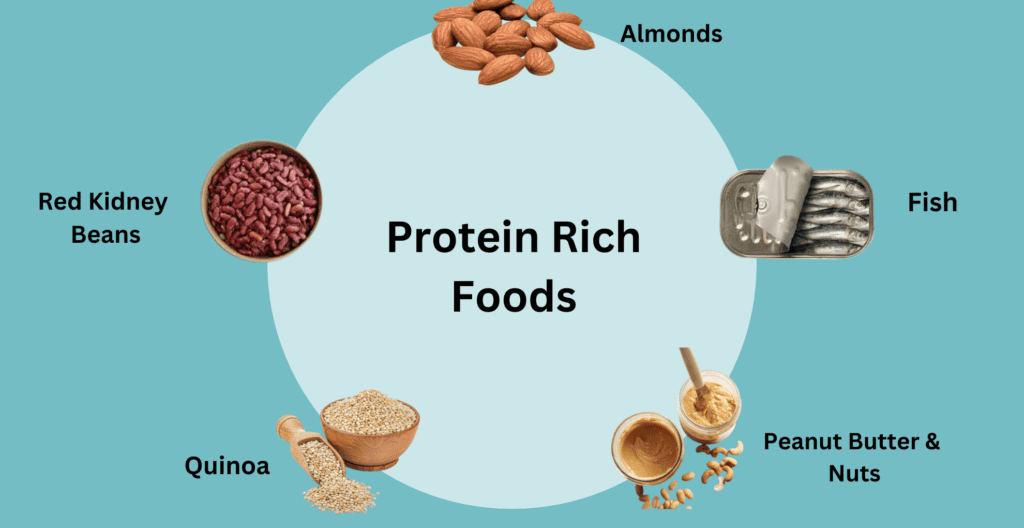
What are Protein Rich Foods?
Have you also wondered what protein rich foods consist of? If yes, then, you are in the right place to guide yourself about protein and what protein-rich foods are. Protein is an essential nutrient in every single cell of the human body, and it plays an important role in the growth, development, and repair of tissues and cells to perform crucial bodily functions correctly. The primary sources of protein are plants and animals. Building blocks of proteins are amino acids, which come in 20 types, with 9 of them being essential. Studies have proven that animal meat contains all essential amino acids and is called complete proteins. Plant-based proteins are called incomplete proteins because they lack at least one essential amino acid.
Top 20 High Protein Foods
These top 20 high protein foods offer chicken, meat, nuts, seeds, fruits and vegetables, dairy products, and other Protein Rich Fruits that fulfil your daily protein requirement. These high protein foods help you meet your dietary goals and improve your overall health, fulfilling your nutrition and protein requirements. These protein rich foods fit well with supporting your balanced lifestyle.
Here’s a list of 20 High Protein foods along with their protein content per 100 grams:
1. Chicken Breast (cooked, skinless) – 31 grams of protein
2. Turkey Breast (cooked, skinless) – 29 grams of protein
3. Salmon (cooked) – 25 grams of protein
4. Tuna (cooked) – 30 grams of protein
5. Trout (cooked) – 20 grams of protein
6. Eggs (cooked) – 13 grams of protein
7. Greek Yogurt (plain, non-fat) – 10 grams of protein
8. Cottage Cheese (low-fat) – 11 grams of protein
9. Lean Beef (cooked, top round) – 36 grams of protein
10. Lentils (cooked) – 9 grams of protein
11. Chickpeas (cooked) – 8 grams of protein
12. Quinoa (cooked) – 4 grams of protein
13. Firm Tofu – 8 grams of protein
14. Edamame (cooked) – 11 grams of protein
15. Pumpkin Seeds (roasted) – 30 grams of protein
16. Almonds (dry roasted) – 21 grams of protein
17. Peanut Butter (smooth, unsalted) – 25 grams of protein
18. Whey Protein Powder – 70 grams of protein
19. Chickpea Pasta (cooked) – 20 grams of protein
20. Bison (cooked, top sirloin) – 33 grams of protein
1. Chicken Breast
Number one on our high protein food list is Chicken breast or Grilled Chicken breast. Due to its nutritional composition and health-promoting qualities, eating chicken breast can provide many advantages, and it’s worth it to know more about Chicken Nutrition.
| Serving Size | Amount of Protein |
| 100 g (roasted, cooked, skinless) | 31 grams |
Benefits of consuming chicken breast:
- High Protein Content: Chicken breast is an excellent protein-rich food, providing approximately 25 grams of protein per 3-ounce serving. Protein is necessary for tissue growth, repair, muscular support, and immune system maintenance.
- Low in Fat: Chicken breast is a go-to meal for any health-conscious person. Grilled chicken breast has a relatively low-fat content than other chicken cuts with higher fat content. It is a fantastic choice for anyone seeking to keep their weight in check or watch their fat intake.
- Rich in Essential Nutrients: Chicken breast is an excellent source of vitamins B6, B3, and B5, which help in healthy cell function, brain function, and energy metabolism. Additionally, it contains minerals like phosphorus, selenium, and zinc, which are crucial for the immune system, bone health, and general wellness.
