Have you ever thought about the “keto diet meaning” and what it involves? The keto diet, short for ketogenic diet, is a low-carbohydrate and high-fat eating plan. The fundamental principle of the keto diet involves significantly reducing carbohydrate intake while increasing the consumption of fats. This drastic reduction in carbs forces the body to enter a metabolic state known as ketosis. By limiting carbohydrates, the body depletes its glycogen stores and begins breaking down fats into ketones for energy. Let us learn about the science behind it, how this keto works, it’s types and precautions to follow.
What is a Ketogenic Diet?
A ketogenic diet is a low-carb diet. In the 19th century, the ketogenic diet was commonly used to help control diabetes. Then, it was used to treat Epilepsy. The primary goal of the ketogenic diet is to shift the body’s metabolism into a state of ketosis. It is called ketosis, a metabolic form where the body prefers to utilise fat as its primary fuel source.
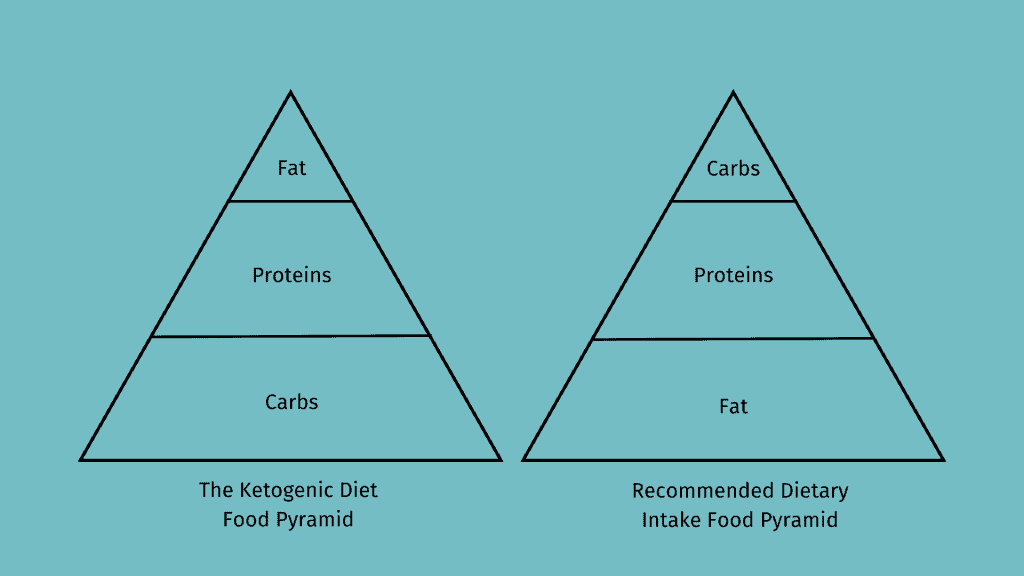
The macronutrient distribution in a ketogenic diet involves reduced carbohydrate intake, usually below 50 grams daily, and increased fat consumption. Here’s a representation of the Ketogenic Diet food pyramid-
What are the Rules of Keto Diet?
The Keto diet guidelines revolve around significantly reducing carbohydrate intake and substituting it with fats. These principles and methods aid in attaining and maintaining ketosis, a crucial aspect of this dietary approach. Here are the rules of the ketogenic diet;
- Low Carbohydrate Intake: According to the Harvard School of Public Health, there isn’t a singular “standard” ketogenic diet defined by a fixed ratio of macronutrients (carbohydrates, protein, fat). Generally, the ketogenic diet involves limiting total carbohydrate intake to below 50 grams per day.
- High Fat Consumption: Healthy fats become the primary energy source in the keto diet. Foods rich in healthy fats, such as avocados, nuts, seeds, olive oil, and fatty fish, are encouraged.
- Moderate Protein Intake: While protein is essential, excessive intake can hinder ketosis. The keto diet emphasises reasonable protein intake, focusing on quality sources.
