidosis is often found in people with Type 1 Diabetes as their bodies cannot produce enough insulin. |
How Do You Achieve Ketosis Successfully?
Being in ketosis can help you burn fat more effectively. Ketosis meaning, the presence of ketones in your body. Below are a few things that will ensure you can achieve ketosis successfully.
1. Cut down on carbs
The first step to getting into ketosis is reducing your carb consumption. In a ketogenic diet, very little priority is given to carb consumption. The cells in our body mainly use glucose for energy, but they can also use fat and ketones for energy. When you reduce the consumption of carbs, the glycogen stores in the body also reduce, and the body starts to use fat for energy and fuel which is one of ketosis causes. Did you know you can make some fantastic Keto diet recipes.
2. Exercising
Exercising or being more physically active can help your body get into ketosis faster. This is because when you exercise, your body depletes the glycogen stores much faster. This makes your liver produce more ketones, which can be used as an alternate energy source, thus, making your body get into ketosis a lot faster, which is one of the many causes of ketosis. Take a look at these great Keto diet success stories.
3. Increase intake of fat
An increase in fat consumption is one of the ketosis causes. A ketogenic diet consists of high-fat content and low-carb and protein content. Consumption of fats can increase the levels of ketones in the body if your body does not have an alternate energy source such as carbohydrates. Increasing your fat intake can also help you get started with a ketogenic diet.
4. Fasting for shorter periods
Fasting can help a person get into ketosis faster and can be one of the many causes of ketosis. Doing an intermittent fast can burn the glycogen stores in your body for energy. This can then induce the production of ketones from the liver to be used as fuel for the body. However, no strong evidence supports that fasting can help get you into ketosis faster.
How Can You Help Prevent or Treat Ketosis?
A frequently asked question is related to the prevention of ketosis. It’s important to clarify that ketosis is not a disorder, and there’s no need for concern. It is a metabolic process in which your body utilises fat as the primary fuel source for its functions, instead of relying on carbohydrates. And, when you want to get out of this metabolic state, firstly aim to reduce the ketosis symptoms and gradually get out of it by doing the below-mentioned things;
1. Increase your carb intake
A Ketogenic diet involves a higher intake of fats and a low intake of carbs to produce more ketones in the body. To reduce the ketosis symptoms, you need to provide the body with an alternate source of energy, and this can be done by eating more carbs in your diet which will later convert into glucose for the body to use.
2. Cut down on fat
If you want to treat ketosis, you must reduce your fat intake. In ketosis, the body uses fats as the primary source of energy. Cutting down on fat will not allow the body to turn fat into ketones, which is one of the leading ketosis causes. You can increase your intake of carbs to help your body with energy.
Tips For Getting Into Healthy Ketosis
Here are some tips for getting into healthy ketosis:
- Eat plenty of healthy fats. This will help your body produce ketones, which are the energy molecules that are used in ketosis. Good sources of healthy fats include avocados, nuts, seeds, and olive oil.
- Limit carbohydrates. One of the vital ketosis causes is a significant reduction in carbohydrate intake, typically to less than 50 grams per day. When you reduce your carbohydrate intake, your body burns fat for energy.
- Increase protein intake. Protein helps to build and repair muscle tissue. It is also important for satiety, which can help you feel full and satisfied after eating. Good protein sources include meat, poultry, fish, eggs, and dairy products.
- Exercise regularly. Exercise helps to burn calories and build muscle. It also helps improve insulin sensitivity, making it easier to experience ketosis symptoms and getting into it a healthy manner.
Please remember that talking to your doctor before starting any new diet is essential, especially if you have any underlying health conditions.
References
Batch, Jennifer T. 2020. “Advantages and Disadvantages of the Ketogenic Diet: A Review Article.” NCBI. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7480775/.
“Diet Review: Ketogenic Diet for Weight Loss | The Nutrition Source | Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health.” n.d. Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health. Accessed October 19, 2023. https://www.hsph.harvard.edu/nutritionsource/healthy-weight/diet-reviews/ketogenic-diet/.
“Ketogenic Diet and Epilepsy: What We Know So Far.” 2019. NCBI. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6361831/.
FAQs
How long does it take to get into ketosis?
Getting into ketosis usually takes a few days to a week. It depends on how strictly you limit your carbohydrate intake. When you eat very few carbs, your body starts using its stored glucose, and after a while, it begins to burn fat for energy, putting you into a state of ketosis.
What are the side effects of ketosis?
When starting a ketogenic diet, some people may experience side effects, (different from ketosis symptoms) such as bad breath (often described as fruity or metallic), constipation due to reduced fibre intake, and temporary fatigue. These symptoms are often referred to as the “keto flu.” Staying hydrated and consuming electrolytes can help manage these symptoms.
How Does Ketosis Affect Weight Loss?
Ketosis causes weight loss by forcing the body to burn fat for energy instead of carbohydrates. When in ketosis, the body produces molecules called ketones, which break down fats. It’s crucial to maintain a balanced diet, focusing on healthy fats, proteins, and vegetables while being mindful of portion sizes.
Is Ketosis Safe and Healthy for Everyone?
Ketosis causes the body to use fat as the primary source of energy and is generally safe for most people, but it might not be suitable for individuals with certain health conditions, such as pancreatic disorders or liver diseases. It’s crucial to consult a healthcare provider, especially if you have pre-existing medical conditions or are pregnant.
How is Ketosis and Diabetes related?
Ketosis can be related to diabetes management, particularly in type 1 diabetes. Ketosis causes a decrease in insulin levels, making it an attractive dietary strategy for managing blood sugar levels in individuals with diabetes. By reducing carbohydrate intake, the body requires less insulin, which can lead to more stable blood sugar levels.