2. Turkey Breast
Next on our high-protein food list is turkey breast. Turkey breast is a nutritious and lean source of protein that can be enjoyed as part of a balanced diet. It’s an excellent choice for those seeking high-quality protein with the added benefit of being low in fat and calories.
| Serving Size | Amount of Protein |
| 100 g (cooked, skinless) | 29 grams |
Benefits of consuming Turkey Breast:
- Nutrient-dense: Turkey breast is one of the many excellent foods with protein, vitamin B6 (pyridoxine), and vitamin B3 (Niacin), which are essential for brain development and function. Niacin is involved in synthesising neurotransmitters, which affect mood and cognitive health.
- Weight Loss and Maintenance: The combination of high-quality protein, low-fat content, and the potential for satiety can support weight loss and maintenance efforts. Protein is known for controlling appetite, reducing hunger, and preventing overeating.
- Low-Sodium Option: When choosing turkey breast products, it’s possible to find options that are low in sodium or have no added salt, making them suitable for individuals looking to manage their salt intake.
- Turkey breast contains significant protein, zinc, and selenium levels, which may help with immune function. If you prepare turkey breast with healthier alternatives, it can be the best protein food.
3. Salmon
Salmon is a great source of protein and fats loaded with nutrients and reduces several risk factors. Salmon is rich in dense nutrients. For example, fresh catch of salmon is higher in protein when compared with farmed salmon, which is slightly higher in protein. Salmon is an excellent source of heart-healthy fats, which reduce inflammation and support brain function, omega-3 fatty acids and vitamin B12, which produces red blood cells.
| Serving Size | Amount of Protein |
| 100g (cooked) | 25 grams |
Benefits of consuming Salmon:
- High in omega-3 fatty acids: Salmon is rich in long-chain omega-3 fatty acids, particularly EPA and DHA, essential for various health benefits, including reducing inflammation, lowering blood pressure, and improving arterial function. Consuming at least two servings of salmon per week is recommended to meet omega-3 needs.
- Excellent source of protein: Salmon is an excellent source of high-quality protein, essential for healing, bone health, and maintaining muscle mass. Each serving provides approximately 22-25 grams of protein.
- Rich in B vitamins: Salmon is rich in B vitamins, essential for energy production, DNA repair, and reducing inflammation. It contains significant amounts of Vitamin B12, Niacin, Vitamin B6, Riboflavin, Pantothenic acid, Thiamine, and Folic acid.
- Rich in selenium: Salmon contains selenium, a mineral important for bone health, thyroid function, and potentially reducing cancer risk. A serving provides 75–85% of the DV for selenium.
- Weight loss: Salmon’s high protein content and omega-3 fats can aid weight management by reducing appetite, boosting metabolism, and decreasing belly fat. Is ia great source of Protein Rich Foods for weight loss.
4. Tuna
Tuna is found in seas and oceans and is scientifically known as Thunnini. It is a rich source of protein and essential nutrients like omega-3 and vitamin B12. According to a study, its omega-3 fatty acids reduce bad cholesterol and LDL cholesterol, which is harmful as it accumulates in the arteries and can damage our hearts.
| Serving Size | Amount of Protein |
| 100g (cooked) | 30 grams |
Benefits of Tuna:
- Blood Pressure: Consuming tuna lowers blood pressure as it is rich in potassium and omega-3 fatty acids, which smooth the regulation of blood pressure. It also reduces the risk of heart attack and sudden strokes.
- Triglyceride: A study found that triglyceride is an unhealthy fat that accumulates in the blood and circulates all over the body. Tuna contains HDL, or good cholesterol, which fights with LDL, or bad cholesterol, to fight the harmful effects of triglyceride.
- Immune system: Tuna is a great source of macronutrients that help control cellular metabolism.
- Low risk of cancer: Tuna is rich in omega-3 fatty acids, which restrict the growth of tumour cells. These antioxidants are anti-inflammatory and fight cancer cells.
5. Trout
Trout is another rich source of protein in our protein-rich foods list. Like all other fish sources, it also contains omega-3 fatty acids, vitamin B12, niacin, and vitamin B6. It is also rich in potassium and selenium, which reduces blood pressure and maintains the overall health of our body.
| Serving Size | Amount of Protein |
| 100g (cooked) | 20 grams |
Benefits of trout:
- Muscle building: Trout helps build muscle and maintain a healthy weight. It contains proper nutritional values, which support high energy levels during workout sessions.
- Healthy heart: Omega-3 fatty acids help maintain heart health. Trout is a great source of lean proteins, which help maintain healthy heart functions, such as pumping blood that keeps us alive. This also helps enhance our brain power.
- Niacin is an important mineral that converts food into energy while assisting with digestion and nervous system function within the body.
- Vitamin B: This vitamin is essential for producing red blood cells and supporting brain health. It also helps maintain energy levels and overall health.
6. Eggs
Next on our protein food list is Eggs (know more about egg nutrition). Eggs are very nutrient-dense foods with protein and have a variety of health advantages. They are an excellent protein rich food. One large egg contains approximately 6 grams of protein, making it a convenient and affordable source of high protein foods.
| Serving Size | Amount of Protein |
| 100 g (cooked, edible part, excluding shells) | 13 grams |
Benefits of Consuming Eggs:
- Complete Protein: Eggs are considered a complete protein source, as they contain all the essential amino acids the body needs for various functions, including muscle maintenance and repair.