- Tracking Macronutrients: Many individuals on the keto diet track their macronutrient intake meticulously. This involves monitoring the grams of carbohydrates, fats, and proteins consumed to maintain the desired ratios.
- Avoiding Sugar and Processed Foods: High-sugar foods and processed carbohydrates are strictly limited. This includes sugary beverages, sweets, most grains, and processed snacks.
- Hydration and Electrolytes: Adequate hydration is crucial, and attention to electrolyte balance with sources like salt, potassium, and magnesium is often recommended.
- Intermittent Fasting: Some keto practitioners incorporate intermittent fasting, cycling between periods of eating and fasting, to enhance the effects of the diet.
- Ketone Level Monitoring: Some individuals track their ketone levels using urine strips, blood tests, or breath analysers to ensure they are in a state of ketosis.
What are the types of Ketogenic Diets?
According to a study by the Research Gate, there are many types of keto diets, and out of these four kinds of ketogenic diets, each has one common thing: the state of ketosis. Each diet has a different composition of macronutrients, pros and cons and is suitable for varied health conditions. Let’s now look at some of the different types of Ketogenic diet to understand the Keto diet meaning better:
1. Classic Ketogenic Diet
2. Modified Atkins Diet
3. Medium Chain Triglyceride Keto Diet
4. Low Glycemic Index Keto Diet
Let us discuss each of these in detail.
1. Classic Ketogenic Diet
Nature of this diet: Very Restrictive
Understanding the mechanism: The classic keto diet refers to the rigorous high-fat, low-carbohydrate diet used since the 1920s to treat Epilepsy. This is a strict diet plan, consisting of 90% fat, 6% protein, and 4% carbohydrates, and maintains a ratio of 4 grams of fat for every 1 gram of combined carbohydrate and protein. Most calories come from fats when you follow a classic ketogenic diet.
Best For: Patients with Epilepsy can take this, mainly introduced in hospital setups.
2. Modified Atkins Diet
Nature of this diet: Easy to follow, can be introduced in home settings.
Understanding the mechanism: The Modified Atkins Diet permits a daily intake of 10-20 grams of carbohydrates and encourages a higher intake of fats. Unlike other diets, it doesn’t require counting calories or measuring food portions, making meals simpler and easier to prepare. According to Dr Radhika Dhamija, who published research in the Research Gate, following the Atkins diet has plenty of long-term benefits.
Best For: Individuals who are willing to lose weight sustainably.
3. Medium Chain Triglyceride Keto Diet
Nature of this diet: Can’t be followed in the home setting, involves measuring and weight of food and has Gastrointestinal side effects.
Understanding the mechanism: Introduced in 2003, this is an alternative to the traditional Classic Keto Diet, allowing for more protein and calorie intake flexibility. When we talk about fats in our diet, most of them are long-chain triglycerides. But there’s another type called medium-chain triglycerides (MCTs), which come from specific fatty acids called octanoic and decanoic acids. Now, these MCTs produce more ketones, which are like energy molecules, compared to regular fats. This means you can eat more carbohydrates and protein because you don’t need as much fat in this diet.
Best For: The MCT Keto Diet plan best suits people who want to lose weight, improve their cognitive function, or manage Epilepsy.
4. Low Glycemic Index Keto Diet
Nature of this diet: Restrictive, allows only low glycemic index foods.
Understanding the mechanism: The low glycemic index treatment involves a controlled low-carbohydrate diet, typically restricting carbohydrate intake to 40-60 grams daily. Only foods with a low glycemic index (below 50) are included in this approach. If you are interested in following a low glycemic diet, here are some low GI foods that you can include in your diet:
- High-protein foods, such as lean meat and fish
- Dairy products, such as milk and natural yoghurt
- Unsweetened soy milk
- Vegetables such as broccoli, green peas, and leafy greens
- Low-sugar fruits, such as apples, oranges, and blueberries
- Porridge made with steel-cut oats and water.
