Omega-3 fatty acids and vitamins D and B2 are abundant in fish (riboflavin). In addition to being an excellent source of minerals like iron, zinc, iodine, magnesium, and potassium, fish is also high in calcium and phosphorus. A healthy diet should include fish at least twice a week, according to the American Heart Association. Protein, vitamins, and nutrients found in fish can lower blood pressure and help lower the risk of a heart attack or stroke. Fish is also a great source of nutrition.
Nutritional Value of Fish
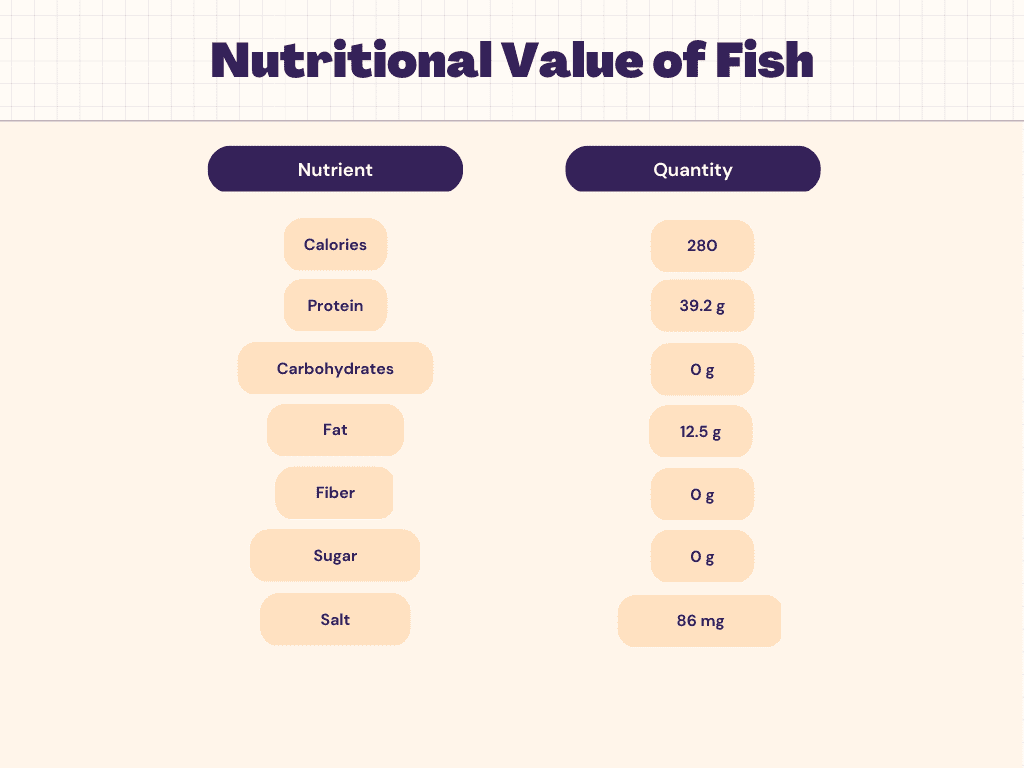
Nutritional Facts of Fish
Fish (1 oz, boneless, uncooked; yield after cooking) has:
- 30 calories
- 0.7g of fat
- 5.5g of protein
- 0g of net carbohydrates.
Health Benefits Of Fish
- Lowers the risk of heart disease – A lower risk of heart disease has also been linked to omega fatty acids. Regular consumption of omega-3 fatty acids seems to be linked to preventing and decreasing coronary heart disease. These fatty acids aid to lessen blood pressure, reducing triglyceride levels, and limit coronary plaque.
- Decreases the risk of depression – Omega-3 fatty acids are also good for your mental wellness. Omega-3 fatty acids have a strong connection to a decline in depressive symptoms. Some anti-depressant drugs have been shown to be more successful when taken with omega fatty acids, probably because these fats improve brain function.
- Boosts brain health – As you age, your brain function frequently deteriorates. Mild mental deterioration is common, however, there are also significant neurodegenerative illnesses like Alzheimer’s disease. Numerous observational studies reveal that those who consume more fish age mentally more slowly.
- Helps prevent and treat depression – Low spirits, sorrow, less energy, and a lack of enthusiasm in life and activities are its hallmarks. Depression is currently one of the largest health issues in the world while receiving far less attention than heart disease or obesity.
The Bottom Line
One of the world’s healthiest foods is fish. Important nutrients like protein and vitamin D are abundant in it. Omega-3 fatty acids, which are vital for your body and brain, are also abundant in fish.
FAQs
How much Fish should I eat in a day?
At least two meals of fish each week, one of which should be an oily fish, are necessary for a healthy, well-balanced diet. The majority of us don’t consume this much. A serving weighs about 140g (4.9oz).
Should I eat Fish before or after exercise?
You want to consume a balanced diet of protein and carbohydrates following exercise. Lean meat, such as fish and poultry, as well as grains like quinoa, provide excellent post-workout protein options.
What are the benefits of Fish?
- Lowers the risk of heart attacks and strokes
- Boosts brain health
- Contains important nutrients
- Helps in the prevention of depression
- Good source of vitamin D
- Reduces the risk of autoimmune diseases
- Might help prevent asthma in children
What is the best time to eat Fish?
The finest foods to consume before bedtime are seafood, such as clams, octopus, seaweed, shrimp, lobster, crab, and lobster. This is due to the fact that they contain a lot of tryptophan, a necessary amino acid that our bodies cannot create on their own.