- Rich in nutrients: Vitamins and minerals like vitamin B12, vitamin D, vitamin A, vitamin E, selenium, choline, and iron are abundant in eggs. These nutrients are essential for many biological processes, including immunological, ocular, and brain functioning.
- Heart Health: Contrary to popular belief, evidence indicates that moderate egg consumption in healthy persons does not significantly raise the risk of heart disease. In truth, when included in a balanced diet in moderation, eggs can be a part of a heart-healthy diet.
- Choline: Eggs are a great source of choline, a vitamin crucial for the brain’s health and various metabolic processes.
7. Greek Yogurt
Next on our protein food list is Greek Yogurt (Read more about Yogurt Nutrition). Greek yogurt has a thicker and creamier texture than conventional yogurt because the whey has been removed during the straining process. It is a popular choice for many people because it offers several health advantages.
| Serving Size | Amount of Protein |
| 100 g (plain, non-fat) | 10 grams |
Benefits of consuming Greek Yogurt:
- High Protein Content: Greek yogurt is a protein-rich food (a 6-ounce serving contains approximately 12 grams of protein). Protein is needed for tissue growth and repair, muscle support, and general health. It is an excellent choice for people trying to enhance their protein consumption because it often includes more protein than regular yogurt.
- Probiotics: Greek yogurt frequently includes probiotics, a type of healthy bacteria that can help support gut health. Probiotics can help with digestion, strengthen the immune system, and enhance gut health in general, all of which can benefit overall well-being.
Greek yoghurt generally has fewer carbohydrates than regular yoghurt, making it a good choice for anyone on a low-carb or ketogenic diet. It can support weight management efforts and support blood sugar regulation
8. Cottage Cheese
Next on our protein food list is Cottage Cheese (learn how to make cottage cheese at home). Cottage cheese, a well-liked dairy product formed from cow’s milk curds, is renowned for its distinct flavour, texture, and adaptability. It can be included in the protein foods list.
| Serving Size | Amount of Protein |
| 100 g (low-fat, creamed) | 11 grams |
Benefits of consuming Cottage Cheese:
- Complete protein: Cottage cheese is a great protein-rich food, with a half-cup serving containing approximately 14 grams of protein. Protein is necessary for the growth and repair of tissues, the preservation of lean body mass, and the support of immune system function. As a complete protein source, it has all the essential amino acids required for good health.
- Low in calories: Cottage cheese is a beautiful choice for people limiting their calorie intake because it has a low caloric content. It offers sufficient protein without too many calories, making it a fantastic option for anyone trying to maintain or reduce weight.
- Vitamins and minerals are abundant. It is a good source of calcium, phosphorus, selenium, vitamin B12, and vitamin B2 (riboflavin). Strong bones and teeth require adequate calcium and phosphorus, while selenium and B vitamins support metabolism and overall health.
9. Lean Beef
Lean beef, commonly known as red meat, is less fat-rich than skinless chicken breast or thigh. Every 100 grams of lean beef contains 10 grams of fat, 5 grams of saturated fat, less than 95 milligrams of cholesterol, and 36 grams of protein.
| Serving Size | Amount of Protein |
| 100g (cooked, top round) | 36 grams |
Benefits of lean beef:
- Muscle growth: Lean beef is a healthier and a great source of protein, which improves muscle growth and helps in the proper development of muscle mass. Considering its rich protein content, it fulfills the protein requirements for muscle building.
- Good fats: Lean beef is high in good fats and omega-3 fatty acids that help protect your body and mind against numerous health risks.
- Rich in minerals: Lean beef is a rich source of minerals like zinc and iron, which promote healthy body growth, the production of new cells, and immunity.
10. Lentils
Next on our protein food list is Lentils. Tiny legume seeds called lentils are incredibly nutrient-dense and have many positive health effects. They are well-known for their flexibility in the kitchen and are a mainstay in many different cuisines worldwide.
| Serving Size | Amount of Protein |
| 100 g (cooked) | 9 grams |
Benefits of consuming lentils:
- Plant-based Protein: Lentils are a great plant-based protein rich food (with one cup of cooked lentils containing approximately 18 grams of protein), making them a great option for vegetarians, vegans, or anybody trying to cut back on their meat consumption. Building and mending tissues, fostering the growth of muscles, and enhancing general health depend on protein.
- High nutritional value: Lentils have a high nutrient density, which means they contain important vitamins, minerals, and other healthy ingredients. They complement a healthy diet since they are a great source of fibre, folate, iron, potassium, magnesium, and plant-based protein.
- Low in Fat and Cholesterol: Lentils are a heart-healthy meal option because they are naturally low in fat and cholesterol. Eating lentils as part of a balanced diet can help lower the risk of cardiovascular diseases and enhance heart health.
Lentils, thus, are one of the best foods with protein that one must include as part of their dietary habits. If you prepare them with healthy variations, they can be the best protein food.
11. Chickpeas
Chickpeas, also known as garbanzo beans, are a versatile and nutritious legume widely appreciated for their protein content and numerous health benefits.
| Serving Size | Amount of Protein |
| 100 g (cooked) | 8 grams |
Here are some key advantages of using chickpeas as a source of protein:
- Complete Protein: Chickpeas offer a complete protein profile, which means they contain all the essential amino acids the body needs for various functions, including muscle maintenance and growth.