- Legumes, pulses, and beans such as chickpeas, lentils, and kidney beans
Best For: Individuals who have Type 2 Diabetes.
How does Keto Diet work?
The keto diet alters how your body generates and uses energy. Usually, our bodies rely on carbohydrates as the primary energy source, breaking them down into glucose. However, in a ketogenic diet, carbohydrate intake is significantly reduced, forcing the body to shift its energy source to fats.
Here’s a step-by-step breakdown of how the keto diet works:
Step 1- Low Carbohydrate Intake: The keto diet involves a drastic reduction in carbohydrate intake, usually around 20-50 grams daily. This depletion of available carbohydrates prompts the body to look for alternative fuel sources.
Step 2- Transition to Ketosis: With limited carbohydrates, the body enters a metabolic state known as ketosis. During ketosis, the liver starts breaking down fats into molecules called ketones. These ketones become the primary fuel source for the body, including the brain.
Step 3- Fat as the Primary Energy Source: In ketosis, the body becomes highly efficient at burning stored fat for energy. This process not only aids in weight loss but also provides a steady energy supply.
Step 4- Stabilising Blood Sugar Levels: Since the keto diet minimises fluctuations in blood sugar levels, it can be particularly beneficial for individuals with insulin resistance or diabetes. The diet helps stabilise blood sugar by reducing the need for insulin.
Step 5- Appetite Suppression: Ketones produced during ketosis have been associated with a decreased appetite. While following the Keto diet recipes, many individuals naturally consume fewer calories because the diet helps regulate hunger hormones.
Now, let us look at the health benefits of the keto diet in detail.
Health Benefits of Keto Diet
Keto is a low-carb diet, and there are noteworthy benefits of low-carb diets proven in several research studies. The diet pattern of such nature impacts heart health and improves insulin sensitivity. Even though the diet is strict, it does not involve calorie counting, and is easy to understand, making it suitable to follow in home setups where you can easily gather the keto diet products. Read on to learn about how the keto diet plan benefits you in the following areas:
1. Heart Health
2. Hormones and Metabolism
3. Weight Loss
4. Brain Health
5. Reduces the Risk of Fatal Diseases
Let us understand the mechanics of the keto diet in detail in each of these health benefits.
1. Heart Health
The ketogenic diet has gained attention for its potential impact on heart health, particularly in addressing conditions like dyslipidemia and hypertension. Research suggests that the ketogenic diet can benefit heart health by positively influencing lipid profiles.
Dyslipidemia refers to unhealthy levels of one or more kinds of lipid (fat) in your blood. Following a keto diet tends to reduce the amount of lipids. This reduction in lipids contributes to a lower risk of cardiovascular issues. The ketogenic diet may improve hypertension or high blood pressure by promoting weight loss, reducing inflammation, enhancing insulin sensitivity, improving endothelial function, and influencing sodium and fluid balance, collectively contributing to better blood pressure regulation.
2. Hormones and Metabolism
In the case of Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS), where hormonal imbalances can lead to various symptoms, the keto diet may offer relief. PCOS is linked to multiple metabolic and hormonal issues, such as problems with insulin, high insulin levels (hyperinsulinemia), type 2 diabetes, and more. By reducing carbohydrate intake, the diet aids in improving insulin sensitivity, addressing hormonal irregularities, and potentially alleviating PCOS-related symptoms. Furthermore, for individuals with diabetes, the diet’s ability to enhance insulin sensitivity becomes a valuable aspect of diabetes management.
A keto diet may improve diabetes by reducing carbohydrate intake, lowering blood sugar levels and enhancing insulin sensitivity. The diet’s focus on fat metabolism helps stabilise blood glucose, potentially aiding in diabetes management.
3. Weight Loss
One of the well-known benefits of the keto diet is its effectiveness in promoting weight loss. Shifting the body’s energy source from carbohydrates to fats encourages the burning of stored fat, leading to a reduction in body weight. The diet also tends to help control appetite, contributing to sustainable weight management.
