This article focuses on Medication For Hypothyroidism: Tips & Supplements
Diagnosis
Hypothyroidism symptoms can differ from person to person. And they frequently resemble symptoms of other health issues. As a result, a diagnosis of hypothyroidism does not rely solely on symptoms. It is usually determined by the results of blood tests.
The first blood test used to diagnose hypothyroidism measures thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) levels in the blood. If it is too high, the test is repeated, as is a blood test for the thyroid hormone T-4. The diagnosis is hypothyroidism if the TSH level is high and the T-4 level is low. In some cases, the thyroid hormone T-3 may be measured as well.
If the second test shows high TSH but T-4 and T-3 are in the standard range, then the diagnosis is subclinical hypothyroidism. It usually doesn’t cause any noticeable symptoms.
TSH tests are also crucial in the long-term management of hypothyroidism. They assist your doctor in determining and maintaining the appropriate medication dosage for you.
The results of these blood tests can be affected by some medicines or supplements. This includes biotin, a vitamin that can be taken alone or as part of a multivitamin. Inform your doctor about any medications or supplements you are taking before having blood tests.
Understanding the Causes of Hypothyroidism
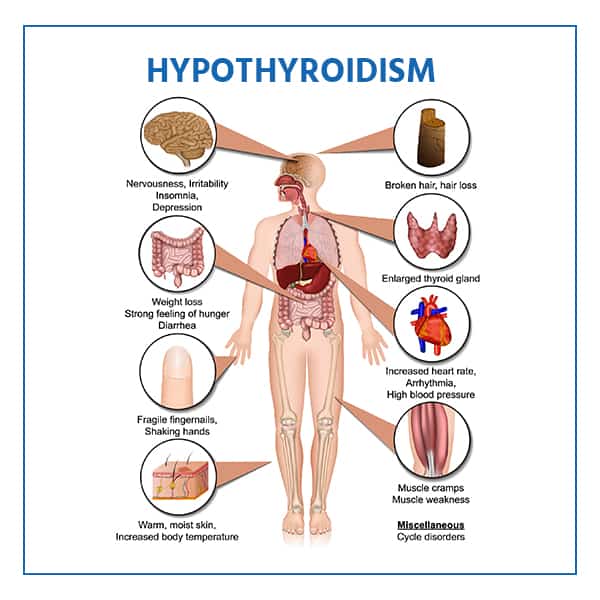
Your thyroid is a butterfly-shaped gland located at the base of your neck that regulates many of your body’s metabolic processes. Hypothyroidism (or low thyroid) occurs when the thyroid gland does not produce enough thyroid hormones, such as triiodothyronine (T3) and thyroxine (T4).
While there is no single cause of hypothyroidism, Hashimoto’s thyroiditis (also known as Hashimoto’s hypothyroidism), an autoimmune disease likely caused by genetics, is the leading cause of the majority of cases.
Because there is no cure for hypothyroidism, you will need to take medication for the rest of your life to feel better and reduce the risk of complications such as heart disease. Many people, however, are relieved to learn that once they and their doctors determine the best type and dosage of medication for them, many of the most distressing hypothyroidism symptoms, such as fatigue, high cholesterol, and weight gain, may be reversed.
Hypothyroidism Treatments to Consider
- Synthetic T4 Hormones to Replace Insufficient Thyroid Hormones
Thyroid hormone replacement therapy is the most commonly used treatment for hypothyroidism, and synthetic T4 medication is the most effective. While these hormones are identical to the natural T4 that the thyroid makes, several factors can affect the exact dosage you need. Synthetic T4 is available as a prescription medication called levothyroxine, which is marketed under the brand names Levothroid and Synthroid. Every day, on an empty stomach, you must take synthetic thyroxine. Allow at least 30 minutes before eating or drinking anything (with the exception of water). Skipping doses can throw your thyroid out of whack. If you miss a dose, make sure to take it the following day on your regular schedule. Don’t double your dose by taking two pills at once, as this can cause your levels to skyrocket.
- Combination Medications with Synthetic T3 and T4 Hormones
Combination medications containing both synthetic T4 and T3 hormones are also available on the market, but they are not usually recommended. For one thing, most patients’ conditions improve with synthetic T4 alone due to the thyroid’s ability to convert these hormones to T3 when needed. In some cases, your doctor may advise you to take liothyronine (Cytomel) in addition to levothyroxine.
- Subclinical hypothyroidism
If you are diagnosed with subclinical hypothyroidism, talk about treatment with your healthcare provider. Thyroid hormone medication may be ineffective for a mild increase in TSH. Thyroid hormones may help some symptoms if your TSH level is higher but still in the subclinical range.
Treating Hypothyroidism Naturally and Safely
- Some patients choose to supplement their treatment with alternative therapies, often to help with symptoms like fatigue, weight gain, stress, and mental fog. Yoga, meditation, hypnosis, vitamins, and special diets are some of the treatments available.
- One small study of 20 female patients with hypothyroidism found that yoga did help patients manage their disease symptoms.
- While patients with thyroid disease are often advised to eat a low-iodine diet (which can worsen hypothyroidism) or to take vitamin D or calcium supplements, no diet or nutrient can cure thyroid disease.