- Nutrient Density: Chickpeas are nutrient-dense, providing essential vitamins and minerals such as folate, iron, magnesium, potassium, and phosphorus. These nutrients are necessary for various bodily functions, including energy metabolism and blood pressure regulation.
- Antioxidants: Chickpeas contain antioxidants such as flavonoids, polyphenols, and saponins, which help protect cells from oxidative damage and reduce the risk of chronic diseases.
- Heart Health: Chickpeas’ combination of protein, fibre, and antioxidants supports heart health by reducing cholesterol levels, lowering blood pressure, and reducing the risk of cardiovascular diseases.
- Weight Management: Chickpeas’ protein and fibre content can promote a feeling of fullness, potentially reducing overall calorie intake and aiding weight management. They are naturally low in fat, particularly saturated fat. They serve as a lean source of protein, helping to reduce the overall calorie and fat content of your meals.
12. Quinoa
Next on our protein food list is Quinoa (Read more about Quinoa Nutrition). Quinoa is a distinctive pseudo-grain that is very nutritious and has grown in popularity recently due to its health advantages. This protein rich food is renowned for its adaptability in the kitchen, nutty flavour, and various health-enhancing qualities.
| Serving Size | Amount of Protein |
| 100 g (cooked) | 4 grams |
Benefits of consuming quinoa:
- Gluten-Free: Quinoa is naturally gluten-free, which means it doesn’t contain the proteins known as gluten, specifically glutenin and gliadin, found in wheat, barley, and rye. This makes it suitable for those with gluten sensitivity or celiac disease.
- Weight Management: Quinoa’s protein and fibre content can help with satiety, making it a satisfying food that may help you feel full and reduce the urge to snack between meals. When talking about calories, while it is not particularly low in calories, it is lower in calories than many other staple foods like rice, pasta, or potatoes.
- Antioxidants: Quinoa contains antioxidants, such as quercetin and kaempferol, which can help protect cells from oxidative damage and reduce the risk of chronic diseases.
13. Firm Tofu
Firm tofu is made of soy milk converted into a solid white block similar to processed cheese. It is high in protein and contains all the essential amino acids required for the proper functioning of the human body. Tofu provides 3 grams of carbs, 9 grams of fat, 144 calories and 17 grams of protein per 100 grams.
| Serving Size | Amount of Protein |
| 100g | 8 grams |
Benefits of consuming tofu:
- Low risk of heart disease: Firm tofu lowers cholesterol levels and LDL(bad) cholesterol by 4%. The combination of proteins, fibers, and isoflavones benefits heart health.
- Isoflavones are natural plant compounds found in soybeans and function as phytoestrogens, meaning they can activate estrogen receptors in our body by attaching to them. One gram of soy protein provides about 3.5 milligrams of isoflavones.
- Rich in Antinutrients: Tofu contains two antinutrients: phytates and trypsin inhibitors. Phytates reduce the body’s absorption of minerals such as calcium, zinc, and iron. In contrast, trypsin inhibitors block the absorption of trypsin enzymes needed for proper protein digestion. Indigestion causes pain in the abdominal region and slow absorption of certain minerals. A nutrient-rich diet will not cause any problems, but a nutrient-poor diet will encourage these enzymes to show their results.
14. Edamame
Edamame is a legume and the best low-calorie snack option. It is immature soybeans eaten whole, and 160 grams of cooked edamame contains 230 calories, more than 10% of a person’s daily calorie intake, depending on their age, sex, and physical activity level.
| Serving Size | Amount of Protein |
| 100g (cooked) | 11 grams |
Benefits of consuming edamame:
- Vitamins and minerals: Edamame is rich in vitamins, minerals, and fiber. One cup of cooked edamame has 224 calories and 37% protein. It also contains around 56% of vitamin K and 100% folate, the daily value.
- Low risk of breast cancer: Estrogen might promote certain types of cancer, such as breast cancer, and edamame is rich in isoflavones, which mimic weak estrogen receptors to estrogen. Studies have shown that in the Asian population, due to the high consumption of soy-based food, there is a reduced risk of breast cancer.
- Reduce menopausal symptoms: Due to the isoflavone-rich content of edamame, some studies have shown reduced symptoms during menopause. Certain bacteria convert isoflavones into equol, which provides many health benefits.
15. Pumpkin Seeds
Pumpkin seeds are a source of healthy fats, magnesium, and other beneficial nutrients for the heart’s and bone’s health. Pumpkin seeds are a high source of iron, polyunsaturated fatty acids and antioxidants such as beta-carotene and selenium. One portion of pumpkin seeds contains around 10 milligrams of iron.
| Serving Size | Amount of Protein |
| 100g (roasted) | 30 grams |
Benefits of consuming pumpkin seeds:
- Weight loss: 30 grams of pumpkin seeds contain 1.8 grams of fiber, which helps maintain weight. Pumpkin seeds also improve digestion and manage blood sugar levels.
- Healthy immune system: Rich in vitamin E and antioxidants, it help strengthen the immune system and maintain blood flow.
- Sexual health: In male fertility, pumpkin seeds play a crucial role. They are packed with zinc, which enhances both sperm quality and quantity.