4. Brain Health
The ketogenic diet may benefit brain health through several mechanisms. Ketones, produced during ketosis, serve as an alternative energy source for the brain, potentially enhancing cognitive function. Additionally, the diet’s anti-inflammatory effects, improved insulin sensitivity, and increased brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) production may contribute to neuroprotection and better overall brain health.
5. Reduces the Risk of Fatal Diseases
Reducing the chances of fatal disorders is a notable potential benefit associated with the ketogenic diet. By promoting weight loss, the diet addresses a key risk factor for various life-threatening conditions, such as heart disorders, diabetes, and certain cancers. Additionally, the keto diet’s influence on metabolic health, including insulin sensitivity and blood lipid profile improvements, may contribute to a lowered risk of fatal disorders. The diet’s anti-inflammatory effects and potential impact on oxidative stress further reduce overall health risks.
Foods to Eat on Keto Diet
Choosing the right foods on a keto diet is essential. Prioritising foods that make you feel full, like healthy fats and protein, helps control your appetite and stick to the diet. This careful food selection meets the diet’s needs and allows for personalised nutrition, making it easier to sustain and align with various health goals. Read on to learn about foods to eat on the keto diet:
1. Protein Rich Foods
- Meat: Meat is a staple protein source on the ketogenic diet. Choices like beef, poultry, and pork provide essential amino acids without significant carbohydrate content.
- Fatty Fish: Fatty fish, such as salmon and mackerel, not only offer protein but also provide beneficial omega-3 fatty acids, supporting overall health and well-being.
- Eggs: Eggs are an excellent source of high-quality protein and healthy fats, making them a versatile and nutrient-dense addition to a keto diet.
2. Dairy Products
- Cheese: Cheese, particularly varieties like cheddar, mozzarella, and cream cheese, is rich in protein and fats while containing minimal carbohydrates.
- Full-Fat Yoghurt: Opting for full-fat yoghurt without added sugars ensures a creamy and satisfying dairy option that aligns with the keto macronutrient ratios.
- Heavy Cream: Heavy cream is a high-fat dairy choice, suitable for adding richness to dishes and beverages without introducing excessive carbohydrates.
3. Nuts and Seeds
- Chia Seeds and Flaxseeds: Chia seeds and flaxseeds are low in net carbs and high in fibre, contributing to digestive health. They also provide a source of healthy fats and essential nutrients.
- Almonds and Walnuts: Almonds and walnuts offer a crunchy and satisfying snack, delivering a combination of protein, healthy fats, and vitamins. They are ideal for enhancing satiety. It’s essential to avoid certain high-carb nuts during the ketogenic diet, including cashews and pistachios.
Foods to Avoid on Keto Diet
The central approach of the ketogenic diet is the strict restriction of carbohydrates, as these macronutrients stimulate insulin production and hinder the state of ketosis—the metabolic condition critical for the diet’s effectiveness. So, let us learn about the foods that are high in carbs and need to be avoided while you’re following this diet:
1. Carb:
- Grains: Bread, pasta, rice, cereals, and crackers are high in carbohydrates and will kick you out of ketosis.
- Starchy Vegetables: Potatoes, corn, peas, and yams are loaded with carbs, so it’s better to avoid them.
- Sugary Treats: Candy, cookies, cakes, and ice cream are packed with sugar, the ultimate enemy of ketosis.
- Fruits: While some berries are enjoyed in moderation, most fruits like bananas, mangoes, and grapes are high in sugar and best avoided.
2. Hidden Carbs:
- Condiments: Ketchup, BBQ sauce, salad dressings, and dips often contain hidden sugars and carbs. Always check labels and choose sugar-free or low-carb versions.
- Processed Foods: Packaged snacks, pre-made meals, and frozen dinners are often loaded with hidden carbs and unhealthy fats. Stick to whole, unprocessed foods for optimal results.