16. Almonds
Almonds are next on our protein food list (know more about Almond nutrition). Nutrient-rich food like almonds has several health advantages. One of them is that they are one of the best foods with protein. Almonds are also a valuable source of other essential nutrients, including healthy fats, fibre, vitamins, and minerals.
| Serving Size | Amount of Protein |
| 100 g (dry roasted, raw) | 21 grams |
Benefits of Consuming Almonds:
- Heart-Healthy Fats: Almonds are abundant in monounsaturated fats, which can help lower LDL cholesterol (bad cholesterol) levels and minimise the risk of heart disease. They also contain many antioxidants, like vitamin E, which help prevent inflammation and oxidative stress and further support heart health.
- Almonds are plant-based, high-protein foods. It has approximately 21 grams of protein per 100 grams, which is relatively high for a nut. A typical serving of almonds, around 1 ounce or 28 grams (about 23 almonds), provides approximately 6 grams of protein.
- Vitamins and Minerals: Almonds are an excellent source of calcium, magnesium, and phosphorus, three minerals necessary for strong, healthy bones. Eating them regularly, particularly in postmenopausal women, can maintain bone health and lower the incidence of osteoporosis.
- Regulates Blood Sugar: Almonds’ low glycemic index indicates that they can help control blood sugar levels and help prevent blood sugar increases after meals. They also include beneficial fats, fibre, and protein that can slow the digestion of carbohydrates and help to regulate blood sugar levels.
17. Peanut Butter
Next on our protein food list is peanut butter and nuts. You can enjoy this spread during breakfasts, pre-workouts and post-workouts as well. Add a scoop of peanut butter to your smoothies, and you get a fantastic taste in just one blend! You can source the peanut butter from supermarkets or even prepare a batch at home.
| Serving Size | Amount of Protein |
| 100 g (smooth, unsalted) | 25 grams to 30 grams |
Benefits of consuming Peanut Butter:
- Nutrient-dense: Peanut butter and nuts are some of the best foods with protein, fibre, healthy fats, vitamins, and minerals. They are also minimal in carbohydrates, making them an excellent choice for those on a low-carb diet.
- Complete Protein: The protein in peanut butter is considered complete, as it contains all the essential amino acids necessary for your body’s functions. These amino acids are the building blocks for various proteins in your body, making peanut butter a valuable source of this essential nutrient.
- Healthy Fats: Besides protein, peanut butter is a source of healthy monounsaturated and polyunsaturated fats. These fats are heart-healthy and can help reduce the risk of heart disease when consumed in moderation. They also play a role in the absorption of fat-soluble vitamins.
18. Whey Protein Powder
Next on our protein food list is Protein Powder. As the name suggests, protein powder is one of the best foods with protein, providing an excellent way to include the same in your diet.
| Serving Size | Amount of Protein |
| 100 g | 70 grams |
Benefits of consuming protein powder:
- Protein powder is a great food with protein and dietary supplements popular among athletes, bodybuilders, and those looking to increase their protein consumption. Here are some of the possible advantages of consuming protein powder:
- Protein powder is a convenient and efficient method to increase protein intake, which is important for muscle growth and repair following exercise.
- Protein powder can help foster feelings of fullness and reduce overall calorie intake, which can help with weight loss efforts.
- Consuming protein powder before or after exercise has been shown to increase muscle endurance, strength, and recovery.
- Protein is essential for keeping bones healthy and preventing osteoporosis, especially in older adults.
- Blood pressure may be reduced.
You can also consume weight loss protein powder after consulting a health coach if you are looking to lose weight.
19. Chickpea Pasta
The second last on our protein-rich foods list is chickpea pasta, made of chickpea flour and comes in various shapes and sizes. It is gluten-free, making it suitable for those seeking a gluten-free option. One serving of chickpea pasta has less than 190 calories, 32 grams of carbs, and 14 grams of protein.
| Serving Size | Amount of Protein |
| 100g (cooked) | 20 grams |
Benefits of consuming chickpea pasta:
- Heart health: Eating chickpea pasta may reduce heart disease risk due to its fiber and polyphenol content. One study found that consuming beans more than three times weekly reduced heart disease risk by 35% and replacing red meat with legumes and other plant-based proteins may decrease heart disease risk by 14%.
- Blood Sugar Control: Chickpeas’ high fiber and protein content helps maintain healthy blood sugar levels. Chickpea pasta offers more fiber and protein than white or wheat pasta, which improves blood sugar management.
- Digestive health: Chickpeas contain soluble and insoluble fiber, promoting digestive health. They also have prebiotic fiber, supporting a healthy gut microbiome. Fiber-rich diets reduce the risk of inflammatory bowel disease and colorectal cancer while improving bowel movements. Chickpea pasta offers similar digestive health benefits due to its fiber content.
- Weight management: Chickpea pasta, which is rich in fiber and protein, helps you feel full longer and helps with weight management. Studies suggest replacing refined grains with fiber—and protein-rich foods may regulate appetite and reduce overall food intake.
20. Bison
Bison meat is growing in popularity because it is a healthier red meat than beef. It contains protein, iron, zinc, selenium, and B vitamins. A 114-gram serving of cooked bison has 124 calories, 17 grams of protein, and 6 grams of fat.
| Serving Size | Amount of Protein |
| 100g (cooked, top sirloin) | 33 grams |
Benefits of consuming Bison:
- Vitamins and minerals: Bison meat is rich in vitamins, providing 68%, 19%, and 28% of the daily values for vitamin B12, B6, and niacin, respectively, per 114 grams serving. These vitamins support energy production and red blood cell formation. It is a good source of iron, selenium, and zinc, essential for red blood cell formation, antioxidant function, and immune support, with a 114-gram serving providing 13%, 31%, and 35% of the daily value for each mineral, respectively.
- Low calories: Bison meat is relatively low in fat and calories, with only 6 grams of fat and 124 calories per 114 grams serving. This makes it suitable for individuals aiming to control their calorie intake while obtaining essential nutrients.
Why Do You Need High Protein Foods?
There are plenty of reasons to have protein rich food. High-protein foods are important for a number of reasons, including:
- Building and repairing muscle tissue. Protein is the essential macronutrient for building and repairing muscle tissue.
- Reducing hunger and promoting weight loss. Protein is more satiating than other macronutrients, meaning it helps you feel full after eating.
- Supporting the immune system. Protein is needed to produce antibodies and other white blood cells that protect the body from infection.
- Producing hormones and enzymes. Hormones and enzymes are essential for various body functions, including metabolism, growth, and development. Protein is needed to produce these hormones and enzymes.
We should note the difference between high protein sources and the best protein source for your body. High protein sources can be defined with the scientific approach and best protein sources with a subjective approach— ‘Protein Package’. When we eat protein foods, we also eat everything that comes alongside it: the different fats, fibre, sodium, and more. So, the best protein source differs from person to person depending what other nutrients are required by your body.
Benefits of eating Protein Rich Foods
Consuming protein in daily dosage according to your body’s requirements is a must to maintain the healthy functioning of the body and mind. Here comes the role of protein rich foods, which are high in amino acids, long-chain omega-3 fatty acids, vitamin B, potassium and selenium. Protein-rich foods that fall under the highest nutrient-dense food are grilled chicken breast, tuna salad, briskets and vegetable salads. Protein is essential for the growth and maintenance of every cell in our bodies. According to dieticians at Thomas F. Chapman Family Cancer Wellness at Piedmont, proteins help our body stay in shape and manage weight. Let us look at the benefits of consuming protein-rich foods:
1. Muscle growth and repair
Protein-rich foods help muscles grow and repair by building blocks for new muscle tissue and restoring small muscle tears. Eating enough protein keeps muscles strong at every age because it speeds up recovery after workouts. Protein also helps you feel full, strengthens your immune system, and supports regaining muscle health. Including chicken, lean meats, fish, eggs, dairy, beans, and legumes ensures a good protein intake.
2. Weight management
According to the National Library of Medicine, eating protein can help you lose weight and improve your body’s composition. It reduces fat while keeping your lean muscle mass intact, even when you’re following a low-calorie or regular diet. Studies conducted over several months have shown that a high-protein diet leads to weight loss and can help you maintain that weight loss in the long run.
3. Improved metabolism
Protein-rich foods such as eggs contain 6.3 grams of protein. Protein increases the body’s metabolic rate and uses energy to digest it, which tells us that protein is one of the essential nutrients required for the functioning of the human body. Research has shown that people who consume 29% of their total daily calorie intake through protein have higher metabolic rates than those who consume 11% of total calories from protein.
4. Blood sugar control
To maintain your blood sugar level, a good involvement in a protein-rich diet is a must and food that is high in protein, such as chicken, fish, meat, and cheese, can make a significant difference in your blood sugar level. Plant-based protein foods such as kidney beans, lentils, peas, edamame and soy nuts provide quality protein with healthy fats, carbs and fiber.
5. Bone health
Calcium-rich protein sources such as milk, cheese and other dairy foods, soya beans, green leafy vegetables such as cabbage and broccoli, and nuts are good sources of calcium. Vitamin D sources such as fish oil, salmon, sardines, and egg yolks are rich sources of vitamin D. Recent studies have shown that combining adequate calcium and vitamins improves bone health and increases bone growth.
6. Healthy ageing
A decline in muscle mass that occurs with age is called sarcopenia, and this is curable by promoting a Protein Diet Plan for healthy ageing. If protein intake is adequate from sources such as chicken, meat, vegetables and beans, then ageing can be improved, which means free from any chronic disease.
7. Immune function
All the bodily functions are carried out by our immune system, which consists of tissues, cells, organs and proteins. The immune system fights viruses, bacteria, pathogens and foreign bodies by releasing antibodies into the system, which attach to antigens on the pathogens and kill them. Blueberries, broccoli, spinach, sweet potato, turmeric and fish oil are some of the greatest boosters for our immune system, providing proteins and nutrients for the healthy development of our immune system.
8. Hair, skin, and nail health
Collagen, a protein, is crucial for skin, hair, and nail health and appearance. Including adequate protein in your diet can help maintain healthy, vibrant skin and strong hair and nails.
9. Hormone regulation
Hormones are made up of amino acids, which are the building blocks of proteins. Proper hormone function is essential for various bodily functions, including growth and development, stress response, and regulation of metabolic processes.
10. Heart health
Protein-rich food is the most excellent way to eliminate any heart risks, and selecting the proper protein-rich food diet, such as legumes, nuts, seeds, fish, and seafood, are among the most excellent sources of proteins. Processed meat can increase your risk of heart disease and should be avoided with a limited intake of red meat.