- Sweeteners: While some artificial sweeteners are keto-friendly, others can raise blood sugar and stall ketosis. Be mindful of your sweetener choices and stick to approved options.
Drinks to Have on Keto Diet
Selecting keto-friendly drinks is vital for maintaining the metabolic state of ketosis and supporting overall health. High-carb or sugary beverages can disrupt ketosis, spike blood sugar levels, and hinder the effectiveness of the ketogenic diet. Let us look at the beneficial drinks to have on the keto diet;
- Water: Staying hydrated with water is essential for overall health and supports ketosis without adding carbs.
- Coffee: Black coffee is low in calories and carbs. Adding minimal amounts of high-fat additives like heavy cream is a keto-friendly option.
- Tea: Unsweetened tea, both hot and cold, is carb-free and provides variety without compromising the diet.
- Bone Broth: A nutrient-rich option that supports electrolyte balance and provides essential minerals without added carbs.
- Sparkling Water: Refreshing and carb-free, sparkling water is a satisfying alternative to sugary sodas.
- Diet Soda (in moderation): Some keto followers choose diet sodas occasionally, but it’s essential to monitor artificial sweetener consumption.
Drinks to Avoid on Keto Diet
Limiting certain drinks on a keto diet is crucial to maintaining the state of ketosis, where the body primarily burns fat for fuel. Drinks high in sugars and carbohydrates can quickly disrupt this metabolic state, leading to spikes in blood sugar levels and hindering the diet’s effectiveness.
By avoiding these below-mentioned beverages, you can better control your carb intake, support weight loss, and maximise the benefits of the keto lifestyle;
- Regular Soda: Packed with sugars and carbohydrates, regular sodas can kick you out of ketosis and contribute to weight gain.
- Fruit Juices: Even 100% fruit juices contain high levels of natural sugars, making them unsuitable for maintaining a low-carb state.
- Sweetened Tea: Teas with added sugars can quickly increase carb intake, disrupting the metabolic benefits of a ketogenic diet.
- High-Sugar Alcoholic Beverages: Cocktails and mixed drinks with sugary mixers can be laden with carbs. Opt for low-carb options like dry wine or spirits with soda water.
- Energy Drinks: Many energy drinks contain sugars and carbs, potentially affecting blood sugar levels and interfering with ketosis.
- Milk: Regular milk is relatively high in carbs. Choosing alternatives like unsweetened almond milk or heavy cream aligns better with keto principles.
Precautions Before Starting Ketogenic Diet
Certain precautions and steps must be followed before you start the keto diet plan journey. Read on to the following steps and noteworthy points to consider:
1. Educate Yourself About Keto
2. Prepare Mentally and Logistically
3. Consult a Doctor
4. Track your Health Status
Let us discuss each of these in detail!
1. Educate Yourself About Keto
Learn the Keto diet meaning, its pattern, the science behind it and its mechanism via various trusted sources. You can refer to Keto diet blogs, videos and research articles for the same. Understand the essential fat, protein, and carbs ratios required for optimal ketosis. Researching meal plans and recipes will help you guide through diet principles effectively.
2. Prepare Mentally and Logistically
Prepare yourself for the upcoming changes, remembering that the keto lifestyle is a lasting commitment, not a rapid solution. Once you’ve understood the rules and intricacies of this diet, cultivate a resilient mindset to initiate and adhere to it. Furthermore, you may find a community or support group of people narrating keto diet success stories, experiences, tips, and valuable encouragement.
3. Consult a Doctor or a Healthcare Professional
Seeking professional medical advice is a critical precautionary step. Consult with your healthcare provider, especially if you have underlying health conditions or are on medication. Your doctor can provide personalised recommendations based on your health history and may conduct relevant tests to ensure your keto diet is safe. Consider asking these questions;
- Understand the keto diet meaning, can the diet effectively manage particular health conditions you may have?
- What potential side effects should you be aware of when adopting the ketogenic diet?
- Are there specific vitamins or supplements you should consider taking or continuing during the diet?