How to get a High Protein Diet
Including a high-protein diet in our daily meals puts us on the right track to boosting muscle mass, supporting metabolism, and feeling fuller for longer. To start the journey, one should focus on including protein rich foods in every meal and snack through lean protein sources like chicken, fish, and tofu, while avoiding heavily processed options. A balanced diet is a key factor and with whole foods like red meat, chicken, whole grains and fresh vegetables, and don’t forget healthy fats from sources like avocados and nuts foster your plans to prepare meals and snacks in advance to ensure you’re hitting your protein targets. Start your day with a protein-rich breakfast and pick high-protein snacks like Greek yogurt or bacon. If you need extra push, consider protein supplements, but whole foods should always be your primary source of nutrition. Remember to stay hydrated and listen to your body’s hunger and fullness cues to avoid overeating. You’ll be well on your way to achieving a successful high-protein diet through the following tips. let’s discus these in more detail:
1. Include protein-rich foods in each meal and snack.
Including high protein-rich foods in every meal and snack helps maintain muscle mass, supports metabolic function, and keeps you feeling full longer. Aim for about 20-30 grams of protein per meal; specifically for snacks, aim for 10-15 grams also, you can be precise if you use the Protein Intake Calculator to keep track of your protein intake. Incorporate various sources, such as:
- Protein breakfast: Eggs, Greek yogurt, cottage cheese, protein pancakes, or protein smoothies.
- High-protein lunch and dinner: Grilled chicken, turkey, fish, tofu, beans, lentils, or tempeh.
- Protein-rich snacks: Boiled eggs, cheese, edamame, or peanut butter on whole-grain toast.
2. Choose lean protein sources like poultry, fish, and legumes.
Lean proteins are generally lower in saturated fat, making them a healthier choice for a high-protein diet plan. Consider these examples:
- Low-fat proteins: Chicken and turkey are great generic sources of low-fat protein (skinless, boneless cuts are best).
- Protein-rich fish and seafood: Salmon, tuna, trout, cod, shrimp, and halibut are some protein-rich fish options. These also contain healthy omega-3 fatty acids.
- Vegetarian protein sources: Tofu, tempeh, lentils, beans, and edamame are great plant-based vegetarian protein sources.
3. Eat whole, minimally processed foods.
Eating whole foods provides more nutrients and minimal additives than processed foods, contributing to overall health and reducing the risk of chronic diseases. Opt for:
- Whole cuts of meat instead of processed meats.
- Whole grains like quinoa, brown rice, and whole-grain bread.
- Freshly harvested vegetables and fruits.
4. Balance macronutrients by pairing protein with carbohydrates and healthy fats.
A balance of macronutrients by pairing protein with carbohydrates and healthy fats provides a balanced macronutrient intake, helps in maintaining body energy levels and provides a broader range of nutrients. Here are some examples of balanced meals:
- Carbohydrates: Whole grains, sweet potatoes, and legumes.
- Healthy fats: Avocados, nuts, seeds, and olive oil.
- High-protein meals: Choose from the sources mentioned earlier.
5. Plan meals and snacks in advance.
Planning meals in advance ensures you consistently meet your daily protein targets. You can create a weekly protein food diet chart or use meal prep containers to prepare meals ahead of time. Consider:
- Protein meal prep: Preparing bulk meals, like chicken and vegetable stir-fry, to use throughout the week.
- High-protein snacks like boiled eggs, Greek yogurt, or hummus with veggies.
- Leftovers in protein meals: Use leftovers creatively, such as making protein-packed wraps or salads.
6. Start your day with a protein-rich breakfast.
A protein-rich breakfast provides sustained energy and can help curb cravings. Consider these ideas:
- Egg-based breakfast: Scrambled eggs with veggies, omelets, or breakfast burritos.
- Yogurt-based breakfast: Greek yogurt with nuts, seeds, and fruit.
- Protein smoothies: Blend protein powder with fruits, spinach, and nut butter for a nutritious start.
7. Opt for protein-rich snacks between meals.
High protein-rich snacks can stabilise your energy levels and help avoid overeating at meals. Consider:
- Dairy-based snacks: Cottage cheese or cheese sticks.
- Meat-based snacks: Chicken breast, Bison meat, Beef jerky, turkey slices, or smoked salmon.
- Plant-based snacks: Hummus with vegetables, edamame, or nuts.
8. Consider protein supplements if needed.
If you need help reaching your protein goals, protein supplements can be helpful. However, they should not replace whole foods. Use them to complement your diet:
- Whey protein powder: Mix into smoothies or shakes and consume to replenish your protein requirements.
- Protein bars: Look for ones with minimal sugar and whole-food ingredients.
- Collagen supplement: An excellent option for those interested in skin, hair, and joint health.
9. Stay hydrated.
Proper hydration and water intake are crucial for protein digestion and general health. Drink plenty of water throughout the day. You can also try:
- Flavoured water: Add slices of fruit or cucumber for flavour.
- Hydration drinks: Herbal teas or other low-calorie beverages.
- Monitoring hydration: Urine colour should be pale yellow to clear.
10. Listen to your body’s hunger and fullness cues.
Our body always drops signs and signals for various needs and requirements to flourish in high-protein diet intake. When it feels hungry, our body starts demanding or craving protein-rich food to feel full and to gain its energy back. Avoid overeating or undereating by:
- Listen to your body: Eat when you’re hungry and stop when you’re full.