- How long is it advisable to remain on the keto diet, and are there recommended phases for this dietary approach?
- Are there particular keto variations that align better with your health conditions? Inquire about the specific nuances of each keto diet meanings to better understand which one might be most suitable for you.
- Should exercise be incorporated into your routine, and if yes, what is the recommended frequency and intensity for your specific situation?
4. Track your Health Status
Following your discussion with a doctor, the next step is to monitor your health status. This may involve obtaining recent reports on current medical conditions, undergoing blood checks, and other essential tests such as assessing the levels of vitamins in your body. Once you’re done with this process, you can begin your keto journey and track your progress at regular intervals.
Expert Review on Ketogenic Diet
There are various modifications to the keto diet, each with slightly different macronutrient ratios and levels of carbohydrate restriction. Choosing the one that best suits your individual needs and preferences is critical. Consulting a registered dietitian or healthcare professional can help determine if keto is right for you and develop a personalised plan to ensure optimal health and safety.
Beyond weight management and treatment of Epilepsy, the ketogenic diet shows promise in promoting heart health by addressing dyslipidemia and hypertension, positively influencing hormonal imbalances in conditions like PCOS, and improving insulin sensitivity in diabetes management. Here are specific noteworthy points to remember to get the benefits of the keto diet and get the most out of it;
- Choose appropriate foods, like protein-rich meats, fatty fish, eggs, cheese, full-fat yoghurt, and nuts, which are staples. While whole grains, starchy vegetables, and high-sugar items are strictly avoided.
- Proper hydration is vital to any healthy diet; the keto diet is no exception. However, as you reduce carbohydrate intake, your body may excrete more water and electrolytes. This can lead to dehydration and imbalances in minerals like sodium, potassium, and magnesium. To counteract this, prioritise adequate water intake and consider supplementing with electrolytes.
References
“,.” 2023. , – YouTube.
https://www.tandfonline.com/doi/abs/10.1080/1028415X.2019.1627769.
Al-Sowayan, Noorah. n.d. “(PDF) The Effect of Ketogenic-Diet on Health.” ResearchGate.
Accessed December 16, 2023.
https://www.researchgate.net/publication/340836452_The_Effect_of_Ketogenic-Diet_on_Health.
“Ketogenic Diet – StatPearls.” 2023. NCBI. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK499830/.
FAQs
Can I build muscle on a keto diet?
Yes, muscle building is possible on a ketogenic diet through careful planning and attention to protein intake. While the diet is low in carbohydrates, the body can adapt to using ketones and fatty acids for energy. Adequate protein intake and incorporating strength training exercises are essential for muscle growth.
What are the Cons of the Ketogenic Diet?
The ketogenic diet has potential drawbacks, including nutrient deficiencies, the “keto flu” during adaptation, its restrictive nature impacting food choices and social situations, and the possibility of digestive issues due to a lack of fibre. Addressing these concerns with a well-balanced approach and monitoring health markers is crucial.
Is it safe to follow the keto diet?
The ketogenic diet is generally safe for most people when followed for short to moderate durations. Consultation with healthcare professionals is advised for individuals with specific medical conditions, and regular monitoring of health markers, such as cholesterol levels, is recommended. Maintaining a well-balanced diet is crucial for overall safety and effectiveness.
How much protein should I eat on a ketogenic diet?
Protein intake on a ketogenic diet ranges from 15% to 25% of total daily caloric intake, with a standard guideline suggesting 0.6 to 1.0 grams of protein per pound of lean body mass. Adequate protein is crucial for maintaining muscle mass and supporting various physiological functions in a ketogenic diet.
Are there any risks of the keto diet?
While the ketogenic diet can be practical, potential risks include nutrient deficiencies, the threat of ketoacidosis in individuals with diabetes, possible increases in LDL cholesterol levels, and side effects like the “keto flu” and constipation. Consultation with healthcare professionals before starting the diet and ongoing monitoring is essential to address individual needs and potential risks.