- Portion control: Pay attention to portion sizes to avoid excessive intake.
- Adjust protein intake based on activity level. Active individuals may require more protein to support muscle recovery and growth.
Tips to include Protein Rich Foods in your Daily Diet
Consuming enough protein can be a challenge though it’s essential for maintaining energy, building muscle, and staying full throughout the day, but the good news is that there are simple tips to include more protein rich food in your daily diet without sacrificing flavour or variety. Following tips will quickly boost your protein intake, and you will enjoy delicious food through balanced meals every day.
1. Prioritize protein at every meal.
To prioritize protein at every meal, one must ensure that each meal has a high protein food, which can be included through eggs or Greek yogurt for breakfast, grilled chicken breast or legumes like edamame for lunch, and fishes like tuna or trout and firm tofu for dinner. Consistent protein consumption helps maintain energy and muscle health while keeping you full longer.
2. Snack smartly with protein-rich options.
Smart snacking involves choosing protein-rich foods over unhealthy, sugary, or high-carb options. Nuts, edamame, cheese, chicken nuggets, hard-boiled eggs, protein bars, or Greek yogurt are great high-protein snacks that can curb hunger and help stabilize blood sugar levels.
3. Build balanced plates with protein, carbohydrates, and healthy fats.
Creating a balanced plate with a combination of proteins, carbohydrates, and healthy fats supports high energy levels and nutrient absorption in our bodies. A typical balanced plate features grilled chicken for high protein, quinoa for good carbs, avocado for healthy fats, and added vegetables for rich fibers and vitamins.
4. Prep protein in advance for easy meal assembly.
To make protein meal prep easier in advance, cook protein-rich meals in bulk at the beginning of the day or week. Roasted chicken or grilled chicken, baked firm tofu, or cooked lentils to create quick meals throughout the day. This approach ensures you have high protein sources readily available, which helps you stay consistent with your diet.
5. Experiment with recipes featuring protein-rich ingredients.
Try new recipes that focus on protein-rich ingredients to keep your diet interesting. Experiment with various cuisines and cooking methods, such as air frying, baking, or grilling. Dishes like quinoa and black bean salad, grilled chicken and grilled salmon, or scrambled eggs with vegetables add variety, making it easier to maintain a high protein-rich diet while enjoying diverse flavours.
References
Fernando, Imashi. 2023. “39 high-protein foods for weight loss.” Medical News Today. https://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/321522#high-protein-foods-for-weight-loss.
Koh, Gwanpyo. 2020. “Clinical Evidence and Mechanisms of High-Protein Diet-Induced Weight Loss.” NCBI. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7539343/.
“Protein | The Nutrition Source | Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health.” n.d. Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health. Accessed October 21, 2023. https://www.hsph.harvard.edu/nutritionsource/what-should-you-eat/protein/.
Wei, Cong. n.d. “The Research on the High-Protein Low-Calorie Food Recipe for Teenager Gymnastics Athletes.” NCBI. Accessed October 21, 2023. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4645922/.
FAQs
1. What foods are highest in protein?
Yes, all animal-based protein sources, such as chicken, beef, fish, turkey, and dairy products, are high in protein. Chicken foods like grilled chicken breast, chicken liver, chicken nuggets, chicken stew, lean chicken breast, tuna fish, and healthy chicken salad are the highest nutrient-dense foods. Plant-based sources like tofu, lentils, beans, and quinoa are also high in protein.
2. What vegetables are high in protein?
Vegetables with higher protein content include chickpeas, spinach, broccoli, sweet corn, brussels sprouts, and edamame. They all contain high amounts of amino acids and essential nutrients.
3. Is cucumber high in protein?
No, cucumbers are not high in protein. A 140-gram serving provides 0.8 grams of protein, or 0.5 grams per 100 grams of cucumber, and 17 calories. Cucumbers primarily consist of water, about 95%, and their protein content is very low.
4. Is potato high in protein?
No, potatoes have a modest protein content, around 2 grams per 100 grams, which is lower than other protein sources such as wheat, rice, and corn.
5. Do oats have protein?
Yes, oats contain protein, around 13 grams per 100 grams of dried oats. They also have a good balance of essential amino acids and are loaded with important vitamins, proteins, and minerals.
6. Is a banana a good source of protein?
No, bananas are not the primary source of proteins as they are high in carbohydrates. They contain less than 1 gram of protein per banana.
7. Is peanut butter high in protein?
Yes, peanut butter is high in protein. Two tablespoons contain 8 grams of protein, which is high for a person who is always on a vegetarian or vegan diet.
8. Are almonds high in protein?
Yes, almonds are high in protein. About 6 grams of protein and 3.5 grams of fiber are in 28 grams of almonds. Almonds are also rich in antioxidants, which contribute to cell development and the prevention of illnesses.
9. Are eggs high in protein?
Yes, eggs are a good source of proteins or the perfect source of proteins. One large egg contains 6.3 grams of protein distributed between the yolk (2.7 g) and white portions (3.6 g).
10. What food has 30 gm of protein?
Cooked chicken breast (120 grams), grilled salmon (130 grams), lentils (240 grams), hard-boiled eggs (4 eggs), and ground beef patty (28 grams) are protein-rich foods that provide 30 grams of protein. Remember that the protein content can vary based on preparation and other factors.